Abstract
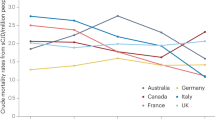
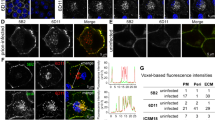
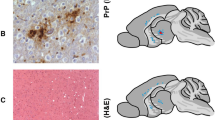
We studied prion proteins (PrP) in skin and brains of Libyan Jews carrying the E200K mutation who died of familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD). Unexpectedly, studies with brain showed that PrP molecules encoded both by the wild–type (wt) and mutant alleles exhibit altered properties characteristic of the prion protein associated with prion diseases (PrPSc). Using monospecific antisera, we found that wtPrP was insoluble in the brains of three patients who were heterozygous for the E200K mutation, whereas mutant PrP was both insoluble and protease–resistant. Our results argue that both wild–type and mutant PrP undergo conformational changes and are particularly intriguing, because the normal isoform PrPc is soluble in nondenaturing detergents and is readily digested by proteases, whereas PrPSc is insoluble and resistant to proteolytic digestion. Our findings indicate that insoluble wtPrP represents a conformational intermediate, the first to be identified, within a pathway in which PrPc is converted to PrPSc.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prusiner, S.B. Inherited prion diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 4611–4614 (1994).
Masters, C.L., Gajdusek, D.C. & Gibbs, C.J., Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Brain 1O4, 559–588 (1981).
Hsiao, K. et al. Linkage of a prion protein missense variant to Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Nature 338, 342–345 (1989).
Goldfarb, L.G. et al. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: Disease phenotype determined by a DNA polymorphism. Science 258, 806–808 (1992).
Kahana, E., Milton, A., Braham, J. & Sofer, D. Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: Focus among Libyan Jews in Israel. Science 183, 90–91 (1974).
Goldfarb, L., Korczyn, A., Brown, P., Chapman, J. & Gajdusek, D.C. Mutation in codon 200 of scrapie amyloid precursor gene linked to Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Sephardicjews of Libyan and non-Libyan origin. Lancet 336, 637–638 (1990).
Hsiao, K. et al. Mutationof the prion proteininLibyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 324, 1091–1097 (1991).
Gabizon, R. et al. Mutation and polymorphism of the prion protein gene in Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 33, 828–835 (1993).
Goldfarb, L.G., Mitrova, E., Brown, P., Toh, B.H. & Gajdusek, D.C. Mutation in codon 200 of scrapie amyloid protein gene in two clusters of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Slovakia. Lancet 336, 514–515 (1990).
Brown, P. et al. Familial Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Chile is associated with the codon 200 mutation of the PRNP amyloid precursor gene on chromosome 20. J. Neural. Sci. 112, 65–67 (1992).
Collinge, J. et al. Inherited prion disease (PrP lysine 200) in Britain: Two case reports. Br. Med. J. 306, 391–392 (1993).
Bertoni, J.M., Brown, P., Goldfarb, L., Gajdusek, D. & Omaha, N.E., Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease with the PRNP codon 200lys mutation and supranuclear palsy but without myoclonus or periodic EEG complexes (Abstr). Neurology 42 (No.4 Suppl. 3), 350 (1992).
Chapman, J., Ben-Israel, J., Goldhammer, Y. & Korczyn, A.D. The risk of developing Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in subjects with the PRNP gene codon 200 point mutation. Neurology 44, 1683–1686 (1994).
Spudich, S. et al. Complete penetrance of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Libyan Jews carrying the E200K mutation in the prion protein gene. Mol. Med. 1, 607–613 (1995).
Prusiner, S.B. Molecular biology of prion diseases. Science 252, 1515–1522 (1991).
Pan, K.-M. et al. Conversion of a-helices into b-sheets features in the formation of the scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10962–10966 (1993).
Huang, Z. et al. Proposed three-dimensional structure for the cellular prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7139–7143 (1994).
Safar, J., Roller, P.P., Gajdusek, D.C. & Gibbs, C.J., Jr. Conformational transitions, dissociation, and unfolding of scrapie amyloid (prion) protein. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 20276–20284 (1993).
Kitamoto, T., Yamaguchi, K., Doh-ura, K. & Tateishi, J. A prion protein missense variant is integrated in kuru plaque cores in patients with Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome. Neurology 41, 306–310 (1991).
Kitamoto, T., Iizuka, R., & Tateishi, J. An amber mutation of prion protein in Gerstmann-Straussler syndrome with mutant PrP plaques. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 192, 525–531 (1993).
Tagliavini, F. et al. Amyloid fibrils in Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease (Indiana and Swedish kindreds) express only PrP peptides encoded by the mutant allele. Cell 79, 695–703 (1994).
Meyer, R.K. et al. Separation and properties of cellular and scrapie prion proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 2310–2314 (1986).
Kascsak, R.J. et al. Mouse polyclonal and monoclonal antibody to scrapie-asso-ciated fibril proteins. J. Virol. 61, 3688–3693 (1987).
Rogers, M., Taraboulos, A., Scott, M., Groth, D. & Prusiner, S.B. Intracellular accumulation of the cellular prion protein after mutagenesis of its Asn-linked gly-cosylation sites. Glycobiology 1, 101–109 (1990).
Goldfarb, L.G. et al. New mutation in scrapie amyloid precursor gene (at codon 178) in Finnish Creutzfeldt–Jakob kindred. Lancet 337, 425 (1991).
Hsiao, K. et al. Mutant prion proteins in Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease with neurofibrillary tangles. Nature Genet. 1, 68–71 (1992).
Monari, L. et al. Fatal familial insomnia and familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: Different prion proteins determined by a DNA polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 2839–2842 (1994).
Gasset, M., Baldwin, M.A., Fletterick, R.J. & Prusiner, S.B. Perturbation of the secondary structure of the scrapie prion protein under conditions associated with changes in infectivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 1–5 (1993).
Gabizon, R., McKinley, M.P., Groth, D.F., Kenaga, L. & Prusiner, S.B. Properties of scrapie prion liposomes. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 4950–4955 (1988).
Goldfarb, L.G. et al. Synthetic peptides corresponding to different mutated regions of the amyloid gene in familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease show enhanced in vitro formation of morphologically different amyloid fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 4451–4454 (1993).
Gasset, M. et al. Predicted α-helical regions of the prion protein when synthesized as peptides form amyloid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10940–10944 (1992).
Come, J.H., Fraser, P.E. & Lansbury, P.T., A kinetic model for amyloid formation in the prion diseases: Importance of seeding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 5959–5963 (1993).
Forloni, G. et al. Neurotoxicity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 362, 543–546 (1993).
Nguyen, J., Baldwin, M.A., Cohen, F.E. & Prusiner, S.B. Prion protein peptides induce α-helix to β-sheet conformation altransitions. Biochemistry 34, 4186–4192 (1995).
Meiner, Z., Halimi, M., Polakiewicz, R.D., Prusiner, S.B. & Gabizon, R. Presence of the prion protein in peripheral tissues of Libyan Jews with Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Neurology 42, 1355–1360 (1992).
Taraboulos, A. et al. Acquisition of protease resistance by prion proteins in scrapie-infected cells does not require asparagine-linked glycosylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 8262–8266 (1990).
Prusiner, S.B. et al. Transgenetic studies implicate interactions between homologous PrP isoforms in scrapie prion replication. Cell 63, 673–686 (1990).
Kimberlin, R.H. & Walker, C.A. The antiviral compound HPA-23 can prevent scrapie when administered at the time of infection. Arch. Virol. 78, 9–18 (1983).
Ehlers, B. & Diringer, H. Dextran sulphate 500 delays and prevents mouse scrapie by impairment of agent replication in spleen. J. Gen. Virol. 65, 1325–1330 (1984).
Diringer, H. & Ehlers, B. Chemoprophylaxis of scrapie in mice. J. Gen. Virol. 72, 457–460 (1991).
Caughey, B. & Race, R.E. Potent inhibition of scrapie-associated PrP accumulation by Congo red. J. Neumchem. 59, 768–771 (1992).
Caughey, B. & Raymond, G.J. Sulfated polyanion inhibition of scrapie-associated PrP accumulation in cultured cells. J. Virol. 67, 643–650 (1993).
Ladogana, A. et al. Sulphate polyanions prolong the incubation period of scrapie-infected hamsters. J. Gen. Virol. 73, 661–665 (1992).
Ingrosso, L., Ladogana, A. & Pocchiari, M. Congo red prolongs the incubation period in scrapie-infected hamsters. J. Virol. 69, 506–508 (1995).
Gabizon, R., Meiner, Z., Halimi, M. & Ben-Sasson, S.A. Heparin-like molecules bind differentially to prion-proteins and change their intracellular metabolic fate. J. Cell. Physiol. 157, (1993).
Telling, G.C. et al. Transmission of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease from humans to transgenic mice expressing chimeric human-mouse prion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 9936–9940 (1994).
Telling, G.C. et al. Prion propagation in mice expressing human and chimeric PrP transgenes implicates the interaction of cellular PrP with another protein. Cell 83, 79–90 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gabizon, R., Telling, G., Meiner, Z. et al. Insoluble wild–type and protease–resistant mutant prion protein in brains of patients with inherited prion disease. Nat Med 2, 59–64 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0196-59
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0196-59
This article is cited by
-
Prion strains viewed through the lens of cryo-EM
Cell and Tissue Research (2023)
-
Phenotypic diversity of genetic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: a histo-molecular-based classification
Acta Neuropathologica (2021)
-
Characterization of Anchorless Human PrP With Q227X Stop Mutation Linked to Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker Syndrome In Vivo and In Vitro
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Familial human prion diseases associated with prion protein mutations Y226X and G131V are transmissible to transgenic mice expressing human prion protein
Acta Neuropathologica Communications (2018)
-
PrP charge structure encodes interdomain interactions
Scientific Reports (2015)