Abstract
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the weight gain after Sibutramine 10 mg daily discontinuation. To evaluate the effect of Sibutramine 10 mg daily in patients who were on a diet for 6 months.
DESIGN: After a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel, prospective phase for 6 months, the treatments were crossed over and the patients continued in double-blind observation for another 6-month period.
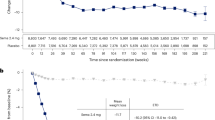
SUBJECTS: Forty out of 44 patients who were on Sibutramine and 42/44 who were on placebo switched the trial medication. All the patients were obese at the beginning of the trial (body mass index, BMI>30 kg/m2). During the first phase, the weight loss in the Sibutramine group was 7.52 kg (95% confidence intervals (95% CI) 6.15; 8.9) and that in the placebo group 3.56 kg (95% CI 2.41; 4.7) (using last observation carried forward (LOCF)).
MEASUREMENTS: Body weight, BMI, waist, medical history, assessment of hunger, satiety and diet compliance, standard laboratory assessments, blood pressure, heart rate and ECG.
RESULTS: Thirty out 40 patients in the Sibutramine/placebo (S/P) group and 32 out of 42 in the placebo/Sibutramine (P/S) group completed the second phase of the trial. During the second part of the trial the S/P gained 3.21 (95% CI 2.15; 4.26) kg, 1.21 (0.82; 1.59) kg/m2, and 2.83 (1.55; 4.12) waist cm. The P/S group lost 1.62 (2.62; 0.61), 0.67 (1.09; −0.25) kg/m2, and 1.85 (3.18; 0.53) waist cm. Eleven patients in the S/P group suffered 14 adverse events, mainly blood pressure increase (n=4); 19 patients in the P/S group had 29 adverse events, mainly dry mouth (n=8), constipation (n=5) and blood pressure increase (n=4). Only one P/S patient withdrew because of an adverse event.
CONCLUSIONS: After Sibutramine discontinuation patients had weight gain but they did not reach the baseline body weight. No significant adverse events presented after Sibutramine discontinuation. When Sibutramine was administrated to patients after 6 months of diet, the weight plateau was broken. Early Sibutramine administration had better effects than late post-diet administration. Sibutramine was well tolerated by the patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pi-Sunyer XA . A review of long-term studies evalutating the efficacy of weight loss in ameliorating disorders associated with obesity Clin Ther 1996 18: 1006–1036.
No author listed . Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: Executive summary Am J Clin Nutr 1998 68: 899–917.
Stern JS, Hirsch J, Blair SN, Foreyt JP, Frank A, Kumanyika SK, Madans JH, Marlatt GA, St Jeor ST and Stunkard AJ . Weighing the options: criteria for evaluating weight-management programs. The Committee to Develop Criteria for Evaluating the Outcomes of Approaches to Prevent and Treat Obesity Obes Res 1995 3: 591–604.
DePue JD, Clark MM, Ruggiero L, Mediros ML and Pera V Jr . Maintenance of weight loss: a needs assessment Obes Res 1005 3: 241–8.
National Task Force on the Prevention and Treatment of Obesity . Long-term Pharmacotherapy in the management of obesity JAMA 1996 276: 1907–1915.
Stock MJ . Sibutramine: a review of the pharmacology of a novel anti-obesity agent Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997 21 (Suppl 1): S25–S29.
Cole JO, Levin A, Beake B, Kaiser PE and Schienbaum ML . Sibutramine: A new weight loss agent without evidence of the abuse potential associated with amphetamines J Clin Psycopharmacol 1998 18: 231–236.
Schuh LM, Schuster CR, Hooper JA, Mendel CM . Abuse liability assessment of Sibutramine, a novel weight control agent Psycopharmacology (Berl). 2000 147: 339–346.
Hansen DL, Toubro S, Stock MJ, Macdonald IA and Astrup A . Thermogenic effects of Sibutramine in humans Am J Clin Nutr 1998 68: 1180–1186.
Weintraub M, Rubio A, Golik A, Byrne L and Scheinbaum ML . Sibutramine in weight control: A dose-ranging, efficacy study Clin Pharmacol Ther 1991 50: 33–337.
Bray GA, Ryan DH, Gordon D, Heidingfelder S, Cerise F and Wilson K . A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial of Sibutramine Obes Res 1996 4: 263–270.
Bray GA, Blackburn GL, Ferguson JM, Greenway FL, Jain AK, Mendel CM, Mendels J, Ryan DH, Schwartz SL, Scheinbaum ML, Seaton TB . Sibutramine produces dose-related weight loss Obes Res 1999 7: 189–198.
Hanotin C, Thomas F, Jones SP, Leutenegger E and Drouin P . Efficacy and tolerability of Sibutramine in obese patients: a dose- ranging study Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22 32–38.
Matínez-Cuellar GE, Martínez-Ruiz A, Revilla-Monsalve MC, Berber A . Six-month treatment of obesity with Sibutramine 15 mg; a double-blind, placebo-controlled monocenter clinical trial in a Hispanic population Obes Res 2000 8: 71–82.
Goldstein DJ, Potvin JH . Long-term weight loss: the effect of pharmacologic agents Am J Clin Nutr 1994 60: 647–657.
Goldstein DJ, Rampey AH Jr, Enas GG, Potvin JH, Fludzinski LA, Levine LR . Fluoxetine: a randomized clinical trial in the treatment of obesity Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1994 18: 129–135.
No authors listed . Guidelines for the approval and use of drugs to treat obesity. A position paper of the North American Association for the Study of Obesity Obes Res 1995 3: 473–478.
Apfelbaum M, Vague P, Ziegler O, Hanotin C, Thomas F, Leutenegger E . Long-term maintenance of weight loss after a very-low-caloric diet: A randomized blinded trial of the efficacy and tolerability of Sibutramine A J Med 1999 106: 179–184.
Ballor DL, Poehlman ET . A meta-analysis of the effects of exercise and/or dietary restriction on resting metabolic rate Eur J Appl Physiol 1995 71 535–542.
Thompson JL, Manore MM, Thomas JR . Effects of diet and diet-plus-exercise programs on resting metabolic rate: a meta-analysis Int J Sport Nutr 1996 6 41–61.
Walsh KM, Leen E, Lean ME . The effects of Sibutramine on resting energy expenditure and adrenaline-induced thermogenesis in obese females Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 1009–1015.
Hansen DL, Toubro S, Stock MJ, MacDonald IA, Astrup A . The effect of Sibutramine on energy expenditure and appetite during chronic treatment without dietary restriction Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1999 23: 1016–1024.
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Miss Lucila Velasco for reviewing the manuscript. This Study was supported by Química Knoll de Mexico, Mexico City, Mexico.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanghänel, G., Cortinas, L., Sánchez-Reyes, L. et al. Second phase of a double-blind study clinical trial on Sibutramine for the treatment of patients suffering essential obesity: 6 months after treatment cross-over. Int J Obes 25, 741–747 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801592
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801592
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy for obesity: moving towards efficacy improvement
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2024)
-
Systematic review of long-term weight loss studies in obese adults: clinical significance and applicability to clinical practice
International Journal of Obesity (2005)
-
Sibutramine lost and found
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity (2002)