Abstract
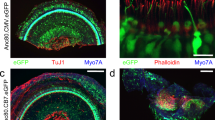
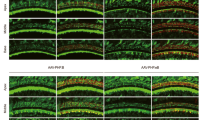
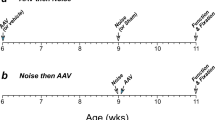
We have previously demonstrated that both age-related and noise-induced hearing loss are reduced in transgenic mice that ubiquitously overexpress X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP). In view of the therapeutic implications of these findings, we have developed a minimally invasive surgical method to deliver adenoid-associated virus (AAV) across the round window membrane (RWM) of the cochlea, enabling efficient gene transfer to hair cells and sensory neurons in this enclosed structure. This RWM approach was used in the present study to evaluate the effectiveness of AAV-mediated XIAP overexpression in protecting against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Two weeks following surgery, AAV-derived XIAP was detected in the majority of inner and outer hair cells, resulting in a threefold elevation of this antiapoptotic protein in the cochlea. The protection of AAV-mediated XIAP overexpression was evaluated in animals treated with cisplatin at a dose of 4 mg kg−1 per day for 4–7 consecutive days. The XIAP overexpression was found to attenuate cisplatin-induced hearing loss by ~22 dB. This was accompanied by a reduction of the loss of vulnerable hair cells and sensory neurons in the cochlea by 13%.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Cancer Institute Cancer Drug Information: Cisplatin. National Institute of Health, 2014, http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/druginfo/cisplatin.
Langer T, am Zehnhoff-Dinnesen A, Radtke S, Meitert J, Zolk O . Understanding platinum-induced ototoxicity. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2013; 34: 458–469.
Brock PR, Knight KR, Freyer DR, Campbell KC, Steyger PS, Blakley BW et al. Platinum-induced ototoxicity in children: a consensus review on mechanisms, predisposition, and protection, including a new International Society of Pediatric Oncology Boston ototoxicity scale. J Clin Oncol 2012; 30: 2408–2417.
Wightman FL . Psychoacoustic correlates of hearing loss. In: Hamernik RP, Henderson D, Salvi RJ (eds). New Perspectives on Noise-Induced Hearing Loss. Raven Press: New York, NY, USA, pp 375–394 1982.
van Ruijven MW, de Groot JC, Klis SF, Smoorenburg GF . The cochlear targets of cisplatin: an electrophysiological and morphological time-sequence study. Hear Res 2005; 205: 241–248.
Meech RP, Campbell KC, Hughes LP, Rybak LP . A semiquantitative analysis of the effects of cisplatin on the rat stria vascularis. Hear Res 1998; 124: 44–59.
Sluyter S, Klis SF, de Groot JC, Smoorenburg GF . Alterations in the stria vascularis in relation to cisplatin ototoxicity and recovery. Hear Res 2003; 185: 49–56.
Hamers FP, Wijbenga J, Wolters FL, Klis SF, Sluyter S, Smoorenburg GF . Cisplatin ototoxicity involves organ of Corti, stria vascularis and spiral ganglion: modulation by alphaMSH and ORG 2766. Audiol Neurootol 2003; 8: 305–315.
Goncalves MS, Silveira AF, Teixeira AR, Hyppolito MA . Mechanisms of cisplatin ototoxicity: theoretical review. J Laryngol Otol 2013; 127: 536–541.
Devarajan P, Savoca M, Castaneda MP, Park MS, Esteban-Cruciani N, Kalinec G et al. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in auditory cells: role of death receptor and mitochondrial pathways. Hear Res 2002; 174: 45–54.
Carleton BC, Ross CJ, Bhavsar AP, Amstutz U, Pussegoda K, Visscher H et al. Role of TPMT and COMT genetic variation in cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2013; 95: 253.
Rednam S, Scheurer ME, Adesina A, Lau CC, Okcu MF . Glutathione S-transferase P1 single nucleotide polymorphism predicts permanent ototoxicity in children with medulloblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013; 60: 593–598.
Waissbluth S, Daniel SJ . Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: transporters playing a role in cisplatin toxicity. Hear Res 2013; 299: 37–45.
Waissbluth S, Salehi P, He X, Daniel SJ . Systemic dexamethasone for the prevention of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2013; 270: 1597–1605.
Gopal KV, Wu C, Shrestha B, Campbell KC, Moore EJ, Gross GW . d-Methionine protects against cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity in cortical networks. Neurotoxicol Teratol 2012; 34: 495–504.
Poirrier AL, Pincemail J, Van Den Ackerveken P, Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B . Oxidative stress in the cochlea: an update. Curr Med Chem 2010; 17: 3591–3604.
Choi J, Im GJ, Chang J, Chae SW, Lee SH, Kwon SY et al. Protective effects of apocynin on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in an auditory cell line and in zebrafish. J Appl Toxicol 2013; 33: 125–133.
Waissbluth S, Pitaro J, Daniel SJ . Gene therapy for cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: a systematic review of in vitro and experimental animal studies. Otol Neurotol 2012; 33: 302–310.
Abi-Hachem RN, Zine A, Van De Water TR . The injured cochlea as a target for inflammatory processes, initiation of cell death pathways and application of related otoprotectives strategies. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 2010; 5: 147–163.
Chan DK, Lieberman DM, Musatov S, Goldfein JA, Selesnick SH, Kaplitt MG . Protection against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity by adeno-associated virus-mediated delivery of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein is not dependent on caspase inhibition. Otol Neurotol 2007; 28: 417–425.
Cooper LB, Chan DK, Roediger FC, Shaffer BR, Fraser JF, Musatov S et al. AAV-mediated delivery of the caspase inhibitor XIAP protects against cisplatin ototoxicity. Otol Neurotol 2006; 27: 484–490.
Wang J, Ladrech S, Pujol R, Brabet P, Van De Water TR, Puel JL . Caspase inhibitors, but not c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor treatment, prevent cisplatin-induced hearing loss. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 9217–9224.
Lefebvre PP, Malgrange B, Lallemend F, Staecker H, Moonen G, Van De Water TR . Mechanisms of cell death in the injured auditory system: otoprotective strategies. Audiol Neurootol 2002; 7: 165–170.
Wang J, Menchenton T, Yin S, Yu Z, Bance M, Morris DP et al. Over-expression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein slows presbycusis in C57BL/6J mice. Neurobiol Aging 2010; 31: 1238–1249.
Wang J, Tymczyszyn N, Yu Z, Yin S, Bance M, Robertson GS . Overexpression of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein protects against noise-induced hearing loss in mice. Gene Ther 2011; 18: 560–568.
Wang H, Murphy R, Taaffe D, Yin S, Xia L, Hauswirth WW et al. Efficient cochlear gene transfection in guinea-pigs with adeno-associated viral vectors by partial digestion of round window membrane. Gene Ther 2012; 19: 255–263.
Jayandharan GR, Zhong L, Sack BK, Rivers AE, Li M, Li B et al. Optimized adeno-associated virus (AAV)-protein phosphatase-5 helper viruses for efficient liver transduction by single-stranded AAV vectors: therapeutic expression of factor IX at reduced vector doses. Hum Gene Ther 2010; 21: 271–283.
Zhong L, Li B, Jayandharan G, Mah CS, Govindasamy L, Agbandje-McKenna M et al. Tyrosine-phosphorylation of AAV2 vectors and its consequences on viral intracellular trafficking and transgene expression. Virology 2008; 381: 194–202.
Zhong L, Li B, Mah CS, Govindasamy L, Agbandje-McKenna M, Cooper M et al. Next generation of adeno-associated virus 2 vectors: point mutations in tyrosines lead to high-efficiency transduction at lower doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 7827–7832.
Petrs-Silva H, Dinculescu A, Li Q, Min SH, Chiodo V, Pang JJ et al. High-efficiency transduction of the mouse retina by tyrosine-mutant AAV serotype vectors. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 463–471.
Zilberstein Y, Liberman MC, Corfas G . Inner hair cells are not required for survival of spiral ganglion neurons in the adult cochlea. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 405–410.
Lin HW, Furman AC, Kujawa SG, Liberman MC . Primary neural degeneration in the Guinea pig cochlea after reversible noise-induced threshold shift. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 2011; 12: 605–616.
Kujawa SG, Liberman MC . Adding insult to injury: cochlear nerve degeneration after "temporary" noise-induced hearing loss. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 14077–14085.
Liu L, Wang H, Shi L, Almuklass A, He T, Aiken S et al. Silent damage of noise on cochlear afferent innervation in guinea pigs and the impact on temporal processing. PLoS One 2012; 7: e49550.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jie, H., Tao, S., Liu, L. et al. Cochlear protection against cisplatin by viral transfection of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein across round window membrane. Gene Ther 22, 546–552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.22
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2015.22
This article is cited by
-
Current Advances in Adeno-Associated Virus-Mediated Gene Therapy to Prevent Acquired Hearing Loss
Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology (2022)
-
Gene therapy development in hearing research in China
Gene Therapy (2020)
-
Advances in Inner Ear Therapeutics for Hearing Loss in Children
Current Otorhinolaryngology Reports (2020)