Abstract
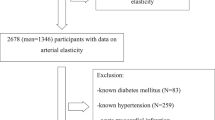
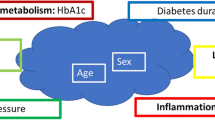
Vascular function is an important pathophysiological factor in cardiovascular disease, and is influenced by many factors, one of the principles being hypertension. Developing evidence suggests that inflammation may be another risk factor. Vascular function and blood pressure haemodynamics can be assessed by arterial stiffness, pulse pressure and plasma markers. Testing the hypothesis of a relationship between inflammatory markers, hypertension and vascular function, we recruited 222 stable coronary artery disease outpatients, assessing inflammation with levels of high sensitivity CRP and interleukin-6 (IL-6), vascular function/arterial stiffness by pulse-wave velocity (PWV), augementation (SphygmoCor system Artcor, Sidney, Australia), aortic and brachial artery pulse pressure, Von Willebrand factor (vWf) and soluble E-selectin (both enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). In multivariate regression analysis, PWVs, augmentation indices and pulse pressures were linked with age, blood pressure and (some) with heart rate (all P<0.01), while vWf was associated with age (P=0.01). We conclude that, in patients with stable coronary artery disease, arterial stiffness and pulse pressure are related strongly and independently with age, blood pressure and heart rate, and that any effect of inflammation is minimal.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nadar S, Blann AD, Lip GYH . Endothelial dysfunction: methods of assessment and application to hypertension. Curr Pharm Des 2004; 10: 3591–3606.
Reriani MK, Lerman LO, Lerman A . Endothelial function as a functional expression of cardiovascular risk factors. Biomark Med 2010; 4: 351–360.
Lim HS, Lip GY . Arterial stiffness: beyond pulse wave velocity and its measurement. J Hum Hypertens 2008; 22: 656–658.
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C . Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010; 55: 1318–1327.
Paulinska P, Spiel A, Jilma B . Role of von Willebrand factor in vascular disease. Hamostaseologie 2009; 29: 32–38.
Roldán V, Marín F, Lip GY, Blann AD . Soluble E-selectin in cardiovascular disease and its risk factors. A review of the literature. Thromb Haemostas 2003; 90: 1007–1020.
Blann AD . Plasma von Willebrand factor, thrombosis, and the endothelium: the first 30 years. Thromb Haemost 2006; 95: 49–55.
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF, Mason RP . Inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 2011; 18: 351–358.
Brevetti G, Giugliano G, Brevetti L, Hiatt WR . Inflammation in peripheral artery disease. Circulation 2010; 122: 1862–1875.
Paffen E, DeMaat MP . C-reactive protein in atherosclerosis: a causal factor? Cardiovasc Res 2006; 71: 30–39.
Jialal I, Devaraj S, Venugopal SK . C-reactive protein: risk marker or mediator in atherothrombosis? Hypertension 2004; 44: 6–11.
Packard RR, Libby P . Inflammation in atherosclerosis: from vascular biology to biomarker discovery and risk prediction. Clin Chem 2008; 54: 24–38.
McDermott MM, Liu K, Ferrucci L, Tian L, Guralnik JM, Tao H et al. Relation of interleukin-6 and vascular cellular adhesion molecule-1 levels to functional decline in patients with lower extremity peripheral arterial disease. Am J Cardiol 2011; 107: 1392–1398.
Boos CJ, Lip GY . Elevated high-sensitive C-reactive protein, large arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis: a relationship between inflammation and hypertension? J Hum Hypertens 2005; 19: 511–513.
Pober JS . Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol 1988; 133: 426–433.
Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP et al. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood 1998; 91: 3527–3561.
Schnabel R, Larson MG, Dupuis J, Lunetta KL, Lipinska I, Meigs JB et al. Relations of inflammatory biomarkers and common genetic variants with arterial stiffness and wave reflection. Hypertension 2008; 51: 1651–1657.
Nakhai-Pour HR, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Muller M, van der Schouw YT . C-reactive protein and aortic stiffness and wave reflection in middle-aged and elderly men from the community. J Hum Hypertens 2007; 21: 949–955.
Yasmin, McEniery CM, Wallace S, Mackenzie IS, Cockcroft JR, Wilkinson IB . C-reactive protein is associated with arterial stiffness in apparently healthy individuals. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 969–974.
Amar J, Ruidavets JB, Sollier CB, Bongard V, Boccalon H, Chamontin B et al. Relationship between C reactive protein and pulse pressure is not mediated by atherosclerosis or aortic stiffness. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 349–355.
Rodondi N, Marques-Vidal P, Butler J, Sutton-Tyrrell K, Cornuz J, Satterfield S et al. Markers of atherosclerosis and inflammation for prediction of coronary heart disease in older adults. Am J Epidemiol 2010; 171: 540–549.
Pietri P, Vyssoulis G, Vlachopoulos C, Zervoudaki A, Gialernios T, Aznaouridis K et al. Relationship between low-grade inflammation and arterial stiffness in patients with essential hypertension. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 2231–2238.
Kampus P, Muda P, Kals J, Ristimäe T, Fischer K, Teesalu R et al. The relationship between inflammation and arterial stiffness in patients with essential hypertension. Int J Cardiol 2006; 112: 46–51.
Mahmud A, Feely J . Arterial stiffness is related to systemic inflammation in essential hypertension. Hypertension 2005; 46: 1118–1122.
Llauradó G, Ceperuelo-Mallafré V, Vilardell C, Simó R, Freixenet N, Vendrell J et al. Arterial stiffness is increased in patients with type 1 diabetes without cardiovascular disease: a potential role of low-grade inflammation. Diabetes Care 2012; 35: 1083–1089.
Mitchell GF, Hwang SJ, Vasan RS, Larson MG, Pencina MJ, Hamburg NM et al. Arterial stiffness and cardiovascular events: the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2010; 121: 505–511.
Gunarathne A, Patel JV, Hughes EA, Lip GY . Measurement of stiffness index by digital volume pulse analysis technique: clinical utility in cardiovascular disease risk stratification. Am J Hypertens 2008; 21: 866–872.
McEniery CM, Yasmin, McDonnell B, Munnery M, Wallace SM, Rowe CV et al Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial Investigators. Central pressure: variability and impact of cardiovascular risk factors: the Anglo-Cardiff Collaborative Trial II. Hypertension 2008; 51: 1476–1482.
Altman DG . Practical Statistics for Medical Research. Chapman and Hall: London, 1991.
Machin D, Campbell M . Chapter 8: significance of the correlation coefficient. Statistical Tables for the Design of Clinical Trials. Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, 1987 pp 89–93.
Pigott R, Dillon LP, Hemingway IH, Gearing AJ . Soluble forms of E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 are present in the supernatants of cytokine activated cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992; 187: 584–589.
Newman W, Beall LD, Carson CW, Hunder GG, Graben N, Randhawa ZI et al. Soluble E-selectin is found in supernatants of activated endothelial cells and is elevated in the serum of patients with septic shock. J Immunol 1993; 150: 644–654.
Schuetz P, Jones AE, Aird WC, Shapiro NI . Endothelial cell activation in emergency department patients with sepsis-related and non-sepsis-related hypotension. Shock 2011; 36: 104–108.
Kaski JC, Fernández-Bergés DJ, Consuegra-Sánchez L, Fernández JM, García-Moll X, Mostaza JM et al. A comparative study of biomarkers for risk prediction in acute coronary syndrome-Results of the SIESTA (Systemic Inflammation Evaluation in non-ST-elevation Acute coronary syndrome) study. Atherosclerosis 2010; 212: 636–643.
van Bussel BC, Schouten F, Henry RM, Schalkwijk CG, de Boer MR, Ferreira I et al. Endothelial dysfunction and low-grade inflammation are associated with greater arterial stiffness over a 6-year period. Hypertension 2011; 58: 588–595.
Ferri C, Bellini C, Desideri G, Giuliani E, De Siati L, Cicogna S et al. Clustering of endothelial markers of vascular damage in human salt-sensitive hypertension: influence of dietary sodium load and depletion. Hypertension 1998; 32: 862–868.
De Caterina R, Ghiadoni L, Taddei S, Virdis A, Almerigogna F, Basta G et al. Soluble E-selectin in essential hypertension: a correlate of vascular structural changes. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 259–266.
Kayal S, Jaïs JP, Aguini N, Chaudière J, Labrousse J . Elevated circulating E-selectin, intercellular adhesion molecule 1, and von Willebrand factor in patients with severe infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998; 157: 776–784.
McGill SN, Ahmed NA, Christou NV . Increased plasma von Willebrand factor in the systemic inflammatory response syndrome is derived from generalized endothelial cell activation. Crit Care Med 1998; 26: 296–300.
Stormorken H, Erikssen J . Plasma antithrombin III and factor VIII antigen in relation to angiographic findings, angina and blood groups in middle-aged men. Thromb Haemost 1977; 38: 874–878.
Reference Values for Arterial Stiffness’ Collaboration. Determinants of pulse wave velocity in healthy people and in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors: ‘establishing normal and reference values’. Eur Heart J 2010; 31: 2338–2350.
Cecelja M, Chowienczyk P . Dissociation of aortic pulse wave velocity with risk factors for cardiovascular disease other than hypertension: a systematic review. Hypertension 2009; 54: 1328–1336.
Schalkwijk CG, Poland DC, van Dijk W, Kok A, Emeis JJ, Dräger AM et al. Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein is increased in type I diabetic patients without clinical macroangiopathy and correlates with markers of endothelial dysfunction: evidence for chronic inflammation. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 351–357.
Osman R, L’Allier PL, Elgharib N, Tardif JC . Critical appraisal of C-reactive protein throughout the spectrum of cardiovascular disease. Vasc Health Risk Manag 2006; 2: 221–237.
Kusche-Vihrog K, Urbanova K, Blanqué A, Wilhelmi M, Schillers H, Kliche K et al. C-reactive protein makes human endothelium stiff and tight. Hypertension 2011; 57: 231–237.
Antonopoulos AS, Margaritis M, Lee R, Channon K, Antoniades C . Statins as anti-inflammatory agents in atherogenesis: molecular mechanisms and lessons from the recent clinical trials. Curr Pharm Des 2012; 18: 1519–1530.
Mäki-Petäjä KM, Booth AD, Hall FC, Wallace SM, Brown J, McEniery CM et al. Ezetimibe and simvastatin reduce inflammation, disease activity, and aortic stiffness and improve endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007; 50: 852–858.
Shahin Y, Khan JA, Chetter I . Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors effect on arterial stiffness and wave reflections: a meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomised controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2012; 221: 18–33.
Olsen MH, Christensen MK, Hansen TW, Gustafsson F, Rasmussen S, Wachtell K et al. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is only weakly related to cardiovascular damage after adjustment for traditional cardiovascular risk factors. J Hypertens 2006; 24: 655–661.
Acknowledgements
Dr Kuzniatsova was supported by a Fellowship from the European Cardiology Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blann, A., Kuzniatsova, N. & Lip, G. Inflammation does not influence arterial stiffness and pulse-wave velocity in patients with coronary artery disease. J Hum Hypertens 27, 629–634 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.17
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.17
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Relationship between pulmonary function and peripheral vascular function in older Chinese: Guangzhou biobank cohort study-CVD
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2018)
-
Genetic Determinants of Arterial Stiffness
Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research (2015)