Abstract
Surgery is the standard treatment for patients in the chronic phase of Peyronie's disease. Reconstructive surgeries function by either shortening the convex side of the tunica albuginea (Nesbit procedure, Yachia technique and penile plication) or lengthening the concave side by incision of the plaque with subsequent grafting. Tunical shortening procedures are ideal for men with good erectile capacity, penile curvatures less than 60° and predicted postprocedural length loss of less than 20% of erect penis length. Tunical lengthening procedures with grafting are indicated in patients with severe penile length loss, curvatures greater than 60° and prominent hourglass deformities. Saphenous vein and tunica albuginea are the most commonly used autologous graft materials. Cadaveric or bovine pericardium and 4-layer small intestinal submucosa are promising nonautologous tissues. Penile implantation of a prosthesis is the standard procedure in men with erectile dysfunction who do not respond to conservative treatment. If residual penile curvature is less than 30° after implantation, no further treatment is required. However, residual curve of greater than 30° can be straightened with manual modeling. Additional procedures such as penile plication, the Nesbit procedure, or grafting can be performed if modeling fails to correct the residual deformity.
Key Points
-
Surgical correction is the gold standard treatment option for Peyronie's disease (PD), but should only be considered after stabilization of the disease
-
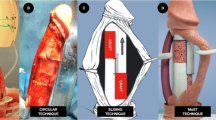
Tunical shortening procedures are ideal for men with good erectile function, penile curvatures less than 60° and predicted postprocedural length loss of <20% of erect penis length
-
Plication is currently the most utilized shortening procedure because extensive surgical experience is not required
-
Penile lengthening surgery is reserved for men with good erectile function but severe penile length loss, curvatures greater than 60° or prominent hourglass deformities
-
Massage and stretch therapy with bedtime use of PDE5 inhibitors are recommended for penile rehabilitation after lengthening procedures
-
Penile prosthesis implantation is the standard of care for patients with PD and concomitant erectile dysfunction nonresponsive to medical treatment
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ralph, D. et al. The management of Peyronie's disease: evidence-based 2010 guidelines. J. Sex. Med. 7, 2359–2374 (2010).
Schwarzer, U. et al. The prevalence of Peyronie's disease: results of a large survey. BJU Int. 88, 727–730 (2001).
Smith, J. F., Walsh, T. J. & Lue, T. F. Peyronie's disease: a critical appraisal of current diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Impot. Res. 20, 445–459 (2008).
Mulhall, J. P. et al. Subjective and objective analysis of the prevalence of Peyronie's disease in a population of men presenting for prostate cancer screening. J. Urol. 171, 2350–2353 (2004).
Levine, L. A., Estrada, C. R., Storm, D. W. & Matkov, T. G. Peyronie disease in younger men: characteristics and treatment results. J. Androl. 24, 27–32 (2003).
Deveci, S. et al. Defining the clinical characteristics of Peyronie's disease in young men. J. Sex. Med. 4, 485–490 (2007).
Kadioglu, A. & Sanli, O. in Peyronie's disease: a guide to clinical management (ed. Levine, L. A.) 9–18 (Humana Press, Totowa, 2007).
Mulhall, J. P., Schiff, J. & Guhring, P. An analysis of the natural history of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 175, 2115–2118 (2006).
Hellstrom, W. J. & Bivalacqua, T. J. Peyronie's disease: etiology, medical and surgical therapy. J. Androl. 21, 347–354 (2000).
Levine, L. A. & Greenfield, J. M. Establishing a standardized evaluation of the man with Peyronie's disease. Int. J. Impot. Res. 15 (Suppl. 5), S103–S112 (2003).
Kadioglu, A. et al. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease: a single center experience with 145 patients. Eur. Urol. 53, 432–439 (2008).
Pryor, J. P. & Ralph, D. J. Clinical presentations of Peyronie's disease. Int. J. Impot. Res. 14, 414–417 (2002).
Bella, A. J., Perelman, M. A., Brant, W. O. & Lue, T. F. Peyronie's disease (CME). J. Sex. Med. 4, 1527–1538 (2007).
Kadioglu, A. et al. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease: a critical analysis. Eur. Urol. 50, 235–248 (2006).
Mulhall, J. P., Anderson, M. & Parker, M. A surgical algorithm for men with combined Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction: functional and satisfaction outcomes. J. Sex. Med. 2, 132–138 (2005).
Levine, L. A. & Lenting, E. L. A surgical algorithm for the treatment of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 158, 2149–2152 (1997).
Nesbit, R. M. Congenital curvature of the phallus: report of three cases with description of corrective operation. 1965. J. Urol. 167, 1187–1188 (2002).
Giammusso, B., Burrello, M., Branchina, A., Nicolosi, F. & Motta, M. Modified corporoplasty for ventral penile curvature: description of technique and initial results. J. Urol. 171, 1209–1211 (2004).
Savoca, G., Scieri, F., Pietropaolo, F., Garaffa, G. & Belgrano, E. Straightening corporoplasty for Peyronie's disease: a review of 218 patients with median follow-up of 89 months. Eur. Urol. 46, 610–614 (2004).
Bokarica, P., Parazajder, J., Mazuran, B. & Gilja, I. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease based on penile length and degree of curvature. Int. J. Impot. Res. 17, 170–174 (2005).
Licht, M. R. & Lewis, R. W. Modified Nesbit procedure for the treatment of Peyronie's disease: a comparative outcome analysis. J. Urol. 158, 460–463 (1997).
Ralph, D. J., al-Akraa, M. & Pryor, J. P. The Nesbit operation for Peyronie's disease: 16-year experience. J. Urol. 154, 1362–1363 (1995).
Yachia, D. Modified corporoplasty for the treatment of penile curvature. J. Urol. 143, 80–82 (1990).
Daitch, J. A., Angermeier, K. W. & Montague, D. K. Modified corporoplasty for penile curvature: long-term results and patient satisfaction. J. Urol. 162, 2006–2009 (1999).
Rehman, J., Benet, A., Minsky, L. S. & Melman, A. Results of surgical treatment for abnormal penile curvature: Peyronie's disease and congenital deviation by modified Nesbit plication (tunical shaving and plication). J. Urol. 157, 1288–1291 (1997).
Essed, E. & Schroeder, F. H. New surgical treatment for Peyronie's disease. Urology 25, 582–587 (1985).
Van Der Horst, C., Martínez Portillo, F. J., Seif, C., Alken, P. & Juenemann, K. P. Treatment of penile curvature with Essed-Schröder tunical plication: aspects of quality of life from the patients' perspective. BJU Int. 93, 105–108 (2004).
Greenfield, J. M., Lucas, S. & Levine, L. A. Factors affecting the loss of length associated with tunica albuginea plication for correction of penile curvature. J. Urol. 175, 238–241 (2006).
Taylor, F. L. & Levine, L. A. Surgical correction of Peyronie's disease via tunica albuginea plication or partial plaque excision with pericardial graft: long-term follow-up. J. Sex. Med. 5, 2221–2228 (2008).
Gholami, S. S. & Lue, T. F. Correction of penile curvature using the 16-dot plication technique: a review of 132 patients. J. Urol. 167, 2066–2069 (2002).
Dugi, D. D. 3rd & Morey, A. F. Penoscrotal plication as a uniform approach to reconstruction of penile curvature. BJU Int. 105, 1440–1444 (2010).
Gelbard, M. K. & Hayden, B. Expanding contractures of the tunica albuginea due to Peyronie's disease with temporalis fascia free grafts. J. Urol. 145, 772–776 (1991).
Egydio, P. H., Lucon, A. M. & Arap, S. A single relaxing incision to correct different types of penile curvature: surgical technique based on geometrical principles. BJU Int. 94, 1147–1157 (2004).
Kadioglu, A. et al. Graft materials in Peyronie's disease surgery: a comprehensive review. J. Sex. Med. 4, 581–595 (2007).
Levine, L. A., Greenfield, J. M. & Estrada, C. R. Erectile dysfunction following surgical correction of Peyronie's disease and a pilot study of the use of sildenafil citrate rehabilitation for postoperative erectile dysfunction. J. Sex. Med. 2, 241–247 (2005).
Lowsley, O. S. & Boyce, W. H. Further experiences with an operation for the cure of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 63, 888–902 (1950).
Wild, R. M., Devine, C. J. Jr & Horton, C. E. Dermal graft repair of Peyronie's disease: survey of 50 patients. J. Urol. 121, 47–50 (1979).
Goyal, N. K. et al. Experience with plaque excision and dermal grafting in the surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease. Singapore Med. J. 49, 805–808 (2008).
O'Donnell, P. D. Results of surgical management of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 148, 1184–1187 (1992).
Kargi, E. et al. Relaxation incision and fascia lata grafting in the surgical correction of penile curvature in Peyronie's disease. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 113, 254–259 (2004).
Shioshvili, T. J. & Kakonashvili, A. P. The surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease: replacement of plaque by free autograft of buccal mucosa. Eur. Urol. 48, 129–133 (2005).
Shioshvili, T. J. & Kakonashvili, A. P. Use of free autografts of various origin for the treatment of Peyronie's disease. Eur. Urol. 37 (Suppl. 2), 58 (2000).
Cormio, L. et al. Surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease by plaque incision and grafting with buccal mucosa. Eur. Urol. 55, 1469–1475 (2009).
Dublin, N. & Stewart, L. H. Oral complications after buccal mucosal graft harvest for urethroplasty. BJU Int. 94, 867–869 (2004).
Levine, L. A. Editorial comment on: surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease by plaque incision and grafting with buccal mucosa. Eur. Urol. 55, 1475–1476 (2009).
Teloken, C. et al. Penile straightening with crural graft of the corpus cavernosum. J. Urol. 164, 107–108 (2000).
Schwarzer, J. U., Mayerhofer, J., Schukai, O. & Mühlen, B. The tunica-albuginea-patch-technique: a new technique of an autologous grafting procedure for patients with Peyronie's disease [abstract V24]. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 4, 277 (2005).
Hatzichristou, D. G. et al. Corporoplasty using tunica albuginea free grafts for penile curvature: surgical technique and long-term results. J. Urol. 167, 1367–1370 (2002).
Da Ros, C. et al. Graft of crural tunica albuginea for the treatment of Peyronie's disease [abstract V743]. Presented at the American Urological Association Annual Meeting 2005.
Hsu, Y. S. et al. Experience of surgical treatment of peyronie's disease with deep dorsal venous patch in Taiwanese men. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 66, 487–491 (2003).
Craatz, S. et al. The dorsal lamina of rectus sheath. a suitable grafting material for the penile tunica albuginea in Peyronie's disease? BJU Int. 97, 134–137 (2006).
Radopoulos, D., Vakalopoulos, I. & Thanos, P. Preputial graft in penile curvature correction: preliminary results. Int. J. Impot. Res. 21, 82–87 (2009).
Krishnamurti, S. Penile dermal flap for defect reconstruction in Peyronie's disease: operative technique and four years' experience in 17 patients. Int. J. Impot. Res, 7, 195–208 (1995).
Chang, J. A., Gholami, S. S. & Lue, T. F. Saphenous vein grafts. Int. J. Impot. Res. 14, 375–378 (2002).
Nowicki, M. et al. Immunocytochemical study on endothelial integrity of saphenous vein grafts harvested by minimally invasive surgery with the use of vascular mayo stripers. A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 27, 244–250 (2004).
Tsui, L. C., Souza, D. S., Filbey, D., Karlsson, M. G. & Dashwood, M. R. Localization of nitric oxide synthase in saphenous vein grafts harvested with a novel “no-touch” technique: potential role of nitric oxide contribution to improved early graft patency rates. J. Vasc. Surg. 35, 356–362 (2002).
Brock, G., Kadioglu, A. & Lue, T. F. Peyronie's disease: a modified treatment. Urology 42, 300–304 (1993).
El-Sakka, A. I., Rashwan, H. M. & Lue, T. F. Venous patch graft for Peyronie's disease. Part II: outcome analysis. J. Urol. 160, 2050–2053 (1998).
Kalsi, J., Minhas, S., Christopher, N. & Ralph, D. The results of plaque incision and venous grafting (Lue procedure) to correct the penile deformity of Peyronie's disease. BJU Int. 95, 1029–1033 (2005).
Adeniyi, A. A., Goorney, S. R., Pryor, J. P. & Ralph, D. J. The Lue procedure: an analysis of the outcome in Peyronie's disease. BJU Int. 89, 404–408 (2002).
Akkus, E. et al. Incision and venous patch graft in the surgical treatment of penile curvature in Peyronie's disease. Eur. Urol. 40, 531–536 (2001).
De Stefani, S. et al. Saphenous vein harvesting by 'stripping' technique and 'W'-shaped patch covering after plaque incision in the treatment of Peyronie's disease. Int. J. Impot. Res. 12, 299–301 (2000).
Montorsi, F. et al. Five year follow-up of plaque incision and vein grafting for Peyronie's disease [abstract 123]. Eur. Urol. Suppl. 3, 33 (2004).
Hsu, G. L. et al. Long-term results of autologous venous grafts for penile morphological reconstruction. J. Androl. 28, 186–193 (2007).
Chun, J. L., McGregor, A., Krishnan, R. & Carson, C. C. A comparison of dermal and cadaveric pericardial grafts in the modified Horton-Devine procedure for Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 166, 185–188 (2001).
Usta, M. F. et al. Patient and partner satisfaction and long-term results after surgical treatment for Peyronie's disease. Urology 62, 105–109 (2003).
Levine, L. A. & Estrada, C. R. Human cadaveric pericardial graft for the surgical correction of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 170, 2359–2362 (2003).
Knoll, L. D. Use of porcine small intestinal submucosal graft in the surgical treatment of Peyronie's disease. Urology 57, 753–757 (2001).
Knoll, L. D. Use of small intestinal submucosa graft for the surgical management of Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 178, 2474–2478 (2007).
Lee, E. W., Shindel, A. W. & Brandes, S. B. Small intestinal submucosa for patch grafting after plaque incision in the treatment of Peyronie's disease. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 34, 191–196 (2008).
Breyer, B. N., Brant, W. O., Garcia, M. M., Bella, A. J. & Lue, T. F. Complications of small intestine submucosa graft for Peyronie's disease. J. Urol. 177, 589–591 (2007).
Kalsi, J. S., Christopher, N., Ralph, D. J. & Minhas, S. Plaque incision and fascia lata grafting in the surgical management of Peyronie's disease. BJU Int. 98, 110–114 (2006).
Kovac, J. R. & Brock, G. B. Surgical outcomes and patient satisfaction after dermal, pericardial and small intestinal submucosal grafting for Peyronie's disease. J. Sex. Med. 4, 1500–1508 (2007).
Sampaio, J. S., Fonseca, J., Passarinho, A., Cristino, J. & Mendes, J. Peyronie's disease: surgical correction of 40 patients with relaxing incision and duramater graft. Eur. Urol. 41, 551–555 (2002).
Moncada-Iribarren, I., Jara, J., Martinez-Salamanca, J. I., Cabello, R., Hernandez, C. Managing penile shortening after Peyronie's disease surgery: a comprehensive review [abstract 750]. Presented at the American Urological Association Annual Meeting 2007.
Montorsi, F., Guazzoni, G., Bergamaschi, F. & Rigatti, P. Patient-partner satisfaction with semirigid penile prostheses for Peyronie's disease: a 5-year followup study. J. Urol. 150, 1819–1821 (1993).
Wilson, S. K. & Delk, J. R. 2nd. A new treatment for Peyronie's disease: modeling the penis over an inflatable penile prosthesis. J. Urol. 152, 1121–1123 (1994).
Levine, L. A. & Dimitriou, R. J. A surgical algorithm for penile prosthesis placement in men with erectile failure and Peyronie's disease. Int. J. Impot. Res. 12, 147–151 (2000).
Carson, C. C. Penile prothesis implantation in the treatment of Peyronie's disease and erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 12 (Suppl. 4), S122–S126 (2000).
Chaudhary, M., Sheikh, N., Asterling, S., Ahmad, I. & Greene, D. Peyronie's disease with erectile dysfunction: penile modeling over inflatable penile prostheses. Urology 65, 760–764 (2005).
Levine, L. A., Benson, J. & Hoover, C. Inflatable penile prosthesis placement in men with Peyronie's disease and drug-resistant erectile dysfunction: a single-center study. J. Sex. Med. 7, 3775–3783 (2010).
Hakim, L. S., Kulaksızoglu, H., Hamill, B. K., Udelson, D. & Goldstein, I. A guide to safe corporotomy incisions in the presence of underlying inflatable penile cylinders: results of in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Urol. 155, 918–923 (1996).
Mulcahy, J. J. & Wilson, S. K. Management of Peyrone's disease with penile prostheses. Int. J. Impot. Res. 14, 384–388 (2002).
Shaeer, O. Trans-corporal incision of Peyronie's plaques. J. Sex. Med. doi:10.1111/j.1743–61092010.02078.x.
Pathak, A. S., Chang, J. H., Parekh, A. R. & Aboseif, S. R. Use of rectus fascia graft for corporeal reconstruction during placement of penile implant. Urology 65, 1198–1201 (2005).
Austoni, E. et al. Soft prosthesis implant and relaxing albugineal incision with saphenous grafting for surgical therapy of Peyronie's disease: a 5-year experience and long-term follow-up on 145 operated patients. Eur. Urol. 47, 223–229 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Kadioglu, F. Küçükdurmaz and O. Sanli contributed equally to the researching of data, discussion of content, writing and editing of this article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadioglu, A., Küçükdurmaz, F. & Sanli, O. Current status of the surgical management of Peyronie's disease. Nat Rev Urol 8, 95–106 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2010.233
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2010.233
This article is cited by
-
Low-intensity shockwave therapy in Peyronie’s disease: long-term results from a prospective, randomized, sham-controlled trial
International Journal of Impotence Research (2022)
-
Plication techniques in Peyronie’s disease: new developments
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)
-
Novel approaches and new grafting materials in Peyronie’s disease reconstructive surgery
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)
-
Current trends in the surgical treatment of congenital penile curvature
International Journal of Impotence Research (2020)
-
Outcomes of Surgery in Peyronie’s Disease Following Intralesional Collagenase Clostridium Histolyticum Injections
Current Urology Reports (2019)