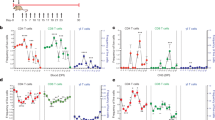
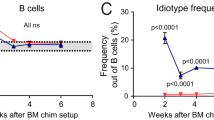
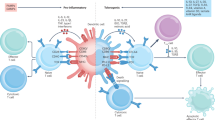
Abstract
A FEATURE common to many animal models of autoimmune disease, for example, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis1, experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis2 and collagen-induced arthritis3, is the presence of self-reactive T cells in healthy animals, which are activated to produce disease by immunization with exogenous antigen. It is unclear why these T cells are not deleted during ontogeny in the thymus and, having escaped tolerance induction, why they are not spontaneously activated by self-antigen. To investigate these questions, we have examined an experimental model in which mice are tolerant to an antigen despite the presence of antigen-reactive T cells4. We find that the T cells that escape tolerance induction are specific for minor determinants on the antigen. We propose that these T cells evade tolerance induction because some minor determinants are only available in relatively low amounts after in vivo processing of the whole antigen. For the same reason, these T cells are not normally activated but can be stimulated under special circumstances to circumvent tolerance.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zamvil, S. S. et al. Nature 317, 255–258 (1985).
Hohlfield, R., Kabies, I., Heinz, F., Kalden, J. & Wekerle, H. J. Immun. 126, 1355–1359 (1981).
Watson, J. M. & Kang, W. C. Fedn Proc. 2, 2950–2956 (1988).
Oki, A. & Sercarz, E. J. exp. Med. 161, 897–911 (1985).
Unanue, E. R. A. Rev. Immun. 2, 395–428 (1984).
Gammon, G. et al. Immunol. Rev. 98, 53–73 (1987).
Allen, P. M., McKean, D. J., Beck, B. N., Scofield, J. & Glimcher, L. H. J. exp. Med. 162, 1264–1274 (1985).
Adorini, L., Apella, E., Doria, G. & Nagy, Z. A. J. exp. Med. 168, 2091–2104 (1988).
Gammon, G. et al. Nature 319, 413–415 (1986).
Gammon, G., Oki, A., Shastri, N. & Sercarz, E. J. exp. Med. 164, 667–672 (1986).
Mueller, D. L., Jenkins, M. K. & Schwartz, R. M. A. Rev. Immun. 7, 445–480 (1989).
Markman, J. et al. Nature 336, 476–479 (1988).
Ràmmensee, H-G., Kroschewski, R. & Frangoulis, B. Nature 339, 541–544 (1989).
Klotz, J. L., Barth, R. K., Kiser, G. L., Hood, L. E. & Kronenberg, M. Immunogenetics 29, 191–201 (1989).
Adorini, L., Harvey, M. A., Miller, A. & Sercarz, E. E. J. exp. Med. 150, 293–306 (1979).
Nossal, G. J. V. Science 245, 147–153 (1989).
Waldmann, H., Cobbold, S., Benjamin, R. & Qin, S. J. Autoimmunity 1, 623–629 (1988).
Oldstone, M. B. A. Cell 50, 819–820 (1987).
White, J. et al. Cell 56, 27–35 (1989).
Shastri, N., Gammon, G., Horvath, S., Miller, A. & Sercarz, E. J. Immun. 137, 911–915 (1986).
Cerottini, J. & McDonald, H. R. A. Rev. Immun. 7, 77–89 (1989).
Palmer, M. & Sercarz, E. in The Immune Response to Structurally Defined Proteins: the Lysozyme Model (eds Smith-Gill, S. & Sercarz, E.) (Adenine, New York, 1989).
Kent, S. & Clark-Lewis, I. in Synthetic peptides in biology and medicine (eds Alitalo, K., Partonen, P. & Vahen, A.) (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gammon, G., Sercarz, E. How some T cells escape tolerance induction. Nature 342, 183–185 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/342183a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/342183a0
This article is cited by
-
Safety of targeting tumor endothelial cell antigens
Journal of Translational Medicine (2016)
-
T Cell Epitope Peptide Therapy for Allergic Diseases
Current Allergy and Asthma Reports (2016)
-
Unconventional recognition of peptides by T cells and the implications for autoimmunity
Nature Reviews Immunology (2012)
-
The Etiology of Paraneoplastic Autoimmunity
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2012)
-
Levees of immunological tolerance
Nature Immunology (2010)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.