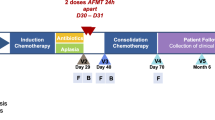
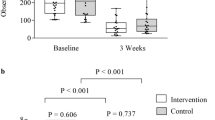
Abstract
Acute GvHD (aGvHD) is the main complication of hematopoietic SCT (HSCT) during the treatment of hematological disorders. We carried out the first longitudinal study to follow the gut microbiota trajectory, from both the phylogenetic and functional points of view, in pediatric patients undergoing HSCT. Gut microbiota trajectories and short-chain fatty acid production profiles were followed starting from before HSCT and through the 3–4 months after transplant in children developing and not developing aGvHD. According to our findings, HSCT procedures temporarily cause a structural and functional disruption of the gut microbial ecosystem, describing a trajectory of recovery during the following 100 days. The onset of aGvHD is associated with specific gut microbiota signatures both along the course of gut microbiota reconstruction immediately after transplant and, most interestingly, prior to HSCT. Indeed, in pre-HSCT samples, non-aGvHD patients showed higher abundances of propionate-producing Bacteroidetes, highly adaptable microbiome mutualists that showed to persist during the HSCT-induced ecosystem disruption. Our data indicate that structure and temporal dynamics of the gut microbial ecosystem can be a relevant factor for the success of HSCT and opens the perspective to the manipulation of the pre-HSCT gut microbiota configuration to favor mutualistic persisters with immunomodulatory properties in the gut.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Hamady M, Fraser-Liggett CM, Knight R, Gordon JI . The human microbiome project. Nature 2007; 449: 804–810.
Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 15718–15723.
Lupp C, Robertson ML, Wickham ME, Sekirov I, Champion OL, Gaynor EC et al. Host-mediated inflammation disrupts the intestinal microbiota and promotes the overgrowth of Enterobacteriaceae. Cell Host Microbe 2007; 2: 204.
Lee YK, Mazmanian SK . Has the microbiota played a critical role in the evolution of the adaptive immune system? Science 2010; 330: 1768–1773.
Candela M, Turroni S, Biagi E, Carbonero F, Rampelli S, Fiorentini C et al. Inflammation and colorectal cancer, when microbiota-host mutualism breaks. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20: 908–922.
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J, Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W et al. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012; 336: 1262–1267.
Segain JP, Raingeard de la Blétière D, Bourreille A, Leray V, Gervois N, Rosales C et al. Butyrate inhibits inflammatory responses through NFκB inhibition: implications for Crohn's disease. Gut 2000; 47: 397–403.
Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van der Veeken J, deRoos P et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature 2013; 504: 451–455.
Fukuda S, Toh H, Hase K, Oshima K, Nakanishi Y, Yoshimura K et al. Bifidobacteria can protect from enteropathogenic infection through production of acetate. Nature 2011; 469: 543–547.
Petersson J, Schreiber O, Hansson GC, Gendler SJ, Velcich A, Lundberg JO et al. Importance and regulation of the colonic mucus barrier in a mouse model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2011; 300: G327–G333.
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010; 464: 59–65.
Candela M, Biagi E, Turroni S, Maccaferri S, Figini P, Brigidi P . Dynamic efficiency of the human intestinal microbiota. Crit Rev Microbiol 2013; 9: 1–7.
Faith JJ, Guruge JL, Charbonneau M, Subramanian S, Seedorf H, Goodman AL et al. The long term stability of the human gut microbiota. Science 2013; 341: 1237439.
Candela M, Biagi E, Maccaferri S, Turroni S, Brigidi P . Intestinal microbiota is a plastic factor responding to environmental changes. Trends Microbiol 2012; 20: 385–391.
Neish AS . Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: 65–80.
Tilg H, Moschen AR . Mechanisms behind the link between obesity and gastrointestinal cancers. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2014; 28: 599–610.
Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K, Sichelstiel AK, Sprenger N, Ngom-Bru C et al. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med 2014; 20: 159–166.
Ferrara JL, Levine JE, Reddy P, Holler E . Graft-versus-host disease. Lancet 2009; 373: 1550–1561.
Pasquini MC, Wang Z, Horowitz MM, Gale RP . 2010 report from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR): current uses and outcomes of haematopoietic cell transplants for blood and bone marrow disorders. Clin Transpl 2010, 87–105.
Blazar BR, Murphy WJ, Abedi M . Advances in graft-versus-host disease biology and therapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2012; 12: 443–458.
van Bekkum DW, Roodenburg J, Heidt PJ, van der Waaij D . Mitigation of secondary disease of allogeneic mouse radiation chimeras by modification of the intestinal microflora. J Natl Cancer Inst 1974; 52: 401–404.
Jenq RR, Ubeda C, Taur Y, Menezes CC, Khanin R, Dudakov JA et al. Regulation of intestinal inflammation by microbiota following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. J Exp Med 2012; 209: 903–911.
Holler E, Butzhammer P, Schmid K, Hundsrucker C, Koestler J, Peter K et al. Metagenomic analysis of the stool microbiome in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation: loss of diversity is associated with use of systemic antibiotics and more pronounced in gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2014; 20: 640–645.
Heimesaat MM, Nogai A, Bereswill S, Plickert R, Fischer A, Loddenkemper C et al. MyD88/TLR9 mediated immunopathology and gut microbiota dynamics in a novel murine model of intestinal graft-versus-host disease. Gut 2010; 59: 1079–1087.
Eriguchi Y, Takashima S, Oka H, Shimoji S, Nakamura K, Uryu H et al. Graft-versus-host disease disrupts intestinal microbial ecology by inhibiting Paneth cell production of α-defensins. Blood 2012; 120: 223–231.
Tawara I, Liu C, Tamaki H, Toubai T, Sun Y, Evers R et al. Influence of donor microbiota on the severity of experimental graft-versus-host-disease. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2013; 19: 164–168.
Taur Y, Jenq RR, Perales MA, Littmann ER, Morjaria S, Ling L et al. The effects of intestinal tract bacterial diversity on mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2014; 124: 1174–1182.
Bucaneve G, Micozzi A, Menichetti F, Martino P, Dionisi MS, Martinelli G et al. Levofloxacin to prevent bacterial infection in patients with cancer and neutropenia. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 977–987.
Saral R, Burns WH, Laskin OL, Santos GW, Lietman PS . Acyclovir prophylaxis of herpes-simplex-virus infections. N Engl J Med 1981; 305: 63–67.
Goodman JL, Winston DJ, Greenfield RA, Chandrasekar PH, Fox B, Kaizer H et al. A controlled trial of fluconazole to prevent fungal infections in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1992; 326: 845–851.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A, Buckner CD, Neiman PE, Clift RA et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A- matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Salonen A, Nikkilä J, Jalanka-Tuovinen J, Immonen O, Rajilić-Stojanović M, Kekkonen RA et al. Comparative analysis of fecal DNA extraction methods with phylogenetic microarray: effective recovery of bacterial and archaeal DNA using mechanical cell lysis. J Microbiol Methods 2010; 81: 127–134.
Centanni M, Turroni S, Consolandi C, Rampelli S, Peano C, Severgnini M et al. The enterocyte-associated intestinal microbiota of breast-fed infants and adults responds differently to a TNF-α-mediated pro-inflammatory stimulus. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e81762.
Schnorr SL, Candela M, Rampelli S, Centanni M, Consolandi C, Basaglia G et al. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nat Commun 2014; 5: 3654.
Smith MI, Yatsunenko T, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Mkakosya R, Cheng J et al. Gut microbiomes of Malawian twin pairs discordant for kwashiorkor. Science 2013; 339: 548–554.
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M et al. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005; 308: 1635–1638.
Dethlefsen L, Huse S, Sogin ML, Relman DA . The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol 2008; 6: e280.
Tremaroli V, Bäckhed F . Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nature 2012; 489: 242–249.
Lee SM, Donaldson GP, Mikulski Z, Boyajian S, Ley K, Mazmanian SK . Bacterial colonization factors control specificity and stability of the gut microbiota. Nature 2013; 501: 426–429.
Fishbach MA, Sonnenburg JL . Eating for two: how metabolism establishes interspecies interactions in the gut. Cell Host Microbe 2011; 10: 336–347.
Zwielehner J, Lassl C, Hippe B, Pointner A, Switzeny OJ, Remely M et al. Changes in human fecal microbiota due to chemotherapy analyzed by TaqMan-PCR, 454 sequencing and PCR-DGGE fingerprinting. PLoS ONE 2011; 6: e28654.
Dignan FL, Potter MN, Ethell ME, Taylor M, Lewis L, Brennan J et al. High readmission rates are associated with a significant economic burden and poor outcome in patients with grade III/IV acute GvHD. Clin Transplant 2013; 27: E56–E63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Bone Marrow Transplantation website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biagi, E., Zama, D., Nastasi, C. et al. Gut microbiota trajectory in pediatric patients undergoing hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant 50, 992–998 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.16
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2015.16
This article is cited by
-
Targeting the gut and tumor microbiota in cancer
Nature Medicine (2022)
-
Microbiota long-term dynamics and prediction of acute graft-versus-host disease in pediatric allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Microbiome (2021)
-
Tandem fecal microbiota transplantation cycles in an allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipient targeting carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae colonization: a case report and literature review
European Journal of Medical Research (2021)
-
The gut microbiome: what the oncologist ought to know
British Journal of Cancer (2021)
-
Allogenic stem cell transplant-associated acute graft versus host disease: a computational drug discovery text mining approach using oral and gut microbiome signatures
Supportive Care in Cancer (2021)