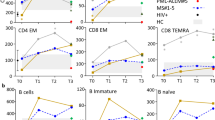
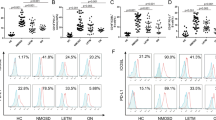
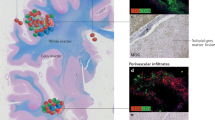
Abstract
Patients with the autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis (MS) typically present with the clinically isolated syndromes (CIS) transverse myelitis (TM) or optic neuritis (ON). B-cell disturbances have been well documented in patients with MS and CIS patients with ON, but not in CIS patients with TM, despite the fact that these patients have the worst clinical outcome of all CIS types. The goal of this study was to characterize the B-cell populations and immunoglobulin genetics in TM patients. We found a unique expansion of CD27high plasmablasts in both the cerebrospinal fluid and periphery of TM patients that is not present in ON patients. Additionally, plasmablasts from TM patients show evidence for positive selection with increased somatic hypermutation accumulation in VH4+ B cells and receptor editing that is not observed in ON patients. These characteristics unique to TM patients may impact disease severity and progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geurts JJ, Bo L, Pouwels PJ, Castelijns JA, Polman CH, Barkhof F . Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis: combined postmortem MR imaging and histopathology. Ajnr 2005; 26: 572–577.
Frohman EM, Racke MK, Raine CS . Multiple sclerosis—the plaque and its pathogenesis. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 942–955.
Trapp BD, Peterson J, Ransohoff RM, Rudick R, Mork S, Bo L . Axonal transection in the lesions of multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 1998; 338: 278–285.
Bitsch A, Schuchardt J, Bunkowski S, Kuhlmann T, Bruck W . Acute axonal injury in multiple sclerosis. Correlation with demyelination and inflammation. Brain 2000; 123 (Pt 6): 1174–1183.
Cepok S, Jacobsen M, Schock S, Omer B, Jaekel S, Boddeker I et al. Patterns of cerebrospinal fluid pathology correlate with disease progression in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2001; 124 (Pt 11): 2169–2176.
Miller D, Barkhof F, Montalban X, Thompson A, Filippi M . Clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis, part I: natural history, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and prognosis. Lancet Neurol 2005; 4: 281–288.
Atkins EJ, Biousse V, Newman NJ . Optic neuritis. Semin Neurol 2007; 27: 211–220.
Kerr DA, Ayetey H . Immunopathogenesis of acute transverse myelitis. Curr Opin Neurol 2002; 15: 339–347.
Frohman EM, Havrdova E, Lublin F, Barkhof F, Achiron A, Sharief MK et al. Most patients with multiple sclerosis or a clinically isolated demyelinating syndrome should be treated at the time of diagnosis. Arch Neurol 2006; 63: 614–619.
Rocca MA, Agosta F, Sormani MP, Fernando K, Tintore M, Korteweg T et al. A three-year, multi-parametric MRI study in patients at presentation with CIS. J Neurol 2008; 255: 683–691.
Patrucco L, Rojas JI, Cristiano E . Assessing the value of spinal cord lesions in predicting development of multiple sclerosis in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. J Neurol 2011; 259: 1317–1320.
Gajofatto A, Monaco S, Fiorini M, Zanusso G, Vedovello M, Rossi F et al. Assessment of outcome predictors in first-episode acute myelitis: a retrospective study of 53 cases. Arch Neurol 2010; 67: 724–730.
Tintore M, Rovira A, Arrambide G, Mitjana R, Rio J, Auger C et al. Brainstem lesions in clinically isolated syndromes. Neurology 2010; 75: 1933–1938.
Kabat EA, Moore DH, Landow H . An electrophoretic study of the protein components in cerebrospinal fluid and their relationship to the serum proteins. J Clin Invest 1942; 21: 571–577.
Kabat EA, Freedman DA et al. A study of the crystalline albumin, gamma globulin and total protein in the cerebrospinal fluid of 100 cases of multiple sclerosis and in other diseases. Am J Med Sci 1950; 219: 55–64.
Kabat EA, Glusman M, Knaub V . Quantitative estimation of the albumin and gamma globulin in normal and pathologic cerebrospinal fluid by immunochemical methods. Am J Med 1948; 4: 653–662.
Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H . Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann Neurol 2000; 47: 707–717.
Raine CS, Cannella B, Hauser SL, Genain CP . Demyelination in primate autoimmune encephalomyelitis and acute multiple sclerosis lesions: a case for antigen-specific antibody mediation. Ann Neurol 1999; 46: 144–160.
Genain CP, Cannella B, Hauser SL, Raine CS . Identification of autoantibodies associated with myelin damage in multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 1999; 5: 170–175.
Esiri MM . Immunoglobulin-containing cells in multiple-sclerosis plaques. Lancet 1977; 2: 478.
Storch MK, Piddlesden S, Haltia M, Iivanainen M, Morgan P, Lassmann H . Multiple sclerosis: in situ evidence for antibody- and complement-mediated demyelination. Ann Neurol 1998; 43: 465–471.
Sadaba MC, Tzartos J, Paino C, Garcia-Villanueva M, Alvarez-Cermeno JC, Villar LM et al. Axonal and oligodendrocyte-localized IgM and IgG deposits in MS lesions. J Neuroimmunol 2012; 247: 86–94.
Corcione A, Casazza S, Ferretti E, Giunti D, Zappia E, Pistorio A et al. Recapitulation of B cell differentiation in the central nervous system of patients with multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 11064–11069.
Cepok S, von Geldern G, Grummel V, Hochgesand S, Celik H, Hartung H et al. Accumulation of class switched IgD-IgM- memory B cells in the cerebrospinal fluid during neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol 2006; 180: 33–39.
Frohman EM, Filippi M, Stuve O, Waxman SG, Corboy J, Phillips JT et al. Characterizing the mechanisms of progression in multiple sclerosis: evidence and new hypotheses for future directions. Arch Neurol 2005; 62: 1345–1356.
Hauser SL, Waubant E, Arnold DL, Vollmer T, Antel J, Fox RJ et al. B-cell depletion with rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 676–688.
Cross AH, Stark JL, Lauber J, Ramsbottom MJ, Lyons JA . Rituximab reduces B cells and T cells in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 2006; 180: 63–70.
Martin Mdel P, Cravens PD, Winger R, Kieseier BC, Cepok S, Eagar TN et al. Depletion of B lymphocytes from cerebral perivascular spaces by rituximab. Arch Neurol 2009; 66: 1016–1020.
Schneider S, Bruns A, Moewes B, Holzknecht B, Hausdorf G, Riemekasten G et al. Simultaneous cytometric analysis of (auto)antigen-reactive T and B cell proliferation. Immunobiology 2002; 206: 484–495.
Sellam J, Rouanet S, Hendel-Chavez H, Abbed K, Sibilia J, Tebib J et al. Blood memory B cells are disturbed and predict the response to rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 3692–3701.
Hansen A, Odendahl M, Reiter K, Jacobi AM, Feist E, Scholze J et al. Diminished peripheral blood memory B cells and accumulation of memory B cells in the salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 2002; 46: 2160–2171.
Jacobi AM, Odendahl M, Reiter K, Bruns A, Burmester GR, Radbruch A et al. Correlation between circulating CD27high plasma cells and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1332–1342.
Chihara N, Aranami T, Sato W, Miyazaki Y, Miyake S, Okamoto T et al. Interleukin 6 signaling promotes anti-aquaporin 4 autoantibody production from plasmablasts in neuromyelitis optica. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 3701–3706.
Lin Q, Gu JR, Li TW, Zhang FC, Lin ZM, Liao ZT et al. Value of the peripheral blood B-cells subsets in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2009; 122: 1784–1789.
Tarlton NJ, Green CM, Lazarus NH, Rott L, Wong AP, Abramson ON et al. Plasmablast frequency and trafficking receptor expression are altered in pediatric ulcerative colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2012; 18: 2381–2391.
Odendahl M, Jacobi A, Hansen A, Feist E, Hiepe F, Burmester GR et al. Disturbed peripheral B lymphocyte homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2000; 165: 5970–5979.
Yang DH, Chang DM, Lai JH, Lin FH, Chen CH . Significantly higher percentage of circulating CD27(high) plasma cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with infection than with disease flare-up. Yonsei Med J 2010; 51: 924–931.
Arce E, Jackson DG, Gill MA, Bennett LB, Banchereau J, Pascual V . Increased frequency of pre-germinal center B cells and plasma cell precursors in the blood of children with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 2001; 167: 2361–2369.
Boekel ET, Prins M, Vrielink GJ, de Kieviet W, Siegert CE . Longitudinal studies of the association between peripheral CD27++ plasma cells and systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity: preliminary results. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70: 1341–1342.
de Graaf M, de Beukelaar J, Bergsma J, Kraan J, van den Bent M, Klimek M et al. B and T cell imbalances in CSF of patients with Hu-antibody associated PNS. J Neuroimmunol 2008; 195: 164–170.
Pranzatelli MR, Travelstead AL, Tate ED, Allison TJ, Verhulst SJ . CSF B-cell expansion in opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome: a biomarker of disease activity. Mov Disord 2004; 19: 770–777.
Blaes F, Tschernatsch M . Paraneoplastic neurological disorders. Expert Rev Neurother 2010; 10: 1559–1568.
Owens GP, Kraus H, Burgoon MP, Smith-Jensen T, Devlin ME, Gilden DH . Restricted use of VH4 germline segments in an acute multiple sclerosis brain. Ann Neurol 1998; 43: 236–243.
Cameron EM, Spencer S, Lazarini J, Harp CT, Ward ES, Burgoon M et al. Potential of a unique antibody gene signature to predict conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2009; 213: 123–130.
Bennett JL, Haubold K, Ritchie AM, Edwards SJ, Burgoon M, Shearer AJ et al. CSF IgG heavy-chain bias in patients at the time of a clinically isolated syndrome. J Neuroimmunol 2008; 199: 126–132.
Owens GP, Winges KM, Ritchie AM, Edwards S, Burgoon MP, Lehnhoff L et al. VH4 gene segments dominate the intrathecal humoral immune response in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol 2007; 179: 6343–6351.
Zuckerman NS, Hazanov H, Barak M, Edelman H, Hess S, Shcolnik H et al. Somatic hypermutation and antigen-driven selection of B cells are altered in autoimmune diseases. J Autoimmun 2010; 35: 325–335.
Monson NL, Brezinschek HP, Brezinschek RI, Mobley A, Vaughan GK, Frohman EM et al. Receptor revision and atypical mutational characteristics in clonally expanded B cells from the cerebrospinal fluid of recently diagnosed mutiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 2005; 158: 170–181.
Harp C, Lee J, Lambracht-Washington D, Cameron E, Olsen G, Frohman E et al. Cerebrospinal fluid B cells from multiple sclerosis patients are subject to normal germinal center selection. J Neuroimmunol 2007; 183: 189–199.
Briney BS, Willis JR, McKinney BA, Crowe JE Jr . High-throughput antibody sequencing reveals genetic evidence of global regulation of the naive and memory repertoires that extends across individuals. Genes Immun 2012; 13: 469–473.
Wardemann H, Yurasov S, Schaefer A, Young JW, Meffre E, Nussenzweig MC . Predominant autoantibody production by early human B cell precursors. Science 2003; 301: 1374–1377.
Kalinina O, Doyle-Cooper CM, Miksanek J, Meng W, Prak EL, Weigert MG . Alternative mechanisms of receptor editing in autoreactive B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 7125–7130.
Brezinschek HP, Brezinschek RI, Lipsky PE . Analysis of the heavy chain repertoire of human peripheral B cells using single-cell polymerase chain reaction. J Immunol 1995; 155: 190–202.
Meffre E, Milili M, Blanco-Betancourt C, Antunes H, Nussenzweig MC, Schiff C . Immunoglobulin heavy chain expression shapes the B cell receptor repertoire in human B cell development. J Clin Invest 2001; 108: 879–886.
Rot U, Ledinek AH, Jazbec SS . Clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, cerebrospinal fluid and electrophysiological characteristics of the earliest multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2008; 110: 233–238.
de Graaf MT, Smitt PA, Luitwieler RL, van Velzen C, van den Broek PD, Kraan J et al. Central memory CD4+ T cells dominate the normal cerebrospinal fluid. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2011; 80: 43–50.
Svenningsson A, Andersen O, Edsbagge M, Stemme S . Lymphocyte phenotype and subset distribution in normal cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol 1995; 63: 39–46.
Haas J, Bekeredjian-Ding I, Milkova M, Balint B, Schwarz A, Korporal M et al. B cells undergo unique compartmentalized redistribution in multiple sclerosis. J Autoimmun 2011; 37: 289–299.
von Budingen HC, Kuo TC, Sirota M, van Belle CJ, Apeltsin L, Glanville J et al. B cell exchange across the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 4533–4543.
Kim SH, Kim W, Li XF, Jung IJ, Kim HJ . Repeated treatment with rituximab based on the assessment of peripheral circulating memory B cells in patients with relapsing neuromyelitis optica over 2 years. Arch Neurol 2011; 68: 1412–1420.
Owczarczyk K, Lal P, Abbas AR, Wolslegel K, Holweg CT, Dummer W et al. A plasmablast biomarker for nonresponse to antibody therapy to CD20 in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med 2011; 3: 101ra92.
Vital EM, Dass S, Buch MH, Henshaw K, Pease CT, Martin MF et al. B cell biomarkers of rituximab responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2011; 63: 3038–3047.
Lazarus MN, Turner-Stokes T, Chavele KM, Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR . B-cell numbers and phenotype at clinical relapse following rituximab therapy differ in SLE patients according to anti-dsDNA antibody levels. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012; 51: 1208–1215.
Cepok S, Rosche B, Grummel V, Vogel F, Zhou D, Sayn J et al. Short-lived plasma blasts are the main B cell effector subset during the course of multiple sclerosis. Brain 2005; 128 (Pt 7): 1667–1676.
Villar LM, Garcia-Sanchez MI, Costa-Frossard L, Espino M, Roldan E, Paramo D et al. Immunological markers of optimal response to natalizumab in multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 2012; 69: 191–197.
Niino M, Hirotani M, Miyazaki Y, Sasaki H . Memory and naive B-cell subsets in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Lett 2009; 464: 74–78.
Kleine TO, Benes L . Immune surveillance of the human central nervous system (CNS): different migration pathways of immune cells through the blood-brain barrier and blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in healthy persons. Cytometry A 2006; 69: 147–151.
Planas R, Jelcic I, Schippling S, Martin R, Sospedra M . Natalizumab treatment perturbs memory- and marginal zone-like B-cell homing in secondary lymphoid organs in multiple sclerosis. Eur J Immunol 2011; 42: 790–798.
Lee-Chang C, Top I, Zephir H, Dubucquoi S, Trauet J, Dussart P et al. Primed status of transitional B cells associated with their presence in the cerebrospinal fluid in early phases of multiple sclerosis. Clin Immunol 2011; 139: 12–20.
Serafini B, Rosicarelli B, Magliozzi R, Stigliano E, Aloisi F . Detection of ectopic B-cell follicles with germinal centers in the meninges of patients with secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Brain Pathol 2004; 14: 164–174.
Corcione A, Aloisi F, Serafini B, Capello E, Mancardi GL, Pistoia V et al. B-cell differentiation in the CNS of patients with multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 2005; 4: 549–554.
Odendahl M, Mei H, Hoyer BF, Jacobi AM, Hansen A, Muehlinghaus G et al. Generation of migratory antigen-specific plasma blasts and mobilization of resident plasma cells in a secondary immune response. Blood 2005; 105: 1614–1621.
Zhang Z, Zemlin M, Wang YH, Munfus D, Huye LE, Findley HW et al. Contribution of Vh gene replacement to the primary B cell repertoire. Immunity 2003; 19: 21–31.
Barbas SM, Ditzel HJ, Salonen EM, Yang WP, Silverman GJ, Burton DR . Human autoantibody recognition of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 2529–2533.
Itoh K, Meffre E, Albesiano E, Farber A, Dines D, Stein P et al. Immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene replacement as a mechanism for receptor revision in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 1151–1164.
Tiller T, Meffre E, Yurasov S, Tsuiji M, Nussenzweig MC, Wardemann H . Efficient generation of monoclonal antibodies from single human B cells by single cell RT-PCR and expression vector cloning. J Immunol Methods 2008; 329: 112–124.
Lefranc MP . IMGT, the international ImMunoGeneTics database. Nucleic Acids Res 2001; 29: 207–209.
Ligocki AJ, Lovato L, Xiang D, Guidry P, Scheuermann RH, Willis SN et al. A unique antibody gene signature is prevalent in the central nervous system of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 2010; 226: 192–193.
Brezinschek HP, Foster SJ, Brezinschek RI, Dorner T, Domiati-Saad R, Lipsky PE . Analysis of the human VH gene repertoire. Differential effects of selection and somatic hypermutation on human peripheral CD5(+)/IgM+ and CD5(-)/IgM+ B cells. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 2488–2501.
Tian C, Luskin GK, Dischert KM, Higginbotham JN, Shepherd BE, Crowe JE Jr . Evidence for preferential Ig gene usage and differential TdT and exonuclease activities in human naive and memory B cells. Mol Immunol 2007; 44: 2173–2183.
Kabat EA, Wu TT, Bilofsky H, Reid-Miller M, Perry H . Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest. United States Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 1983.
Champe PC, Harvey RA . Lippincott's Illustrated Reviews: Biochemistry 2nd edn Lippincott-Raven Publishers, 1994.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients who consented to sampling for this study. Bonnie Darnell, Angie Mobley, Julia McClouth, Ann-Marie Schaefer and Elizabeth Curry are thanked for their technical expertise in cell sorting. This study was supported by Grants from the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) to NLM (RG3267 and RG4653). AJL, WHR, EMC and CTH were supported by Grant no. NIH NRSA5 T32 AI 005284-28 from NIAID. LGC’s contributions were funded by Grant no. 1R01AI097403-01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
EMF has received speaker and consulting fees from TEVA, Biogen Idec, Acorda and Novartis. EMF has received consulting fees from Abbott Laboratories and Genzyme. BG received honoraria from the MSAA and the AAN and has received consulting fees from Biogen Idec, Acorda Therapeutics, Sanofi-Aventis and DioGenix. BG has equity shares in DioGenix. NLM receives funding from MedImmune, Inc., TEVA Neuroscience, DioGenix, Inc. and the National MS Society. NLM is an advisor for Genentech, Inc. All the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ligocki, A., Rounds, W., Cameron, E. et al. Expansion of CD27high plasmablasts in transverse myelitis patients that utilize VH4 and JH6 genes and undergo extensive somatic hypermutation. Genes Immun 14, 291–301 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.18
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2013.18
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adaptive lymphocyte profiles correlate to brain Aβ burden in patients with mild cognitive impairment
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2017)
-
Peripheral VH4+ plasmablasts demonstrate autoreactive B cell expansion toward brain antigens in early multiple sclerosis patients
Acta Neuropathologica (2017)
-
B cells in MS and NMO: pathogenesis and therapy
Seminars in Immunopathology (2014)