Abstract
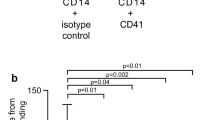
Interleukin (IL)-18 is an important proinflammatory cytokine processed and released from cells of the monocyte lineage by activation of the P2X7 receptor by extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP). We examined if a loss-of-function polymorphism of the human P2X7 receptor (glutamic acid-496 to alanine) impairs this process. Using a whole blood-based assay, ATP-induced release of IL-18 from homozygous subjects after 120 min incubation with ATP was 42% of that from wild-type subjects. Moreover, the level of ATP-induced IL-18 release from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed monocytes of homozygous subjects after 30 and 60 min incubation with ATP was 21 and 44%, respectively, of that from wild-type monocytes. Nigericin, a K+ ionophore, induced a similar release of IL-18 from monocytes of either genotype. ATP-induced ethidium+ uptake in LPS-primed, monocytes of homozygous subjects was only 11% of that in wild-type monocytes, while P2X7 surface expression on LPS-primed, homozygous monocytes was 44% of that on wild-type monocytes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gracie JA, Robertson SE, McInnes IB . Interleukin-18. J Leuk Biol 2003; 73: 213–224.
Dinarello CA, Fantuzzi G . Interleukin-18 and host defense against infection. J Infect Dis 2003; 187: S370–S384.
Gu Y, Kuida K, Tsutusi H et al. Activation of interferon-γ inducing factor mediated by interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 1997; 275: 206–209.
Rubartelli A, Cozzolino F, Talio M, Sitia R . A novel secretory pathway for interleukin-1β, a protein lacking a signal sequence. EMBO J 1990; 9: 1503–1510.
Okamura H, Tsutsi H, Komatsu T et al. Cloning of a new cytokine that induces IFN-γ production by T cells. Nature 1995; 378: 88–91.
Perregaux DG, McNiff P, Laliberte R, Conklyn M, Gabel CA . ATP acts as an agonist to promote stimulus-induced secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 in human blood. J Immunol 2000; 165: 4615–4623.
Mehta VB, Hart J, Wewers MD . ATP-stimulated release of interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18 requires priming by lipopolysaccharide and is independent of caspase-1 cleavage. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 3820–3826.
Rampe D, Wang L, Ringheim GE . P2X7 receptor modulation of β-amyloid- and LPS-induced cytokine secretion from human macrophages and microglia. J Neuroimmunol 2004; 147: 56–61.
Muhl H, Hofler S, Pfeilschifter J . Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide/ATP-induced release of interlekin-18 by KN-62 and glyburide. Eur J Pharmacol 2003; 482: 325–328.
Wheeler RD, Brough D, Le Feuvre RA et al. Interleukin-18 induces expression and release of cytokines from murine glial cells: interactions with interleukin-1β. J Neurochem 2003; 85: 1412–1420.
Gu BJ, Zhang WY, Worthington RA et al. A Glu-496 to Ala polymorphism leads to loss of function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 11135–11142.
Sluyter R, Shemon AN, Wiley JS . Glu496 to Ala polymorphism in the P2X7 receptor impairs ATP-induced IL-1β release from human monocytes. J Immunol 2004; 172: 3399–3405.
Sluyter R, Wiley JS . Extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate induces a loss of CD23 from human dendritic cells via activation of P2X7 receptors. Int Immunol 2002; 14: 1415–1421.
Saunders BM, Fernando SL, Sluyter R, Britton WJ, Wiley JS . A loss-of-function polymorphism in the human P2X7 receptor abolishes ATP mediated killing of mycobacteria. J Immunol 2003; 171: 5442–5446.
Dao-Ung LP, Fuller SJ, Sluyter R et al. Association of the 1513C polymorphism in the P2X7 gene with familial forms of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 2004; 125: 815–817.
Hentze H, Lin XY, Choi MSK, Porter AG . Critical role for cathepsin B in mediating caspase-1-dependent interleukin-18 maturation and capase-1-independent necrosis triggered by the microbial toxin nigericin. Cell Death Diff 2003; 10: 956–968.
Kahlenberg JM, Dubyak GR . Mechanisms of caspase-1 activation by P2X7 receptor-mediated K+ release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2004; 286: C1100–C1108.
Buell G, Chessell IP, Michel AD et al. Blockade of human P2X7 receptor function with a monoclonal antibody. Blood 1998; 92: 3521–3528.
Giedraitis V, He B, Huang W-X, Hillert J . Cloning and mutation analysis of the human IL-18 promoter: a possible role of polymorphisms in expression regulation. J Neuroimmunol 2001; 112: 146–152.
Kruse S, Kuehr J, Moseler M et al. Polymorphisms in the IL 18 gene are associated with specific sensitisation to common allergens and allergic arthritis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 111: 117–122.
Perregaux D, Gabel CA . Interleukin-1β maturation and release in response to ATP and nigericin. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 15195–15203.
Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S et al. Extracellular ATP triggers IL-1β release by activating the purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophages. J Immunol 1997; 159: 1451–1458.
Wiley JS, Dao-Ung LP, Li C et al. An Ile-568 to Asn polymorphism prevents normal trafficking and function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 17108–17113.
Gu BJ, Sluyter R, Skarratt KK et al. An Arg307 to Gln polymorphism within the ATP binding site causes loss of function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 31287–31295.
Labasi JM, Petrushova N, Donovan C et al. Absence of the P2X7 receptor alters leukocyte function and attenuates an inflammatory response. J Immunol 2002; 168: 6436–6445.
Wei X, Leung BP, Arthur HML, McInnes IB, Liew FY . Reduced incidence and severity of collagen-induced arthritis in mice lacking IL-18. J Immunol 2001; 166: 517–521.
Solle M, Labasi J, Perregaux DG et al. Altered cytokine production in mice lacking P2X7 receptors. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 125–132.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia and the Leukaemia Foundation of Australia. We thank Dr Stephen Fuller for coordinating the collection of some blood samples, Dr Ben Gu for preparation of the anti-P2X7 antibody and Ms Anne Shemon for critically reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sluyter, R., Dalitz, J. & Wiley, J. P2X7 receptor polymorphism impairs extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate-induced interleukin-18 release from human monocytes. Genes Immun 5, 588–591 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364127
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364127
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Purinergic Regulation of Neuroinflammation in Traumatic Brain Injury
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2022)
-
Association of P2X7 receptor genetic polymorphisms and expression with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in a sample of the Iranian population: a case-control study
Clinical Rheumatology (2021)
-
Identification of rs11615992 as a novel regulatory SNP for human P2RX7 by allele-specific expression
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2020)
-
A central role for P2X7 receptors in human microglia
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2018)
-
Epistasis with HLA DR3 implicates the P2X7 receptor in the pathogenesis of primary Sjögren's syndrome
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2013)