Abstract
Objective:
The objective of the study was to evaluate anti-factor Xa levels with therapeutic enoxaparin anticoagulation in pregnancy.
Study Design:
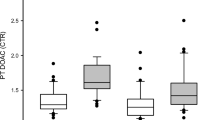
A total of 15 pregnant subjects on therapeutic doses of enoxaparin (1 mg/kg ±20% subcutaneously (s.c.) twice daily (b.i.d.)) were enrolled prospectively in this cross-sectional pilot project. Three blood levels for anti-factor Xa activity were examined: before the enoxaparin dose (trough), 3- to 4-h later (peak) and 8-h later. Anti-factor Xa activity level between 0.5 and 1.2 U/ml was considered therapeutic.
Result:
Mean anti-factor Xa activity levels were: trough 0.45±0.18, peak 0.9±0.25 and 8-h after dose 0.72±0.23 U/ml. All peak levels were therapeutic; 20% (3/15) of the 8 h and 73% (11/15) of the trough levels were sub-therapeutic.
Conclusion:
Trough and 8-h post-dose anti-factor Xa activity levels were sub-therapeutic in a substantial number of patients receiving a b.i.d. regimen of therapeutic enoxaparin.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rutherford SE, Phelan JP . Thromboembolic disease in pregnancy. Clin Perinatol 1986; 13: 719–739.
Curtis SL, Trinder J, Stuart AG . Acute thrombosis of a prosthetic mitral valve in pregnancy in spite of adjusted-dose low-molecular-weight heparin and aspirin. J Heart Valve Dis 2008; 17: 133–134.
Descarries LM, Leduc L, Khairy P, Mercier LA . Low-molecular-weight heparin in pregnant women with prosthetic heart valves. J Heart Valve Dis 2006; 15: 679–685.
James AH, Brancazio LR, Gehrig TR, Wang A, Ortel TL . Low-molecular-weight heparin for thromboprophylaxis in pregnant women with mechanical heart valves. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2006; 19: 543–549.
Oran B, Lee-Parritz A, Ansell J . Low molecular weight heparin for the prophylaxis of thromboembolism in women with prosthetic mechanical heart valves during pregnancy. Thromb Haemost 2004; 92: 747–751.
Lepercq J, Conard J, Borel-Derlon A, Darmon JY, Boudignat O, Francoual C et al. Venous thromboembolism during pregnancy: a retrospective study of enoxaparin safety in 624 pregnancies. BJOG 2001; 108: 1134–1140.
Greer I, Hunt BJ . Low molecular weight heparin in pregnancy: current issues. Br J Haematol 2005; 128: 593–601.
Ellison J, Walker ID, Greer IA . Antenatal use of enoxaparin for prevention and treatment of thromboembolism in pregnancy. BJOG 2000; 107: 1116–1121.
Chan WS, Anand S, Ginsberg JS . Anticoagulation of pregnant women with mechanical heart valves: a systematic review of the literature. Arch Intern Med 2000; 160: 191–196.
Ginsberg JS, Hirsh J . Use of antithrombotic agents during pregnancy. Chest 1998; 114: 524S–530S.
Bates SM, Greer IA, Pabinger I, Sofaer S, Hirsh J . Venous thromboembolism, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8th edition). Chest 2008; 133: 844S–886S.
Rowan JA, McCowan LM, Raudkivi PJ, North RA . Enoxaparin treatment in women with mechanical heart valves during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2001; 185: 633–637.
Casele HL, Laifer SA . Prospective evaluation of bone density in pregnant women receiving the low molecular weight heparin enoxaparin sodium. J Matern Fetal Med 2000; 9: 122–125.
Weitz JI . Low-molecular-weight heparins. N Engl J Med 1997; 337: 688–698.
Forestier F, Daffos F, Rainaut M, Toulemonde F . Low molecular weight heparin (CY 216) does not cross the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy. Thromb Haemost 1987; 57: 234.
Omri A, Delaloye JF, Andersen H, Bachmann F . Low molecular weight heparin Novo (LHN-1) does not cross the placenta during the second trimester of pregnancy. Thromb Haemost 1989; 61: 55–56.
ACOG Committee Opinion. Safety of Lovenox in pregnancy. Number 276, October 2002. Committee on Obstetric Practice. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002; 79: 299–300.
Casele HL, Laifer SA, Woelkers DA, Venkataramanan R . Changes in the pharmacokinetics of the low-molecular-weight heparin enoxaparin sodium during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999; 181: 1113–1117.
Lebaudy C, Hulot JS, Amoura Z, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Serreau R, Ankri A et al. Changes in enoxaparin pharmacokinetics during pregnancy and implications for antithrombotic therapeutic strategy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2008; 84: 370–377.
Jacobsen AF, Qvigstad E, Sandset PM . Low molecular weight heparin (dalteparin) for the treatment of venous thromboembolism in pregnancy. BJOG 2003; 110: 139–144.
Sephton V, Farquharson RG, Topping J, Quenby SM, Cowan C, Back DJ et al. A longitudinal study of maternal dose response to low molecular weight heparin in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2003; 101: 1307–1311.
Barbour LA, Oja JL, Schultz LK . A prospective trial that demonstrates that dalteparin requirements increase in pregnancy to maintain therapeutic levels of anticoagulation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2004; 191: 1024–1029.
Abildgaard U, Gjestvang FT, Lossius P, Hodne E . Low molecular heparin in a pregnant women with heart valve prosthesis. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 1999; 119: 4319–4320.
Fox NS, Laughon SK, Bender SD, Saltzman DH, Rebarber A . Antifactor Xa plasma levels in pregnant women receiving low molecular weight heparin thromboprophylaxis. Obstet Gynecol 2008; 112: 884–889.
Sanderink GJ, LeLiboux A, Jariwala N, Harding N, Ozoux ML, Shoukla U et al. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enoxaparin in obese volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002; 72: 308–318.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Pamela Rumney, RNC and Anita Shell, RNC for their assistance in the conduct of this analysis. Clinical Trials.gov ID: NCT00319176. The funding for this study was provided by the Memorial Health Care Foundation (Research Grant no. 162-04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedrich, E., Hameed, A. Fluctuations in anti-factor Xa levels with therapeutic enoxaparin anticoagulation in pregnancy. J Perinatol 30, 253–257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2009.164
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2009.164
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review of therapeutic enoxaparin dosing in obesity
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2024)
-
Effect of low-molecular-weight heparins on anti-Xa peak levels and adverse reactions in Chinese patients with recurrent spontaneous abortion: a single-center, observational study
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2021)
-
Description of anti-Xa monitoring practices during low molecular weight heparin use
Journal of Thrombosis and Thrombolysis (2019)
-
Anticoagulation during pregnancy in patients with a prosthetic heart valve
Nature Reviews Cardiology (2012)