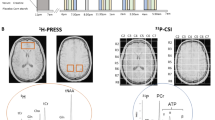
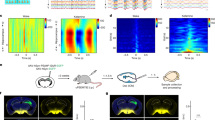
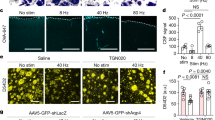
Abstract
THE mechanism of the effects of large doses of L-dopa on brain function is ill-defined. This form of precursor loading produces marked increases in brain dopamine, little or no change in noradrenaline, and a substantial decrease in serotonin with an initial increase in 5-H indolyl-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA)1–3. These observations suggest that serotonin may be released by L-dopa or its metabolites. Isolated synaptosomes (pinched-off nerve endings) actively accumulate exogenously labelled amines into structures which normally contain these amines4–6. Although the distribution of the labelled amine in the endogenous stores is not clearly defined, these structures seem to provide valid models for nerve endings in brain and may afford a direct and sensitive means of assessing the influence of drugs on the release of neurohumours. Using this technique, we have found that L-dopa profoundly affects the efflux of cerebral monoamines.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butcher, L. L., and Engel, J., Brain Res., 15, 223 (1969).
Bartholini, G., DaPrada, M., and Pletscher, A., J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 20, 228 (1968).
Everett, G. M., and Borcherding, J. W., Science, 168, 849 (1970).
Colburn, R. W., Goodwin, F. K., Murphy, D. L., Bunney, jun., W. E., and Davis, J. M., Biochem. Pharmacol., 17, 957 (1968).
Aghajanian, G. K., and Bloom, F. E., J. Pharmacol., 156, 23 (1967).
Coyle, J. T., and Snyder, S. H., J. Pharmacol., 170, 221 (1969).
Whittaker, V. P., Michaelson, I. A., and Kirkland, R. J. A., Biochem. J., 90, 293 (1964).
Häggendal, J., Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest., 14, 537 (1962).
Anton, A. H., and Sayre, D. F., J. Pharmacol., 138, 360 (1962).
Dengler, H. J., Michaelson, I. A., Spiegel, H. E., and Titus, E., Intern. J. Neuropharm., 1, 23 (1962).
Baldessarini, R. J., and Kopin, I. J., Science, 152, 1630 (1966).
Blackburn, K. J., French, P. C., and Merrills, R. J., Life Sci., 6, 1653 (1967).
Shaskan, E. G., and Snyder, S. H., J. Pharmacol., 175, 404 (1970).
Iversen, L. L., and Snyder, S. H., Nature, 220, 796 (1968).
Snyder, S. H., Kuhar, M. J., Green, A. I., Coyle, J. T., and Shaskan, E. G., Intern. Rev. Neurobiol., 13, 127 (1970).
Glowinski, J., and Iversen, L. L., Biochem. Pharmacol., 15, 977 (1966).
Ng, K. Y., Chase, T. N., Colburn, R. W., and Kopin, I. J., Science, 170, 76 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
NG, K., COLBURN, R. & KOPIN, I. Effects of L-Dopa on Efflux of Cerebral Monoamines from Synaptosomes. Nature 230, 331–332 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1038/230331a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/230331a0
This article is cited by
-
Molecular basis of dopamine replacement therapy and its side effects in Parkinson’s disease
Cell and Tissue Research (2018)
-
Serotonin hyperinnervation of the striatum with high synaptic incidence in parkinsonian monkeys
Brain Structure and Function (2016)
-
Molecular imaging of levodopa-induced dyskinesias
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
SERT-to-DAT ratios in early Parkinson’s disease do not correlate with the development of dyskinesias
EJNMMI Research (2013)
-
Mechanisms underlying the onset and expression of levodopa-induced dyskinesia and their pharmacological manipulation
Journal of Neural Transmission (2011)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.