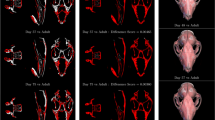
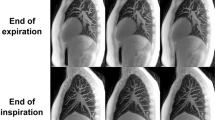
Abstract
THE electrical resistivity of mammalian tissues varies widely1–5 and is correlated with physiological function6–8. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) can be used to probe such variations in vivo, and offers a non-invasive means of imaging the internal conductivity distribution of the human body9–11. But the computational complexity of EIT has severe practical limitations, and previous work has been restricted to considering image reconstruction as an essentially two-dimensional problem10,12. This simplification can limit significantly the imaging capabilities of EIT, as the electric currents used to determine the conductivity variations will not in general be confined to a two-dimensional plane13. A few studies have attempted three-dimensional EIT image reconstruction14,15, but have not yet succeeded in generating images of a quality suitable for clinical applications. Here we report the development of a three-dimensional EIT system with greatly improved imaging capabilities, which combines our 64-electrode data-collection apparatus16 with customized matrix inversion techniques. Our results demonstrate the practical potential of EIT for clinical applications, such as lung or brain imaging and diagnostic screening8.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geddes, L. A. & Baker, L. E. Med. Biol. Engng 5, 271–293 (1967).
Duck, F. A. Physical Properties of Tissue 167–223 (Academic, London, 1990).
Stoy, R. D., Foster, K. R. & Schwan, H. P. Phys. Med. Biol. 27, 501–513 (1982).
Pethig, R. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. A8, 5–12 (1987). (see note below)
McAdams, E. T. & Jossinet, J. Physiol. Meas. A16, A1–A14 (1995).
Dawids, S. G. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. A8, 175–180 (1987).
Dijkstra, A. M. et al. J. med. Engng Technol. 17, 89–98 (1993).
Holder, D. S. & Brown, B. H. in Clinical and Physiological Applications of Electrical Impedance Tomography (ed. Holder, D. S.) 47–60 (University College London Press, London, 1993).
Barber, D. C., Brown, B. H. & Freeston, I. L. Electron. Lett. 19, 933–935 (1983).
Barber, D. C. & Brown, B. H. J. Phys E: Sci. Instrum. 17, 723–733 (1984).
Barber, D. C. in Clinical and Physiological Applications of Electrical Impedance Tomography (ed. Holder, D. S.) 47–60 (University College London Press, London 1993).
Barber, D. C. & Brown, B. H. in Inverse Problems in Partial Differential Equations (eds. Colton, D., Ewing, R. Rundell, W.) 151–164 (Soc. for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, 1990).
Rabbani, K. S. & Kabir, A. M. B. H. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 12, 393–402 (1991).
Morucci, J. P., Granié, M., Lei, M., Chabert, M. & Marsili, P. M. Physiol. Meas. A16, A123–A128 (1995).
Goble, J., Chenney, M. & Isaacson, D. Appl. Comput. Electromagn. Soc. J. 7, 128–147 (1992).
Brown, B. H. et al. (spec. iss. 1) Innov. Tech. Biol. Med. 15, 1–8 (1994).
Brown, B. H. & Seagar, A. D. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. A8, 91–97 (1987).
Geselowitz, D. B. IEEE Trans. biomed. Engng 18, 38–41 (1971).
Kotre, C. J. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 10, 275–281 (1989).
Barber, D. C. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 10, 368–370 (1989).
Witsoe, D. A. & Kinnen, E. Med biol. Engng. 5, 239–248 (1967).
Albert, A. Regression and the Moore-Penrose Pseudo-inverse (Academic, New York, 1972).
Golub, G. H. & Reinsch, C. Numer. Math. 14, 403–420 (1970).
Hansen, P. C. Numer Alg. 6, 1–35 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metherall, P., Barber, D., Smallwood, R. et al. Three-dimensional electrical impedance tomography. Nature 380, 509–512 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/380509a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/380509a0
This article is cited by
-
Soft wearable devices for deep-tissue sensing
Nature Reviews Materials (2022)
-
Uniqueness, stability and global convergence for a discrete inverse elliptic Robin transmission problem
Numerische Mathematik (2021)
-
Brain Tissue Conductivity Measurements with MR-Electrical Properties Tomography: An In Vivo Study
Brain Topography (2021)
-
Validation of conductivity tensor imaging using giant vesicle suspensions with different ion mobilities
BioMedical Engineering OnLine (2020)
-
Noninvasive, simultaneous, and continuous measurements of stroke volume and tidal volume using EIT: feasibility study of animal experiments
Scientific Reports (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.