Abstract
A decade ago, Jurg Tschopp introduced the concept of the inflammasome. This exciting discovery of a macromolecular complex that senses ‘danger’ and initiates the inflammatory response contributed to a renaissance in the fields of innate immunity and cell death. Jurg led the biochemical characterization of the inflammasome complex and demonstrated that spontaneous hyperactivation of this interleukin (IL)-1β processing machinery is the molecular basis of a spectrum of hereditary periodic fever syndromes, caused by mutated forms of the inflammasome scaffolding receptor, NLRP3. The identification of the underlying mechanism in these disorders has led to their now successful therapy, with the use of the IL-1 receptor antagonist in the clinic. Jurg's pioneering work has subsequently defined a number of inflammasome agonists ranging from microbial molecules expressed during infection, to triggers of sterile inflammation, most notably gout-associated uric acid crystals, asbestos, silica and nanoparticles. More recently, Jurg introduced the critical new concept of the metabolic inflammasome, which senses metabolic stress and contributes to the onset of the metabolic syndrome associated with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Jurg was an outstanding and skillful biochemist, an elegant and rigorous researcher often far ahead of his peers. He was a truly amiable person, fair, generous and inspiring, and will be most remembered for his infectious enthusiasm. We write this review article on the inflammasome in his honor and dedicate it to his memory.
Similar content being viewed by others
Facts
-
Tschopp and colleagues discovered the inflammasome platforms and described its biochemistry and clinical relevance in cold-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) or cryopyrinopathies, gout and type 2 diabetes.
-
Tschopp and colleagues identified a number of inflammasome agonists, namely muramyl dipeptide (MDP), viral DNA, monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, asbestos, silica, alum and malaria-associated hemozoin.
-
Tschopp and colleagues showed that the immunosuppressive function of type I interferon was accomplished through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
-
Tschopp and coworkers demonstrated a role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in the metabolic syndrome.
-
Tschopp's research led to the establishment of a number of clinical trials for inflammatory diseases, including CAPS, gout and type 2 diabetes.
Open Questions
-
What is the molecular mechanism that activates the inflammasome?
-
What is the link between inflammation and cell death pathways, and how does the cell decide to engage one but not the other?
-
Although the role of the inflammasome has been well demonstrated in monogenic inflammatory diseases, what is its role in more complex diseases, and what are the potential therapeutic solutions?
Discovery and Molecular Characterization of the Inflammasome
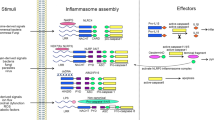
Nucleotide-binding domain (NB) and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) containing receptors (NLR), casually referred to as Nod-like receptors, are cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors that were initially proposed to regulate inflammation through leukocyte apoptosis, based on structural homology with apoptosis effectors. However, a decade ago, their mechanisms of action were obscure, and this initial view has been modified with the discovery of the inflammasome. NLR proteins are evolutionarily related to plant NB–LRR proteins (reviewed in Chisholm et al.1 and Jones and Dangl2) also referred to as disease-resistance or R proteins, for their crucial function in host defense against infection. NLRs are also reminiscent of apoptosis-activating factor (APAF)-1, which assembles the apoptosome following cytochrome c release from the mitochondria, and initiates apoptosis by recruiting and activating caspase-9 (reviewed in Bratton and Salvesen3). NLRs are characterized by a tripartite structure composed of an invariant central domain that mediates nucleotide binding and oligomerization referred to as a NACHT, NOD or NBS domain, a C-terminal LRR domain that senses NLR agonists, but exerts auto-inhibitory effects in their absence (reviewed in Reidl and Salvesen4), and a variable N-terminal region that is required for homotypic protein–protein interactions. The human NLR family consists of 22 members, classified into 4 subfamilies, namely the NLRA, NLRB, NLRC and NLRP subfamilies, on the basis of their N-terminal domain configuration5 (Figure 1). NLRA contains an acidic transactivation domain; NLRB, a baculoviral inhibitory repeat domain; NLRC, a caspase-recruitment and activation domain (CARD); and NLRP, a pyrin domain (PYD). Notably, the CARD and PYD belong to the death-fold structural family, which also encompasses the death domain and death-effector domain, consisting of a tertiary structure commonly found in proteins involved in apoptosis or inflammation-related processes (reviewed in Lahm et al.6).
The human NLR family and inflammasome-associated proteins. There are 22 human NLRs characterized by a central nucleotide-binding domain (NB). The NLR family can be further classified into four subfamilies, depending on the protein's N-terminal domain. CARD and PYD domains enable interaction with caspase-1 or the adaptor ASC, allowing assembly of the inflammasome. The pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) AIM2 and RIG-I are also capable of forming inflammasomes
In 2001, a number of seminal genetic studies have linked mutations in NLR genes to inflammatory diseases. Mutations in CARD15/NOD2 have been found to underlie both Crohn's disease and Blau syndrome,7, 8, 9 and mutations in NLRP3, then termed CIAS1 (cold-induced auto-inflammatory syndrome 1), were identified in individuals affected by familial MuckleWells syndrome (MWS).10 The NLRP3 protein was then termed cryopyrin, and like pyrin, the product of the MEFV gene causing familial Mediterranean fever (FMF)11 was found to be expressed predominantly in peripheral blood leukocytes.10, 11 It was found that NLRP3 is mutated in a spectrum of hereditary periodic fever syndromes, which, in addition to MWS, include familial cold urticaria and neonatal onset multi-system inflammatory disease.
In 2002, Martinon et al.12 described in a pioneering study a large molecular platform required for the oligomerization and activation of the pro-inflammatory protease, caspase-1, which they termed the inflammasome (Figure 2). Using elegant biochemical approaches, cell-free and cell-based systems, they demonstrated that the NLRP1 inflammasome consisted of the NLR protein NLRP1, the adaptor protein ASC (also known as PYCARD), and the two members of the inflammatory caspase subfamily, caspases-1 and -5. Depletion of ASC was shown to impair inflammatory caspase activation and block interleukin (IL)-1β maturation following lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment, indicating for the first time that the inflammasome is an important arm of the innate immune system.12
Tschopp and colleagues13 went on to demonstrate in 2004 that NLRP3, which is mutated in the auto-inflammatory syndromes described above, and homologous to NLRP1, also forms an inflammasome complex comprising ASC, the CARD-containing protein cardinal and caspase-1 (but not caspase-5). They further demonstrated that the molecular basis of NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent disorders is spontaneous and excessive production of active IL-1β as observed using macrophages from MWS patients.
The requirement of ASC within the inflammasome was corroborated by Dixit and colleagues14 in the same year, who reported the generation of Asc and Ipaf (Nlrc4)-deficient mice. This study demonstrated that macrophages from Asc−/− mice exhibited defective maturation of the caspase-1-dependent cytokines IL-1β and IL-18 in response to extracellular ATP or infection with an intracellular pathogen (Salmonella typhimurium). In contrast, Nlrc4-null macrophages were fully responsive to extracellular ATP, but displayed defective inflammasome activation in response to S. typhimurium, indicating some level of specificity determined by the nature of the engaged NLR. Importantly, caspase-1-dependent cell death, later termed pyroptosis,15 was ablated in macrophages lacking either Asc or Nlrc4, providing a molecular link between inflammation and cell death pathways.
Also in 2004, we have described a single-nucleotide polymorphism in a second member of the inflammatory caspase subfamily, namely CASP12, which deletes it from the majority of the human population, but not from a proportion of African descendents. We have shown that expression of caspase-12 resulted in a dampened inflammatory response to endotoxin and was associated with severe sepsis in the clinic.16 We have subsequently demonstrated that the mechanism by which this protein exerted its suppressive effects in sepsis is through inhibition of the inflammasome.17
Altogether, these initial studies identified the inflammasome complex, defined some of its regulatory mechanisms, and demonstrated that its hyperactivation is at the basis of auto-inflammatory disease pathogenesis, whereas its regulated activity is central for host defense and protection from sepsis.
Molecular Regulators of the Inflammasome
The molecular characterization of the inflammasome and its modulation by caspases-5 and -12 has led to a flurry of papers describing regulators of this complex. Human CARD-only proteins, including ICEBERG,18 pseudo-ICE19 and INCA,20 and PYD-only proteins (POPs), such as POP121 and POP2,22 were shown to prevent inflammasome assembly by competitively interacting with the CARD of procaspase-1 or the PYD of ASC, respectively. Of note, PYRIN, which harbors a PYD, was also suggested to function as a negative regulator of caspase-1.23 Mice expressing a truncated pyrin protein were found to be susceptible to LPS endotoxemia, and macrophages from these animals showed an increased maturation of IL-1β, following stimulation.24 It was therefore suggested that pyrin competed with caspase-1 for association with ASC. However, results by others,25, 26 suggesting that full-length pyrin is held in an auto-inhibitory conformation until activated, contradicted the above reports and showed that pyrin rather promoted ASC oligomerization and caspase-1 activation. To address this controversy, Tschopp and colleagues27 revisited the role of pyrin in inflammasome activation and demonstrated that its depletion increased caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion, whereas overexpression of its C-terminal B30.2 (SPRY) domain alone inhibited these processes. More recently, a mouse model of FMF was developed by knock-in of the human SPRY domain carrying an FMF missense mutation into the murine pyrin locus.28 These mice developed an auto-inflammatory phenotype that was dependent on Asc and caspase-1, but independently of Nlrp3. In contrast, pyrin-deficient mice did not exhibit any sign of spontaneous inflammation. Altogether, pyrin appears to modulate the inflammasome through direct engagement of ASC and caspase-1, however, whether it performs stimulatory or inhibitory functions at the steady state remains unresolved.
Two additional important regulators of the inflammasome are the chaperone heat-shock protein 90 KDa (HSP90) and its co-chaperone suppressor of G2 allele of Skp1 (SGT1). Tschopp and colleagues29 have demonstrated that, similarly to plant R protein regulation (reviewed in Chisholm et al.1 and Jones and Dangl2), HSP90 and SGT1 maintain NLRs in a stable, but activation-competent conformation. Consistently, depletion of SGT1 by RNA interference or chemical inhibition of HSP90 blunted inflammasome activation. This regulatory function is not confined to members of the NLRP subfamily of NLRs, as HSP90 inhibition also blocked NOD1-mediated activation of NF-κB,30 further linking plant and mammalian host defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, it is becoming apparent that NLR-dependent innate immunity pathways were grafted to the cell death response over evolutionary time. There are striking parallels between the intrinsic apoptosis machinery and the mechanisms that activate caspase-1. Such similarities may be the result of the co-evolution of these pathways under the pressures imposed by infection. Caspase-1-dependent cell death is initiated by infection, whereas apoptosis is induced by the mitochondria, an organelle reminiscent of bacteria. Both release stimulatory products into the cytosol to activate sensors that undergo oligomerization to form an activation platform (inflammasome and apoptosome) (reviewed in Labbe and Saleh31). Using cryo-EM, Reeds and colleagues32 have shown that oligomers of NLRP1 formed double-ring structures, strikingly similar to the central hub of the Apaf-1 apoptosome, suggesting that the inflammasome might employ similar mechanisms to the apoptosome for oligomerization and activation. In both instances, CARD-containing caspases (caspase-1 and caspase-9) are recruited and activated by proximity-induced catalysis, resulting in substrate recognition and cleavage. In the case of caspase-9, this leads to apoptosis, a tolerogenic form of cell death.33 For caspase-1, the outcome is pyroptosis and immunogenicity. Reed and colleagues34 have also demonstrated that BCL-2 and BCL-XL, which inhibit apoptosis by controlling mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), block the NLRP1 inflammasome. This relationship is reminiscent of the regulatory mechanisms of the apoptosis pathway in C. elegans, whereby the BCL-2 homolog CED-9 inhibits the APAF-1 homolog (and NLR-related protein) CED-4 through direct interaction.35 Moreover, we have reported that BID, a cytosolic BH3-only protein that gains pro-apoptotic potency following processing by caspase-8 or granzyme B,36 interacts directly with two other members of the NLR family, namely NOD1 and NOD2, and regulates their downstream signaling to NF-κB and ERK by recruiting the IKK complex to the nodosome.37
Tschopp has extended the links between cell death and inflammation by recently postulating that the mitochondria do not only hold the key to the life or death of the cell, but is also the sovereign of inflammation.38 Specifically, it was demonstrated that NLRP3 localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and translocates to the mitochondria upon stimulation, and that assembly of the NLRP3 inflammasome occurs in a MOMP-dependent manner.39 Consistently, inhibition of the voltage-dependent anionic channels or overexpression of BCL-2, which blocks MOMP, dampened this response. A second member of the NLR family, NLRX1, also localizes to the mitochondria. However, its sub-mitochondrial distribution and function are currently controversial. Ting and coworkers40 first reported that NLRX1 is localized to the mitochondrial outer membrane and is a negative regulator of anti-viral innate immunity through interaction with the RIG-I and MDA-5 mitochondrial adaptor MAVS. These results were challenged by Girardin and colleagues41, 42 who reported that NLRX1 is found in the mitochondrial matrix, where it regulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and amplifies NF-κB and JNK signaling upon TNF stimulation or Shigella infection.42 The recent generation of NLRX1-deficient mice by the Ting and Tschopp laboratories failed to resolve this controversy. Ting and coworkers43 confirmed their in vitro results as to a role of NLRX1 in the modulation of MAVS signaling, whereas Tschopp and colleagues44 did not observe any major differences in MAVS-dependent IRF3 phosphorylation, and interferon (IFN)-β or IP-10 induction between wild-type and NLRX1-deficient mice following PolyI:C treatment or Sendai virus infection. Furthermore, Tschopp and colleagues have identified an interaction between NLRX1 and a subunit of the complex III of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, ubiquinol–cytochrome-c reductase complex core protein 2, which is consistent with a function of NLRX1 in ROS modulation. It is unclear at the moment what the basis of the controversy is and future careful investigation of this NLR is thus warranted.
Agonists of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Mechanisms of Activation
Tschopp and colleagues45 first demonstrated that the bacterial peptidoglycan moiety muramyl dipeptide (MDP) promoted the release of active IL-1β downstream of caspase-1 activation by the inflammasome independently of Toll-like receptors. This was corroborated by Reed and colleagues32 who described a cell-free reconstitution system of the NLRP1 inflammasome, in which MDP alone, followed by ribonucleoside triphosphates, was sufficient to induce complex formation. Tschopp and coworkers46 also showed that adenoviral infection of macrophages, which leads to expression of viral DNA in the cytoplasm also engaged the NLRP3 inflammasome. Interestingly, this was not specific to viral DNA, as bacterial, mammalian and synthetic dsDNA could all activate caspase-1.46 However, no direct DNA binding to NLRP3 was shown. In contrast, a second PYD-containing cytosolic pattern-recognition receptors, namely the HIN200 protein absent in melanoma (AIM)2 was later shown in four reports to directly bind cytosolic DNA and assemble a distinct inflammasome consisting of AIM2, ASC and caspase-1.47, 48, 49, 50
A seminal finding by Tschopp and coworkers51 was that the NLRP3 inflammasome is not only activated by microbial motifs, but also by danger signals, often associated with sterile inflammatory diseases. In a ground-breaking study, they reported that gout-associated uric acid crystals activated the NLRP3 inflammasome. Upon stimulation with monosodium urate (MSU), human and murine macrophages were shown to secrete IL-1β in an NLRP3-dependent manner. This was further demonstrated in vivo using a crystal-induced peritonitis model, whereby mice deficient in inflammasome pathway components exhibited markedly diminished peritonitis.51
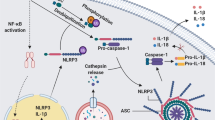
This finding has not only stimulated efforts to understand the activation mechanisms of the inflammasome, but has led to clinical trials for gout (see below). Interestingly, it was later shown that other crystalline structures or particulate matters similarly engaged the NLRP3 inflammasome. For instance, treatment of macrophages with asbestos,52 silica52 and alum,53, 54, 55, 56, 57 Alzheimer's disease-associated amyloid β fibers58 or malaria-associated hemozoin59, 60, 61 caused the release of IL-1β in a NLRP3-dependent fashion. Tschopp and colleagues52 initially proposed that these large crystals led to ‘frustrated phagocytosis’ and ROS production by NADPH oxidase, but later implicated the mitochondria as the source of ROS.39 In either case, ROS seems as a critical component upstream of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and was recently demonstrated to act as a priming signal required for transcriptional upregulation of NLRP3 (signal 1) rather than its direct oligomerization (signal 2; Figure 3).62 Two additional mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation have been reported. The first implicates lysosomal disruption and cathepsin B activity following large crystal engulfment,63 whereas the second conjectures a requirement for potassium efflux through the ATP-gated channel P2X7 or microbial toxins in response to nanoparticles64 and non-crystalline agonists.65 Consistently, phagosomal acidicification, inhibition of cathepsin B's activity,63 antagonism of P2X7 or blockade of potassium efflux (through incubation of the cells with high extracellular concentrations of potassium)66 were shown to blunt the activity of the NLRP3 inflammasome.
Inflammasome activation and regulation. The mitochondria are at the center of inflammasome activation and regulation. Mitochondrial ROS leads to transcriptional induction of pro-IL-1β and NLRP3 through MAPKs, NF-κB and HIF-1, priming the cell for inflammasome activation. The NLRs are bound by Hsp90 and SGT1, which maintain them in an activation competent state, upon which oligomerization with the adaptor ASC and caspase-1 forms a functional inflammasome, leading to the cleavage and release of IL-1β and IL-18. Caspase-5 is associated with the NLRP1 inflammasome, which is activated by MDP and negatively regulated by BCL-XL and BCL-2. Mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (through voltage-dependent anionic channels and inhibited by BCL-2) is essential for NLRP3 inflammasome activation. NLRX1, which resides within the mitochondria, is reported to inhibit MAVS- and TRAF6-mediated signaling, and to modulate ROS generation. The phagocytosis of large crystals leads to lysosomal rupture followed by release of cathepsin B into the cytosol and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Microbial toxins and the ATP ionotropic P2X7 purinergic receptor that functions as an ATP-activated cation channel lead to potassium efflux, which activates the NLRP3 inflammamsome. The saturated fatty acid palmitate inhibits AMPK, which leads to reduced mitophagy and increased ROS production. Palmitate is also metabolized into ceramide, which is detected by NLRP3. High concentrations of glucose also activate NRLP3 through binding of TXNIP. Deregulated activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome has been linked to CAPS, gout, atherosclerosis and type 2 diabetes
It is noteworthy that although some of the agonists described above, more specifically hemozoin and alum, resulted in inflammasome activation in vitro, this was dispensable for the in vivo host response. For instance, caspase-1 is stimulated by Plasmodium-parasitized RBCs (containing hemozoin), but its activity is dispensable during malaria, as Casp1−/− mice are equivalent to wild-type mice in clearing the P. chabaudi parasite or succumbing to P. berghei-induced cerebral malaria.67, 68 Similarly, although it was unanimous that the alum adjuvant stimulated the NLRP3 inflammasome in vitro, whether NLRP3 signaling is required for alum's adjuvanticity has been debated. Indeed, although some studies reported abrogation of antibody production in response to antigen in mice lacking the NLRP3 inflammasome,55, 57 others found a partial inhibition56 or a complete lack of phenotype.53 Therefore, results of inflammasome activation in vitro must be interpreted with caution and require validation in physiological contexts to determine whether this pathway is central to the process under study or whether its activation occurs as a bystander response.
Inflammasome Crosstalk with Innate and Adaptive Immunity Pathways
Inflammation is a physiological response required to restore homeostasis, following an insult with infectious or noxious stimuli. However, when excessive or chronic, it is deleterious and at the basis of multiple disorders including auto-inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. The inflammatory process is tightly controlled, and a number of reports have now demonstrated regulatory feedback mechanisms linking the inflammasome pathway to other arms of the immune system. Notably, Karin and colleagues69 have demonstrated that the NF-κB pathway is a negative regulator of IL-1β production. Mice lacking IKKβ in myeloid cells, or pharmacological inhibition of this kinase, led to exaggerated IL-1β production and consequently increased susceptibility to endotoxic shock, despite transcriptional inhibition of NF-κB-dependent gene expression, including inhibition of IL-1 β gene transcription. Mechanistically, increased IL-1β levels resulted from elevated caspase-1 activity in macrophages, suggesting that NF-κB regulated this process through transcriptional induction of negative regulators of the inflammasome pathway. Interestingly, IL-1β was also produced by neutrophils through the action of serine proteases. These results highlight the close crosstalk between the inflammasome and NF-κB pathways, and point to potential complications of prolonged IKKβ inhibition as an anti-inflammatory therapeutic strategy. Furthermore, they suggest that this negative feedback loop that is necessary to inhibit inflammation might have evolved to boost the host response to infection. As such, the innate immune system retains the ability to control virulent pathogens that target the NF-κB pathway through compensatory upregulation of IL-1β signaling.
A second regulatory mechanism of the inflammasome pathway is mediated by type I IFN. Type I IFN has been a common therapy for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, yet its mechanisms of actions were largely unknown. Tschopp and colleagues70 have recently shown that type I IFN inhibits inflammasome activation and IL-1β production through a two-pronged mechanism. On one hand, type I IFN induces the production of IL-10, which in an autocrine manner inhibits pro-IL-1 gene expression via STAT3. On the other hand, type I IFN targets inflammasome assembly and caspase-1 activation, through a yet undefined mechanism. Consistently, macrophages from Il10r−/− mice or myeloid-specific Stat3−/− mice were shown to produce increased pro-IL-1 levels compared with controls, and type I IFN induction by PolyI:C administration in mice was demonstrated to dampen IL-1β production. It was further shown that through blunting of the inflammasome response, type I IFN led to decreased granulocyte recruitment in a model of peritonitis, and enhanced susceptibility to Candida albicans infection. Altogether, these findings explain the effectiveness of type I IFN therapy in inflammatory diseases and the immunosuppressive effects of type I IFN induction following viral infections.
The inflammasome is also targeted by the adaptive immune system, specifically by effector and memory T cells. In an NLRP3-dependent peritonitis model, Tschopp and colleagues71 have shown that antigen-specific CD4+ effector T cells blocked caspase-1 activation and IL-1β release, leading to decreased neutrophil recruitment to the peritoneum. This required TCR engagement and was mediated by membrane-bound TNF family ligands such as CD40L.
On the other hand, it has been shown that the immunogenicity of ATP-releasing dying cells relies on the P2RX7-Nlrp3 inflammasome axis. Indeed, Ghiringhelli et al.72 have elegantly demonstrated that anthracyclines or immunogenic chemotherapies against cancer mediate protective cytotoxic T lymphocyte immune responses through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. Specifically, IL-1β was demonstrated to be indispensable for IFNγ production by CD8+ T cells, and that the IL-1β/IL-1R pathway is mandatory for the success of chemotherapy.72
Collectively, these studies place the inflammasome as a central node of the inflammatory process that is tightly regulated by both innate and adaptive mechanisms.
The Inflammasome and the Metabolic Syndrome
Tschopp and coworkers73 were the first to implicate the inflammasome, specifically NLRP3, in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes (T2D). They demonstrated that TXNIP, a thioredoxin-interacting protein linked to insulin resistance, was bound to NLRP3 in response to elevated glucose levels, resulting in inflammasome activation and IL-1β production in islets. Consistently, they showed that similarly to Txnip−/− mice, Nlrp3−/− mice exhibited improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Since this discovery, a number of groups have followed on these initial findings to more closely characterize the involvement of the inflammasome in metabolic stress. O’Neill and colleagues74 have shown that oligomers of islet amyloid polypeptide, commonly deposited in the pancreas of T2D patients, activated the NLRP3 inflammasome in macrophages and dendritic cells. Netea and Dixit, and their colleagues75, 76 demonstrated that hyperglycemia stimulated the expression of NLRP3, pro-IL-1β and TXNIP in mouse and human adipose tissue. Reciprocally, calorie restriction and exercise-mediated weight loss in obese patients with T2D was associated with dampened NLRP3 levels. Netea and coworkers77 have shown that Casp1−/−, Il1−/− and Nlrp3−/− mice were resistant to diet-induced obesity and T2D, and that caspase-1 activity, through IL-1β, modulated adipocyte differentiation. Consistently, Casp1−/− and Nlrp3−/− mice displayed more metabolically active fat cells and enhanced fatty acid oxidation compared with wild-type mice. Furthermore, treatment of obese mice with a caspase-1 inhibitor significantly enhanced their insulin sensitivity.77 Dixit and coworkers76 corroborated these findings; however, they did not find evidence of inflammasome involvement in regulating adipocyte differentiation. Instead, they demonstrated a role of the inflammasome in activating macrophage- and effector T-cell-driven obesity-induced inflammation. Notably, they have implicated lipotoxicity-associated ceramide as an NLRP3 agonist, and have demonstrated inflammasome activation in infiltrating macrophages in the fat tissue. In addition, they showed that through IL-18 maturation, the inflammasome pathway modulated IFNγ production and effector T-cell activation in adipose tissue.76 Ting and colleagues78 extended these findings by addressing how a high-fat diet activated the inflammasome. They showed that palmitate, a saturated fatty acid whose concentration rises in the plasma following the consumption of a fatty meal, but not unsaturated oleate, induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation, and IL-1β and IL-18 secretion. Interestingly, condensation of palmitate and serine generates 3-ketodihydrosphingosine, which is required for ceramide synthesis,79 suggesting that palmitate might activate the inflammasome through ceramide. Ting and coworkers78 proposed that through inhibition of AMPK, palmitate leads to dampened mitochondrial autophagy (or mitophagy), which results in ROS generation that activates NLRP3. Reciprocally, AICAR, an AMPK agonist, restored autophagy and inhibited both ROS generation and caspase-1 activation by palmitate.78 Collectively, these results implicate the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, specifically the caspase-1-dependent cytokines IL-1β and IL-18, in insulin resistance and T2D pathogenesis. However, whereas the role of IL-1β in these processes has been consistently demonstrated by a number of groups, that of IL-18 is less clearly defined. Notably, although Dixit and colleagues76 conjecture that IL-18 is pathogenic through its activity on effector T-cell activation in the adipocyte tissue, a previous study has reported that IL-18 deficiency in mice is associated with obesity and insulin resistance.80
Although inflammation has been linked to T2D, the current therapeutic approaches are not based on anti-inflammatory strategies. Interestingly, a clinical trial for T2D with the IL-1R antagonist anakinra has shown some promise, as anakinra improved glycemia and beta-cell secretory function, and reduced markers of systemic inflammation.81 Furthermore, the common anti-diabetic drug, glibenclamide (also known as glyburide), which operates by inhibiting ATP-sensitive potassium channels,82 was shown to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and caspase-1 activation, suggesting that pharmacological modulation of the inflammasome-IL-1β axis might be a viable approach for the treatment of T2D.83 A second drug most commonly used for the treatment of T2D is metformin, which acts by activating AMPK and the upstream kinase LKB1 (reviewed in Hardie84), arguing that its efficacy might be partially mediated by modulating inflammasome activity.
Heart disease is another metabolic disease that is the leading cause of death in the developed world. The involvement of the NLRP3 inflammasome in atherosclerosis was first described by Latz and coworkers,85 who first showed in vitro caspase-1 activation and IL-1β production in response to cholesterol crystals. Cholesterol crystals were shown to rupture the lysosomal membrane, resulting in inflammasome activation, which was dependent on phagosome acidification and lysosomal cathepsins. Furthermore, it was shown that intraperitoneal injection of cholesterol induced neutrophil recruitment, which was reduced in Nlrp3, Il-1- or Il-1r-deficient mice. Using LDLR-deficient mice put on high cholesterol diet as an experimental model of atherosclerosis, Latz and coworkers85 next showed that mice lacking Nlrp3 had reduced atherosclerosis as determined by lesion size. In contrast, using ApoE-deficient mice fed a high-fat diet, Tschopp and colleagues86 reported that atherosclerosis progressed independently of the Nlrp3 inflammasome. They showed no change in size of lesions, plaque stability, or macrophage recruitment to the plaques between Nlrp3-, Asc-, or Casp1-deficient mice on an ApoE-null background versus control animals. It is plausible that differences in the phenotypes may have resulted from the use of different mouse models.
Conclusion
Jurg Tschopp's work involving the inflammasome has nucleated the genesis of a new field of immunology. Tschopp's vision extended beyond the lab, as his work has led to the development of effective therapies for inflammasome-associated disorders and the establishment of a number of currently ongoing clinical trials. Tschopp's discovery of the inflammasome has aided in linking the etiology of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) to mutations in NLRP3, leading to the now successful therapy of CAPS patients in the clinic.87 His 2006 discovery that MSU crystals deposited in the joints of patients with gout activated the inflammasome51 led him to conduct in a pilot clinical study in patients with gouty arthritis treated for 3 days with anakinra.88 The results were spectacular in that all patients responded rapidly to anakinra and showed dramatic improvement without adverse effects. His work linking the inflammasome to metabolic diseases will directly or indirectly impact many lives suffering from obesity and T2D in years to come. Our field has surely lost a giant, and Jurg Tschopp will be dearly missed.
Abbreviations
- APAF-1:
-
apoptosis-activating factor
- CARD:
-
caspase-recruitment and activation domain
- PYD:
-
pyrin domain
- CIAS1:
-
cold-induced auto-inflammatory syndrome 1
- MWS:
-
familial MuckleWells syndrome
- FMF:
-
familial Mediterranean fever
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- POP:
-
PYD-only protein
- MOMP:
-
mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- IFN:
-
interferon
- MDP:
-
muramyl dipeptide
- AIM2:
-
absent In Melanoma 2
- MSU:
-
monosodium urate
- T2D:
-
type 2 diabetes
- CAPS:
-
Cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes
References
Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ . Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell 2006; 124: 803–814.
Jones JD, Dangl JL . The plant immune system. Nature 2006; 444: 323–329.
Bratton SB, Salvesen GS . Regulation of the Apaf-1-caspase-9 apoptosome. J Cell Sci 2010; 123: 3209–3214.
Riedl SJ, Salvesen GS . The apoptosome: signalling platform of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2007; 8: 405–413.
Ting JP, Lovering RC, Alnemri ES, Boss JM, Davis BK, Flavell RA et al. The NLR gene family: a standard nomenclature. Immunity 2008; 28: 285–287.
Lahm A, Paradisi A, Green DR, Melino G . Death fold domain interaction in apoptosis. Cell death and differ 2003; 10: 10–12.
Miceli-Richard C, Lesage S, Rybojad M, Prieur AM, Manouvrier-Hanu S, Häfner R et al. CARD15 mutations in Blau syndrome. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 19–20.
Murillo L, Crusius JB, van Bodegraven AA, Alizadeh BZ, Pena AS . CARD15 gene and the classification of Crohn's disease. Immunogenetics 2002; 54: 59–61.
Ogura Y, Bonen DK, Inohara N, Nicolae DL, Chen FF, Ramos R et al. A frameshift mutation in NOD2 associated with susceptibility to Crohn's disease. Nature 2001; 411: 603–606.
Hoffman HM, Mueller JL, Broide DH, Wanderer AA, Kolodner RD . Mutation of a new gene encoding a putative pyrin-like protein causes familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome and Muckle-Wells syndrome. Nat Genet 2001; 29: 301–305.
Centola M, Wood G, Frucht DM, Galon J, Aringer M, Farrell C et al. The gene for familial Mediterranean fever, MEFV, is expressed in early leukocyte development and is regulated in response to inflammatory mediators. Blood 2000; 95: 3223–3231.
Martinon F, Burns K, Tschopp J . The inflammasome: a molecular platform triggering activation of inflammatory caspases and processing of proIL-beta. Mol Cell 2002; 10: 417–426.
Agostini L, Martinon F, Burns K, McDermott MF, Hawkins PN, Tschopp J et al. NALP3 forms an IL-1beta-processing inflammasome with increased activity in Muckle-Wells autoinflammatory disorder. Immunity 2004; 20: 319–325.
Mariathasan S, Newton K, Monack DM, Vucic D, French DM, Lee WP et al. Differential activation of the inflammasome by caspase-1 adaptors ASC and Ipaf. Nature 2004; 430: 213–218.
Fink SL, Cookson BT . Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 1907–1916.
Saleh M, Vaillancourt JP, Graham RK, Huyck M, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES et al. Differential modulation of endotoxin responsiveness by human caspase-12 polymorphisms. Nature 2004; 429: 75–79.
Saleh M, Mathison JC, Wolinski MK, Bensinger SJ, Fitzgerald P, Droin N et al. Enhanced bacterial clearance and sepsis resistance in caspase-12-deficient mice. Nature 2006; 440: 1064–1068.
Humke EW, Shriver SK, Starovasnik MA, Fairbrother WJ, Dixit VM . ICEBERG: a novel inhibitor of interleukin-1beta generation. Cell 2000; 103: 99–111.
Druilhe A, Srinivasula SM, Razmara M, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES . Regulation of IL-1beta generation by Pseudo-ICE and ICEBERG, two dominant negative caspase recruitment domain proteins. Cell Death Differ 2001; 8: 649–657.
Lamkanfi M, Denecker G, Kalai M, D’hondt K, Meeus A, Declercq W et al. INCA, a novel human caspase recruitment domain protein that inhibits interleukin-1beta generation. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 51729–51738.
Reed JC, Doctor K, Rojas A, Zapata JM, Stehlik C, Fiorentino L et al. Comparative analysis of apoptosis and inflammation genes of mice and humans. Genome Res 2003; 13: 1376–1388.
Bedoya F, Sandler LL, Harton JA . Pyrin-only protein 2 modulates NF-kappaB and disrupts ASC:CLR interactions. J Immunol 2007; 178: 3837–3845.
Woo JS, Imm JH, Min CK, Kim KJ, Cha SS, Oh BH . Structural and functional insights into the B30.2/SPRY domain. EMBO J 2006; 25: 1353–1363.
Chae JJ, Komarow HD, Cheng J, Wood G, Raben N, Liu PP et al. Targeted disruption of pyrin, the FMF protein, causes heightened sensitivity to endotoxin and a defect in macrophage apoptosis. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 591–604.
Seshadri S, Duncan MD, Hart JM, Gavrilin MA, Wewers MD . Pyrin levels in human monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages regulate IL-1beta processing and release. J Immunol 2007; 179: 1274–1281.
Yu JW, Wu J, Zhang Z, Datta P, Ibrahimi I, Taniguchi S et al. Cryopyrin and pyrin activate caspase-1, but not NF-kappaB, via ASC oligomerization. Cell Death Differ 2006; 13: 236–249.
Papin S, Cuenin S, Agostini L, Martinon F, Werner S, Beer HD et al. The SPRY domain of Pyrin, mutated in familial Mediterranean fever patients, interacts with inflammasome components and inhibits proIL-1beta processing. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 1457–1466.
Chae JJ, Cho YH, Lee GS, Cheng J, Liu PP, Feigenbaum L et al. Gain-of-Function pyrin mutations induce NLRP3 protein-independent interleukin-1beta activation and severe autoinflammation in mice. Immunity 2011; 34: 755–768.
Mayor A, Martinon F, De Smedt T, Petrilli V, Tschopp J . A crucial function of SGT1 and HSP90 in inflammasome activity links mammalian and plant innate immune responses. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 497–503.
da Silva Correia J, Miranda Y, Leonard N, Ulevitch R . SGT1 is essential for Nod1 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 6764–6769.
Labbe K, Saleh M . Cell death in the host response to infection. Cell Death Differ 2008; 15: 1339–1349.
Faustin B, Lartigue L, Bruey JM, Luciano F, Sergienko E, Bailly-Maitre B et al. Reconstituted NALP1 inflammasome reveals two-step mechanism of caspase-1 activation. Mol cel 2007; 25: 713–724.
Green DR, Ferguson T, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G . Immunogenic and tolerogenic cell death. Nat Rev 2009; 9: 353–363.
Bruey JM, Bruey-Sedano N, Luciano F, Zhai D, Balpai R, Xu C et al. Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL regulate proinflammatory caspase-1 activation by interaction with NALP1. Cell 2007; 129: 45–56.
Spector MS, Desnoyers S, Hoeppner DJ, Hengartner MO . Interaction between the C. elegans cell-death regulators CED-9 and CED-4. Nature 1997; 385: 653–656.
Billen LP, Shamas-Din A, Andrews DW . Bid: a Bax-like BH3 protein. Oncogene 2008; 27 (Suppl 1): S93–104.
Yeretssian G, Correa RG, Doiron K, Fitzgerald P, Dillon CP, Green DR et al. Non-apoptotic role of BID in inflammation and innate immunity. Nature 2011; 474: 96–99.
Tschopp J . Mitochondria: Sovereign of inflammation? Eur J Immunol 2011; 41: 1196–1202.
Zhou R, Yazdi AS, Menu P, Tschopp J . A role for mitochondria in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Nature 2011; 469: 221–225.
Moore CB, Bergstralh DT, Duncan JA, Lei Y, Morrison TE, Zimmermann AG et al. NLRX1 is a regulator of mitochondrial antiviral immunity. Nature 2008; 451: 573–577.
Arnoult D, Soares F, Tattoli I, Castanier C, Philpott DJ, Girardin SE . An N-terminal addressing sequence targets NLRX1 to the mitochondrial matrix. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 3161–3168.
Tattoli I, Carneiro LA, Jéhanno M, Magalhaes JG, Shu Y, Philpott DJ et al. NLRX1 is a mitochondrial NOD-like receptor that amplifies NF-kappaB and JNK pathways by inducing reactive oxygen species production. EMBO Rep 2008; 9: 293–300.
Allen IC, Moore CB, Schneider M, Lei Y, Davis BK, Scull MA et al. NLRX1 protein attenuates inflammatory responses to infection by interfering with the RIG-I-MAVS and TRAF6-NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Immunity 2011; 34: 854–865.
Rebsamen M, Vazquez J, Tardivel A, Guarda G, Curran J, Tschopp J . NLRX1/NOD5 deficiency does not affect MAVS signalling. Cell Death Differ 2011; 18: 1387.
Martinon F, Agostini L, Meylan E, Tschopp J . Identification of bacterial muramyl dipeptide as activator of the NALP3/cryopyrin inflammasome. Curr Biol 2004; 14: 1929–1934.
Muruve DA, Pétrilli V, Zaiss AK, White LR, Clark SA, Ross PJ et al. The inflammasome recognizes cytosolic microbial and host DNA and triggers an innate immune response. Nature 2008; 452: 103–107.
Burckstummer T, Baumann C, Blüml S, Dixit E, Dürnberger G, Jahn H et al. An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol 2009; 10: 266–272.
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Yu JW, Datta P, Wu J, Alnemri ES . AIM2 activates the inflammasome and cell death in response to cytoplasmic DNA. Nature 2009; 458: 509–513.
Hornung V, Ablasser A, Charrel-Dennis M, Bauernfeind F, Horvath G, Caffrey DR et al. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature 2009; 458: 514–518.
Roberts TL, Idris A, Dunn JA, Kelly GM, Burnton CM, Hodgson S et al. HIN-200 proteins regulate caspase activation in response to foreign cytoplasmic DNA. Science (New York, NY) 2009; 323: 1057–1060.
Martinon F, Petrilli V, Mayor A, Tardivel A, Tschopp J . Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006; 440: 237–241.
Dostert C, Pétrilli V, Van Bruggen R, Steele C, Mossman BT, Tschopp J . Innate immune activation through Nalp3 inflammasome sensing of asbestos and silica. Science (New York, NY) 2008; 320: 674–677.
Franchi L, Nunez G . The Nlrp3 inflammasome is critical for aluminium hydroxide-mediated IL-1beta secretion but dispensable for adjuvant activity. Eur J Immunol 2008; 38: 2085–2089.
McKee AS, Munks MW, MacLeod MK, Fleenor CJ, Van Rooijen N, Kappler JW et al. Alum induces innate immune responses through macrophage and mast cell sensors, but these sensors are not required for alum to act as an adjuvant for specific immunity. J Immunol 2009; 183: 4403–4414.
Eisenbarth SC, Colegio OR, O’Connor W, Sutterwala FS, Flavell RA . Crucial role for the Nalp3 inflammasome in the immunostimulatory properties of aluminium adjuvants. Nature 2008; 453: 1122–1126.
Kool M, Pétrilli V, De Smedt T, Rolaz A, Hammad H, van Nimwegen M et al. Cutting edge: alum adjuvant stimulates inflammatory dendritic cells through activation of the NALP3 inflammasome. J Immunol 2008; 181: 3755–3759.
Li H, Willingham SB, Ting JP, Re F . Cutting edge: inflammasome activation by alum and alum's adjuvant effect are mediated by NLRP3. J Immunol 2008; 181: 17–21.
Halle A, Hornung V, Petzold GC, Stewart CR, Monks BG, Reinheckel T et al. The NALP3 inflammasome is involved in the innate immune response to amyloid-beta. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 857–865.
Dostert C, Guarda G, Romero JF, Menu P, Gross O, Tardivel A et al. Malarial hemozoin is a Nalp3 inflammasome activating danger signal. PloS One 2009; 4: e6510.
Griffith JW, Sun T, McIntosh MT, Bucala R . Pure Hemozoin is inflammatory in vivo and activates the NALP3 inflammasome via release of uric acid. J Immunol 2009; 183: 5208–5220.
Shio MT, Eisenbarth SC, Savaria M, Vinet AF, Bellemare MJ, Harder KW et al. Malarial hemozoin activates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Lyn and Syk kinases. PLoS Pathog 2009; 5: e1000559.
Bauernfeind F, Bartok E, Rieger A, Franchi L, Núñez G, Hornung V . Reactive oxygen species inhibitors block priming, but not activation, of the NLRP3 inflammasome. J Immunol 2011; 187: 613–617.
Hornung V, Bauernfeind F, Halle A, Samstad EO, Kono H, Rock KL et al. Silica crystals and aluminum salts activate the NALP3 inflammasome through phagosomal destabilization. Nat Immunol 2008; 9: 847–856.
Yazdi AS, Guarda G, Riteau N, Drexler SK, Tardivel A, Couillin I et al. Nanoparticles activate the NLR pyrin domain containing 3 (Nlrp3) inflammasome and cause pulmonary inflammation through release of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107.
Schroder K, Tschopp J . The inflammasomes. Cell 2010; 140: 821–832.
Petrilli V, Papin S, Dostert C, Mayor A, Martinon F, Tschopp J . Activation of the NALP3 inflammasome is triggered by low intracellular potassium. Cell Death Differ 2007; 14: 1583–1589.
Labbe K, Miu J, Yeretssian G, Serghides L, Tam M, Finney CA et al. Caspase-12 dampens the immune response to malaria independently of the inflammasome by targeting NF-kappaB signaling. J Immunol 2010; 185: 5495–5502.
Reimer T, Shaw MH, Franchi L, Coban C, Ishii KJ, Akira S et al. Experimental cerebral malaria progresses independently of the Nlrp3 inflammasome. Eur J Immunol 2010; 40: 764–769.
Greten FR, Arkan MC, Bollrath J, Hsu LC, Goode J, Miething C et al. NF-kappaB is a negative regulator of IL-1beta secretion as revealed by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IKKbeta. Cell 2007; 130: 918–931.
Guarda G, Braun M, Staehli F, Tardivel A, Mattmann C, Förster I et al. Type I interferon inhibits interleukin-1 production and inflammasome activation. Immunity 2011; 34: 213–223.
Guarda G, Dostert C, Staehli F, Cabalzar K, Castillo R, Tardivel A et al. T cells dampen innate immune responses through inhibition of NLRP1 and NLRP3 inflammasomes. Nature 2009; 460: 269–273.
Ghiringhelli F, Apetoh L, Tesniere A, Aymeric L, Ma Y, Ortiz C et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in dendritic cells induces IL-1beta-dependent adaptive immunity against tumors. Nat Med 2009; 15: 1170–1178.
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J . Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 136–140.
Masters SL, Dunne A, Subramanian SL, Hull RL, Tannahill GM, Sharp FA et al. Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome by islet amyloid polypeptide provides a mechanism for enhanced IL-1beta in type 2 diabetes. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 897–904.
Koenen TB, Stienstra R, van Tits LJ, de Graaf J, Stalenhoef AF, Joosten LA et al. Hyperglycemia activates caspase-1 and TXNIP-mediated IL-1beta transcription in human adipose tissue. Diabetes 2011; 60: 517–524.
Vandanmagsar B, Youm YH, Ravussin A, Galgani JE, Stadler K, Mynatt RL et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome instigates obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance. Nat Med 2011; 17: 179–188.
Stienstra R, Joosten LA, Koenen T, van Tits B, van Diepen JA, van den Berg SA et al. The inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activation controls adipocyte differentiation and insulin sensitivity. Cell Metab 2010; 12: 593–605.
Wen H, Gris D, Lei Y, Jha S, Zhang L, Huang MT et al. Fatty acid-induced NLRP3-ASC inflammasome activation interferes with insulin signaling. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 408–415.
Hannun YA, Obeid LM . Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008; 9: 139–150.
Netea MG, Joosten LA, Lewis E, Jensen DR, Voshol PJ, Kullberg BJ et al. Deficiency of interleukin-18 in mice leads to hyperphagia, obesity and insulin resistance. Nat Med 2006; 12: 650–656.
Larsen CM, Faulenbach M, Vaag A, Vølund A, Ehses JA, Seifert B et al. Interleukin-1–Receptor Antagonist in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. N Engl J Med 2007; 356: 1517–1526.
Mannhold R . Structure-activity relationships of K(ATP) channel openers. Curr Top Med Chem 2006; 6: 1031–1047.
Lamkanfi M, Mueller JL, Vitari AC, Misaghi S, Fedorova A, Deshayes K et al. Glyburide inhibits the Cryopyrin/Nalp3 inflammasome. J Cell Biol 2009; 187: 61–70.
Hardie DG . AMPK: a key regulator of energy balance in the single cell and the whole organism. Int J Obes 2008; 32: S7–S12.
Duewell P, Kono H, Rayner KJ, Sirois CM, Vladimer G, Bauernfeind FG et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010; 466: 652.
Menu P, Pellegrin M, Aubert JF, Bouzourene K, Tardivel A, Mazzolai L et al. Atherosclerosis in ApoE-deficient mice progresses independently of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Cell Death Dis 2011; 2: e137.
Lachmann HJ, Kone-Paut I, Kuemmerle-Deschner JB, Leslie KS, Hachulla E, Quartier P et al. Use of canakinumab in the cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome. N Engl J Med 2009; 360: 2416–2425.
So A, De Smedt T, Revaz S, Tschopp J . A pilot study of IL-1 inhibition by anakinra in acute gout. Arthritis Res Ther 2007; 9: R28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Edited by G Melino
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagenais, M., Skeldon, A. & Saleh, M. The inflammasome: in memory of Dr. Jurg Tschopp. Cell Death Differ 19, 5–12 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.159
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.159
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Inflammasome inhibitors: promising therapeutic approaches against cancer
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2019)
-
Inflammatory and coagulatory markers and exposure to different size fractions of particle mass, number and surface area air concentrations in Swedish iron foundries, in particular respirable quartz
International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health (2019)
-
Study of the NLRP3 inflammasome component genes and downstream cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with carotid atherosclerosis
Lipids in Health and Disease (2017)
-
HIV-1 Viral Protein R Activates NLRP3 Inflammasome in Microglia: implications for HIV-1 Associated Neuroinflammation
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2017)