Abstract
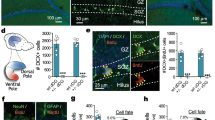
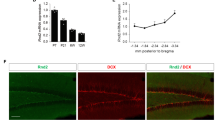
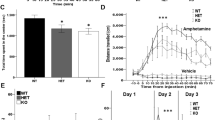
Hippocampal neurogenesis has been proposed to participate in a myriad of behavioral responses, both in basal states and in the context of neuropsychiatric disorders. Here, we identify activating protein 2γ (AP2γ, also known as Tcfap2c), originally described to regulate the generation of neurons in the developing cortex, as a modulator of adult hippocampal glutamatergic neurogenesis in mice. Specifically, AP2γ is present in a sub-population of hippocampal transient amplifying progenitors. There, it is found to act as a positive regulator of the cell fate determinants Tbr2 and NeuroD, promoting proliferation and differentiation of new glutamatergic granular neurons. Conditional ablation of AP2γ in the adult brain significantly reduced hippocampal neurogenesis and disrupted neural coherence between the ventral hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex. Furthermore, it resulted in the precipitation of multimodal cognitive deficits. This indicates that the sub-population of AP2γ-positive hippocampal progenitors may constitute an important cellular substrate for hippocampal-dependent cognitive functions. Concurrently, AP2γ deletion produced significant impairments in contextual memory and reversal learning. More so, in a water maze reference memory task a delay in the transition to cognitive strategies relying on hippocampal function integrity was observed. Interestingly, anxiety- and depressive-like behaviors were not significantly affected. Altogether, findings open new perspectives in understanding the role of specific sub-populations of newborn neurons in the (patho)physiology of neuropsychiatric disorders affecting hippocampal neuroplasticity and cognitive function in the adult brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ming GL, Song H . Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 2011; 70: 687–702.
Alvarez-Buylla A, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Tramontin AD . A unified hypothesis on the lineage of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 287–293.
Zhao C, Teng EM, Summers RG Jr, Ming GL, Gage FH . Distinct morphological stages of dentate granule neuron maturation in the adult mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 2006; 26: 3–11.
Merkle FT, Mirzadeh Z, Alvarez-Buylla A . Mosaic organization of neural stem cells in the adult brain. Science 2007; 317: 381–384.
Hodge RD, Kahoud RJ, Hevner RF . Transcriptional control of glutamatergic differentiation during adult neurogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2012; 69: 2125–2134.
Tozuka Y, Fukuda S, Namba T, Seki T, Hisatsune T . GABAergic excitation promotes neuronal differentiation in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Neuron 2005; 47: 803–815.
Bessa JM, Ferreira D, Melo I, Marques F, Cerqueira JJ, Palha JA et al. The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Mol Psychiatry 2009; 14: 764–773, 739.
Kim JY, Liu CY, Zhang F, Duan X, Wen Z, Song J et al. Interplay between DISC1 and GABA signaling regulates neurogenesis in mice and risk for schizophrenia. Cell 2012; 148: 1051–1064.
Mateus-Pinheiro A, Pinto L, Bessa JM, Morais M, Alves ND, Monteiro S et al. Sustained remission from depressive-like behavior depends on hippocampal neurogenesis. Transl Psychiatry 2013; 3: e210.
Akers KG, Martinez-Canabal A, Restivo L, Yiu AP, De Cristofaro A, Hsiang HL et al. Hippocampal neurogenesis regulates forgetting during adulthood and infancy. Science 2014; 344: 598–602.
Wu MV, Sahay A, Duman RS, Hen R . Functional differentiation of adult-born neurons along the septotemporal axis of the dentate gyrus. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2015; 7: a018978.
Bertrand N, Castro DS, Guillemot F . Proneural genes and the specification of neural cell types. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3: 517–530.
Englund C, Fink A, Lau C, Pham D, Daza RA, Bulfone A et al. Pax6, Tbr2 and Tbr1 are expressed sequentially by radial glia, intermediate progenitor cells, and postmitotic neurons in developing neocortex. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 247–251.
Hack MA, Saghatelyan A, de Chevigny A, Pfeifer A, Ashery-Padan R, Lledo PM et al. Neuronal fate determinants of adult olfactory bulb neurogenesis. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 865–872.
Waclaw RR, Allen ZJ 2nd, Bell SM, Erdelyi F, Szabo G, Potter SS et al. The zinc finger transcription factor Sp8 regulates the generation and diversity of olfactory bulb interneurons. Neuron 2006; 49: 503–516.
Brill MS, Ninkovic J, Winpenny E, Hodge RD, Ozen I, Yang R et al. Adult generation of glutamatergic olfactory bulb interneurons. Nat Neurosci 2009; 12: 1524–1533.
Gotz M, Stoykova A, Gruss P . Pax6 controls radial glia differentiation in the cerebral cortex. Neuron 1998; 21: 1031–1044.
Hevner RF, Hodge RD, Daza RA, Englund C . Transcription factors in glutamatergic neurogenesis: conserved programs in neocortex, cerebellum, and adult hippocampus. Neurosci Res 2006; 55: 223–233.
Esposito MS, Piatti VC, Laplagne DA, Morgenstern NA, Ferrari CC, Pitossi FJ et al. Neuronal differentiation in the adult hippocampus recapitulates embryonic development. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 10074–10086.
Nacher J, Varea E, Blasco-Ibanez JM, Castillo-Gomez E, Crespo C, Martinez-Guijarro FJ et al. Expression of the transcription factor Pax 6 in the adult rat dentate gyrus. J Neurosci Res 2005; 81: 753–761.
Song H, Kempermann G, Overstreet Wadiche L, Zhao C, Schinder AF, Bischofberger J . New neurons in the adult mammalian brain: synaptogenesis and functional integration. J Neurosci 2005; 25: 10366–10368.
Hodge RD, Nelson BR, Kahoud RJ, Yang R, Mussar KE, Reiner SL et al. Tbr2 is essential for hippocampal lineage progression from neural stem cells to intermediate progenitors and neurons. J Neurosci 2012; 32: 6275–6287.
Pinto L, Drechsel D, Schmid MT, Ninkovic J, Irmler M, Brill MS et al. AP2gamma regulates basal progenitor fate in a region- and layer-specific manner in the developing cortex. Nat Neurosci 2009; 12: 1229–1237.
Thewes V, Orso F, Jager R, Eckert D, Schafer S, Kirfel G et al. Interference with activator protein-2 transcription factors leads to induction of apoptosis and an increase in chemo- and radiation-sensitivity in breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2010; 10: 192.
Mori T, Tanaka K, Buffo A, Wurst W, Kuhn R, Gotz M . Inducible gene deletion in astroglia and radial glia—a valuable tool for functional and lineage analysis. Glia 2006; 54: 21–34.
Novak A, Guo C, Yang W, Nagy A, Lobe CG . Z/EG, a double reporter mouse line that expresses enhanced green fluorescent protein upon Cre-mediated excision. Genesis 2000; 28: 147–155.
Brill MS, Snapyan M, Wohlfrom H, Ninkovic J, Jawerka M, Mastick GS et al. A dlx2- and pax6-dependent transcriptional code for periglomerular neuron specification in the adult olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 6439–6452.
Oliveira JF, Dias NS, Correia M, Gama-Pereira F, Sardinha VM, Lima A et al. Chronic stress disrupts neural coherence between cortico-limbic structures. Front Neural Circuits 2013; 7: 10.
Gu Y, Arruda-Carvalho M, Wang J, Janoschka SR, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW et al. Optical controlling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-born dentate granule cells. Nat Neurosci 2012; 15: 1700–1706.
Cerqueira JJ, Mailliet F, Almeida OF, Jay TM, Sousa N . The prefrontal cortex as a key target of the maladaptive response to stress. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 2781–2787.
Garthe A, Behr J, Kempermann G . Adult-generated hippocampal neurons allow the flexible use of spatially precise learning strategies. PLoS One 2009; 4: e5464.
Ruediger S, Spirig D, Donato F, Caroni P . Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning. Nat Neurosci 2012; 15: 1563–1571.
Garthe A, Kempermann G . An old test for new neurons: refining the Morris water maze to study the functional relevance of adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front Neurosci 2013; 7: 63.
Adhikari A, Topiwala MA, Gordon JA . Synchronized activity between the ventral hippocampus and the medial prefrontal cortex during anxiety. Neuron 2010; 65: 257–269.
Varela F, Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J . The brainweb: phase synchronization and large-scale integration. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001; 2: 229–239.
Shen L, Nam HS, Song P, Moore H, Anderson SA . FoxG1 haploinsufficiency results in impaired neurogenesis in the postnatal hippocampus and contextual memory deficits. Hippocampus 2006; 16: 875–890.
Deng W, Saxe MD, Gallina IS, Gage FH . Adult-born hippocampal dentate granule cells undergoing maturation modulate learning and memory in the brain. J Neurosci 2009; 29: 13532–13542.
Jessberger S, Clark RE, Broadbent NJ, Clemenson GD Jr, Consiglio A, Lie DC et al. Dentate gyrus-specific knockdown of adult neurogenesis impairs spatial and object recognition memory in adult rats. Learn Mem 2009; 16: 147–154.
Kodama M, Fujioka T, Duman RS . Chronic olanzapine or fluoxetine administration increases cell proliferation in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of adult rat. Biol Psychiatry 2004; 56: 570–580.
Mateus-Pinheiro A, Patricio P, Bessa JM, Sousa N, Pinto L . Cell genesis and dendritic plasticity: a neuroplastic pas de deux in the onset and remission from depression. Mol Psychiatry 2013; 18: 748–750.
Hodge RD, Kowalczyk TD, Wolf SA, Encinas JM, Rippey C, Enikolopov G et al. Intermediate progenitors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis: Tbr2 expression and coordinate regulation of neuronal output. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 3707–3717.
Urban N, Guillemot F . Neurogenesis in the embryonic and adult brain: same regulators, different roles. Front Cell Neurosci 2014; 8: 396.
Bonaguidi MA, Wheeler MA, Shapiro JS, Stadel RP, Sun GJ, Ming GL et al. In vivo clonal analysis reveals self-renewing and multipotent adult neural stem cell characteristics. Cell 2011; 145: 1142–1155.
Taylor V . Hippocampal stem cells: so they are multipotent!. J Mol Cell Biol 2011; 3: 270–272.
van Praag H, Christie BR, Sejnowski TJ, Gage FH . Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 13427–13431.
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH . New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 2010; 11: 339–350.
Sahay A, Scobie KN, Hill AS, O'Carroll CM, Kheirbek MA, Burghardt NS et al. Increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis is sufficient to improve pattern separation. Nature 2011; 472: 466–470.
Sousa N . The dynamics of the stress neuromatrix. Mol Psychiatry 2016; 21: 302–312.
Fell J, Axmacher N . The role of phase synchronization in memory processes. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 105–118.
Gordon JA . Oscillations and hippocampal–prefrontal synchrony. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2011; 21: 486–491.
Carreno FR, Donegan JJ, Boley AM, Shah A, DeGuzman M, Frazer A et al. Activation of a ventral hippocampus-medial prefrontal cortex pathway is both necessary and sufficient for an antidepressant response to ketamine. Mol Psychiatry 2016; 21: 1298–1308.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the excellent technical expertise of Luís Martins and Andrea Steiner-Mezzadri. We would also like to acknowledge Magdalena Götz for the insightful comments on the paper. AMP, PP, ARS, JS, VMS, NDA and JFO received fellowships from the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT). LP received fellowship from FCT and her work is funded by FCT (IF/01079/2014) and Bial Foundation (427/14) projects. This work was cofunded by the Life and Health Sciences Research Institute (ICVS), and Northern Portugal Regional Operational Programme (NORTE 2020), under the Portugal 2020 Partnership Agreement, through the European Regional Development Fund (FEDER) (projects NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000013 and NORTE-01-0145-FEDER-000023). This work has been also funded by FEDER funds, through the Competitiveness Factors Operational Programme (COMPETE), and by National funds, through the FCT, under the scope of the project POCI-01-0145-FEDER-007038.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Molecular Psychiatry website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mateus-Pinheiro, A., Alves, N., Patrício, P. et al. AP2γ controls adult hippocampal neurogenesis and modulates cognitive, but not anxiety or depressive-like behavior. Mol Psychiatry 22, 1725–1734 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.169
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.169
This article is cited by
-
Neuronal TIMP2 regulates hippocampus-dependent plasticity and extracellular matrix complexity
Molecular Psychiatry (2023)
-
Transcriptomics in the nucleus accumbens shell reveal sex- and reinforcer-specific signatures associated with morphine and sucrose craving
Neuropsychopharmacology (2022)
-
Lithium treatment reverses irradiation-induced changes in rodent neural progenitors and rescues cognition
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Tet3 ablation in adult brain neurons increases anxiety-like behavior and regulates cognitive function in mice
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)
-
Astrocyte-derived TNF and glutamate critically modulate microglia activation by methamphetamine
Neuropsychopharmacology (2021)