Abstract
Low-molecular-weight heparins (LMWHs) are carbohydrate-based anticoagulants clinically used to treat thrombotic disorders, but impurities, structural heterogeneity or functional irreversibility can limit treatment options. We report a series of synthetic LMWHs prepared by cost-effective chemoenzymatic methods. The high activity of one defined synthetic LMWH against human factor Xa (FXa) was reversible in vitro and in vivo using protamine, demonstrating that synthetically accessible constructs can have a critical role in the next generation of LMWHs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn, S.R. et al. Chest 141 (suppl.), e195S–e226S (2012).
Hirsh, J., O'Donnell, M.O. & Eikelboom, J.W. Circulation 116, 552–560 (2007).
Arepally, G.M. & Ortel, T.L. N. Engl. J. Med. 355, 809–817 (2006).
Linhardt, R.J. & Liu, J. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 12, 217–219 (2012).
Melnikova, I. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 353–354 (2009).
Harder, S. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 52, 964–975 (2012).
Weitz, J.I. & Linkins, L.A. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 16, 271–282 (2007).
Petitou, M. & van Boeckel, C.A.A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 43, 3118–3133 (2004).
Moon, A.F. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 5265–5270 (2012).
Chen, J., Jones, C.L. & Liu, J. Chem. Biol. 14, 986–993 (2007).
Zhang, Z. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 12998–13007 (2008).
Xu, Y. et al. Science 334, 498–501 (2011).
Zhang, Z. et al. J. Med. Chem. 51, 5498–5501 (2008).
Turnbull, J.E. Science 334, 462–463 (2011).
Liu, H., Zhang, Z. & Linhardt, R.J. Nat. Prod. Rep. 26, 313–321 (2009).
Sheng, J., Xu, Y., Dulaney, S.B., Huang, X. & Liu, J. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 20996–21002 (2012).
Pempe, E.H., Xu, Y., Gopalakrishnan, S., Liu, J. & Harris, E.H. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 20774–20783 (2012).
Li, L., Zhang, F., Zaia, J. & Linhardt, R.J. Anal. Chem. 84, 8822–8829 (2012).
Harris, E.N., Weigel, J.A. & Weigel, P.H. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 17341–17350 (2008).
Martinez-Gonzalez, J. & Rodriguez, C. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 8, 625–634 (2010).
Lu, G. et al. Nat. Med. 19, 446–451 (2013).
Bianchini, E.P., Fazavana, J., Picard, V. & Borgel, D. Blood 117, 2054–2060 (2011).
Atha, D.H., Lormeau, J.-C., Petitou, M., Rosenberg, R.D. & Choay, J. Biochemistry 24, 6723–6729 (1985).
Lee, S. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 220–226 (2013).
Petitou, M., Jacquinet, J.C., Choay, J., Lormeau, J.C. & Nassr, M. US Patent 4,818,816 (1989).
Zhang, L. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 42311–42321 (2001).
Duncan, M.B., Chen, J., Krise, J.P. & Liu, J. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1671, 34–43 (2004).
Lee, M.K. & Lander, A.D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 2768–2772 (1991).
Liu, R. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 34240–34249 (2010).
Sundaram, M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 651–656 (2003).
Harris, E.N., Weigel, J.A. & Weigel, P.H. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 36201–36209 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.E. Rogers for helpful discussions. This work is supported in part by US National Institutes of Health grants HL094463 (to J.L.), GM102137 (to J.L.), HL62244 (to R.J.L.), HL096972 (to R.J.L.), GM38060 (to R.J.L.) HL096679 (to R.P.) and HL117659 (to N.S.K. and R.P.). E.M.S. is supported by a US National Institutes of Health Research Training Grant (T32-HL007149). K.C. is a recipient of a Royal Thai Government fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.X. synthesized synthetic LMWHs and analyzed in vitro anti-FXa activity and protamine neutralization. C.C. conducted 1D and 2D NMR analysis. K.C. and E.M.S. determined the reversibility of LMWH anti-FXa activity and performed tail bleeding experiments. P.-H.H. conducted NMR analysis. L.L. did the high-resolution MS analysis. T.Q.P. expressed and purified enzymes. N.S.K. and R.P. designed and analyzed the ex vivo protamine neutralization. R.P. designed the tail bleeding experiment. J.S. helped develop synthetic routes. E.N.H. determined the metabolic pathways for synthetic LMWHs. R.J.L. did data analysis and wrote the manuscript. J.L. designed the project and wrote the manuscript. All authors participated in discussions and critically read the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, Supplementary Note and Supplementary Figures 1–36. (PDF 8681 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Cai, C., Chandarajoti, K. et al. Homogeneous low-molecular-weight heparins with reversible anticoagulant activity. Nat Chem Biol 10, 248–250 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1459
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1459
This article is cited by
-
Host heparan sulfate promotes ACE2 super-cluster assembly and enhances SARS-CoV-2-associated syncytium formation
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Novel β1,4 N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase in de novo enzymatic synthesis of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharides
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2023)
-
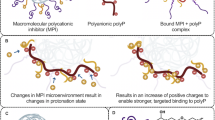
Platelet factor 4 polyanion immune complexes: heparin induced thrombocytopenia and vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia
Thrombosis Journal (2021)
-
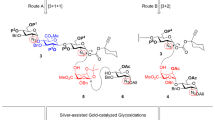
Silver-assisted gold-catalyzed formal synthesis of the anticoagulant Fondaparinux pentasaccharide
Communications Chemistry (2021)
-
Bioengineered production of glycosaminoglycans and their analogues
Systems Microbiology and Biomanufacturing (2021)