Abstract
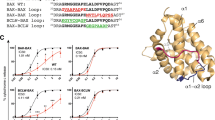
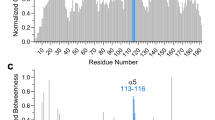
The viral mitochondrial inhibitor of apoptosis (vMIA) encoded by the human cytomegalovirus exerts cytopathic effects and neutralizes the proapoptotic endogenous Bcl-2 family member Bax by recruiting it to mitochondria, inducing its oligomerization and membrane insertion. Using a combination of computational modeling and mutational analyses, we addressed the structure–function relationship of the molecular interaction between the protein Bax and the viral antiapoptotic protein vMIA. We propose a model in which vMIA exhibits an overall fold similar to Bcl-XL. In contrast to Bcl-XL, however, this predicted conformation of vMIA does not bind to the BH3 domain of Bax and rather engages in electrostatic interactions that involve a stretch of amino acids between the BH3 and BH2 domains of Bax and an α-helical domain located within the previously defined Bax-binding domain of vMIA, between the putative BH1-like and BH2-like domains. According to this model, vMIA is likely to bind Bax preferentially in its membrane-inserted conformation. The capacity of vMIA to cause fragmentation of the mitochondrial network and disorganization of the actin cytoskeleton is independent of its Bax-binding function. We found that Δ131–147 vMIA mutant, which lacks both the Bax-binding function and cell-death suppression but has intact mitochondria-targeting capacity, is similar to vMIA in its ability to disrupt the mitochondrial network and to disorganize the actin cytoskeleton. vMIAΔ131–147 is a dominant-negative inhibitor of the antiapoptotic function of wild-type vMIA. Our experiments with vMIAΔ131–147 suggest that vMIA forms homo-oligomers, which may engage in cooperative and/or multivalent interactions with Bax, leading to its functional neutralization.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BBD:
-
Bax-binding domain
- CMV:
-
human cytomegalovirus
- CHAPS:
-
3-((cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio)-1-propane sulfonate
- DiOC6(3):
-
3,3′-dihexyloxacarbocyanine iodide
- GFP:
-
green fluorescent protein
- MLS:
-
mitochondrial localization sequence
- MOMP:
-
mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization
- PI:
-
propidium iodide
- STS:
-
staurosporine
- TMRM:
-
tetra methyl rhodamine methyl ester
- vMIA:
-
viral mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W et al. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25: 3389–3402.
Annis MG, Soucie EL, Dlugosz PJ, Cruz-Aguado JA, Penn LZ, Leber B et al. (2005). Bax forms multispanning monomers that oligomerize to permeabilize membranes during apoptosis. EMBO J 24: 2096–2103.
Antonsson B, Montessuit S, Sanchez B, Martinou JC . (2001). Bax is present as a high molecular weight oligomer/complex in the mitochondrial membrane of apoptotic cells. J Biol Chem 276: 11615–11623.
Arnoult D, Bartle LM, Skaletskaya A, Poncet D, Zamzami N, Park PU et al. (2004). Cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor vMIA blocks Bax- but not Bak-mediated apoptosis by binding and sequestering Bax at mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7988–7993.
Castedo M, Ferri K, Roumier T, Metivier D, Zamzami N, Kroemer G . (2002). Quantitation of mitochondrial alterations associated with apoptosis. J Immunol Methods 265: 39–47.
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ . (2004). Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116: 205–219.
Day CL, Chen L, Richardson SJ, Harrison PJ, Huang DC, Hinds MG . (2005). Solution structure of prosurvival Mcl-1 and characterization of its binding by proapoptotic BH3-only ligands. J Biol Chem 280: 4738–4744.
Froberg MK . (2004). Review: CMV escapes!. Ann Clin Lab Sci 34: 123–130.
Gabb HA, Jackson RM, Sternberg MJ . (1997). Modelling protein docking using shape complementarity, electrostatics and biochemical information. J Mol Biol 272: 106–120.
Galluzzi L, Larochette N, Zamzami N, Kroemer G . (2006). Mitochondria as therapeutic targets for cancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25: 4812–4830.
Garcia-Saez AJ, Mingarro I, Perez-Paya E, Salgado J . (2004). Membrane-insertion fragments of Bcl-xL, Bax, and Bid. Biochemistry 43: 10930–10943.
Goldmacher VS . (2005). Cell death suppression by cytomegaloviruses. Apoptosis 10: 251–265.
Goldmacher VS, Bartle LM, Skaletskaya A, Dionne CA, Kedersha NL, Vater CA et al. (1999). A cytomegalovirus-encoded mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis structurally unrelated to Bcl-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 12536–12541.
Green DR . (2005). Apoptotic pathways: ten minutes to dead. Cell 121: 671–674.
Harkins L, Volk AL, Samanta M, Mikolaenko I, Britt WJ, Bland KI et al. (2002). Specific localisation of human cytomegalovirus nucleic acids and proteins in human colorectal cancer. Lancet 360: 1557–1563.
Hassan M, Bielawski JP, Hempel JC, Waldman M . (1996). Optimization and visualization of molecular diversity and combinatorial libraries. Molecular Diversity 2: 64–74.
Hayajneh WA, Colberg-Poley AM, Skaletskaya A, Bartle LM, Lesperance MM, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG et al. (2001). The sequence and antiapoptotic functional domains of the human cytomegalovirus UL37 exon 1 immediate early protein are conserved in multiple primary strains. Virology 279: 233–240.
Hoever G, Vogel JU, Lukashenko P, Hofmann WK, Komor M, Doerr HW et al. (2005). Impact of persistent cytomegalovirus infection on human neuroblastoma cell gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326: 395–401.
Huang J, Nakamura K, Ito Y, Uzuka T, Morikawa M, Hirai S et al. (2005). Bcl-xL gene transfer inhibits Bax translocation and prolongs cardiac cold preservation time in rats. Circulation 112: 76–83.
Jackson RM, Gabb HA, Sternberg MJ . (1998). Rapid refinement of protein interfaces incorporating solvation: application to the docking problem. J Mol Biol 276: 265–285.
Jurak I, Brune W . (2006). Induction of apoptosis limits cytomegalovirus cross-species infection. EMBO J 25: 2634–2642.
Kelley LA, MacCallum RM, Sternberg MJ . (2000). Enhanced genome annotation using structural profiles in the program 3D-PSSM. J Mol Biol 299: 499–520.
Lang-Rollin I, Maniati M, Jabado O, Vekrellis K, Papantonis S, Rideout HJ et al. (2005). Apoptosis and the conformational change of Bax induced by proteasomal inhibition of PC12 cells are inhibited by bcl-xL and bcl-2. Apoptosis 10: 809–820.
Matsuyama S, Llopis J, Deveraux QL, Tsien RY, Reed JC . (2000). Changes in intramitochondrial and cytosolic pH: early events that modulate caspase activation during apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol 2: 318–325.
Mavinakere MS, Williamson CD, Goldmacher VS, Colberg-Poley AM . (2006). Processing of human cytomegalovirus UL37 mutant glycoproteins in the endoplasmic reticulum lumen prior to mitochondrial importation. J Virol 80: 6771–6783.
McCormick AL, Meiering CD, Smith GB, Mocarski ES . (2005). Mitochondrial cell death suppressors carried by human and murine cytomegalovirus confer resistance to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis. J Virol 79: 12205–12217.
McDonnell JM, Fushman D, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ, Cowburn D . (1999). Solution structure of the proapoptotic molecule BID: a structural basis for apoptotic agonists and antagonists. Cell 96: 625–634.
McGuffin LJ, Jones DT . (2003). Improvement of the GenTHREADER method for genomic fold recognition. Bioinformatics 19: 874–881.
McMartin C, Bohacek RS . (1997). QXP: powerful, rapid computer algorithms for structure-based drug design. J Comput Aided Mol Des 11: 333–344.
Michelson S . (2004). Consequences of human cytomegalovirus mimicry. Hum Immunol 65: 465–475.
Moont G, Gabb HA, Sternberg MJ . (1999). Use of pair potentials across protein interfaces in screening predicted docked complexes. Proteins 35: 364–373.
Muchmore SW, Sattler M, Liang H, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Yoon HS et al. (1996). X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 381: 335–341.
Obeid M, Tesniere A, Ghiringhelli F, Fimia GM, Apetoh L, Perfettini JL et al. (2007). Calreticulin exposure dictates the immunogenicity of cancer cell death. Nat Med 13: 54–61.
Poncet D, Larochette N, Pauleau AL, Boya P, Jalil AA, Cartron PF et al. (2004). An anti-apoptotic viral protein that recruits Bax to mitochondria. J Biol Chem 279: 22605–22614.
Poncet D, Pauleau AL, Szabadkai G, Vozza A, Scholz SR, Le Bras M et al. (2006). Cytopathic effects of the cytomegalovirus-encoded apoptosis inhibitory protein vMIA. J Cell Biol 174: 985–996.
Reboredo M, Greaves RF, Hahn G . (2004). Human cytomegalovirus proteins encoded by UL37 exon 1 protect infected fibroblasts against virus-induced apoptosis and are required for efficient virus replication. J Gen Virol 85: 3555–3567.
Reed JC . (2006). Proapoptotic multidomain Bcl-2/Bax-family proteins: mechanisms, physiological roles, and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Death Differ 13: 1378–1386.
Sali A, Blundell TL . (1993). Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol 234: 779–815.
Samanta M, Harkins L, Klemm K, Britt WJ, Cobbs CS . (2003). High prevalence of human cytomegalovirus in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostatic carcinoma. J Urol 170: 998–1002.
Sattler M, Liang H, Nettesheim D, Meadows RP, Harlan JE, Eberstadt M et al. (1997). Structure of Bcl-xL–Bak peptide complex: recognition between regulators of apoptosis. Science 275: 983–986.
Skaletskaya A, Bartle LM, Chittenden T, McCormick AL, Mocarski ES, Goldmacher VS . (2001). A cytomegalovirus-encoded inhibitor of apoptosis that suppresses caspase-8 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 7829–7834.
Smith MS, Bentz GL, Smith PM, Bivins ER, Yurochko AD . (2004). HCMV activates PI(3)K in monocytes and promotes monocyte motility and transendothelial migration in a PI(3)K-dependent manner. J Leukoc Biol 76: 65–76.
Suzuki M, Youle RJ, Tjandra N . (2000). Structure of Bax: coregulation of dimer formation and intracellular localization. Cell 103: 645–654.
Terrasson J, Allart S, Martin H, Lule J, Haddada H, Caput D et al. (2005). p73-dependent apoptosis through death receptor: impairment by human cytomegalovirus infection. Cancer Res 65: 2787–2794.
Vieira HL, Belzacq AS, Haouzi D, Bernassola F, Cohen I, Jacotot E et al. (2001). The adenine nucleotide translocator: a target of nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, and 4-hydroxynonenal. Oncogene 20: 4305–4316.
Wei MC, Zong WX, Cheng EH, Lindsten T, Panoutsakopoulou V, Ross AJ et al. (2001). Proapoptotic BAX and BAK: a requisite gateway to mitochondrial dysfunction and death. Science 292: 727–730.
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi XG, Youle RJ . (1997). Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139: 1281–1292.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Matsuyama (Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, USA) for Bax expression plasmid. GK is supported by Ligue Nationale contre le cancer, European Community (Active p53, RIGHT), Agence National pour la Recherche contre le Sida (ANRS) and Sidaction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pauleau, AL., Larochette, N., Giordanetto, F. et al. Structure–function analysis of the interaction between Bax and the cytomegalovirus-encoded protein vMIA. Oncogene 26, 7067–7080 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210511
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210511
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Host Mitochondrial Requirements of Cytomegalovirus Replication
Current Clinical Microbiology Reports (2020)
-
Cytomegaloviruses inhibit Bak- and Bax-mediated apoptosis with two separate viral proteins
Cell Death & Differentiation (2010)
-
Bcl-2 family proteins and mitochondrial fission/fusion dynamics
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2010)
-
Mechanisms of pre-apoptotic calreticulin exposure in immunogenic cell death
The EMBO Journal (2009)
-
Unexpected role of the phosphate carrier in mitochondrial fragmentation
Cell Death & Differentiation (2008)