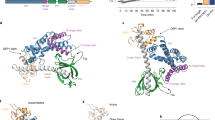
Abstract
Rho GTPases are activated by a family of guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) known as Dbl family proteins. The structural basis for how GEFs recognize and activate Rho GTPases is presently ill defined. Here, we utilized the crystal structure of the DH/PH domains of the Rac-specific GEF Tiam1 in complex with Rac1 to determine the structural elements of Rac1 that regulate the specificity of this interaction. We show that residues in the Rac1 β2–β3 region are critical for Tiam1 recognition. Additionally, we determined that a single Rac1-to-Cdc42 mutation (W56F) was sufficient to abolish Rac1 sensitivity to Tiam1 and allow recognition by the Cdc42-specific DH/PH domains of Intersectin while not impairing Rac1 downstream activities. Our findings identified unique GEF specificity determinants in Rac1 and provide important insights into the mechanism of DH/PH selection of GTPase targets.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Symons, M. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 178–181 (1996).
Hall, A. Science 279, 509–514 (1998).
Cerione, R.A. & Zheng, Y. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 8, 216–222 (1996).
Whitehead, I.P., Campbell, S., Rossman, K.L. & Der, C.J. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1332, 1–23 (1997).
Liu, X. et al. Cell 95, 269–277 (1998).
Aghazadeh, B. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 5, 1098–1107 (1998).
Aghazadeh, B., Lowry, W.E., Huang, X.Y. & Rosen, M.K. Cell 102, 625–633 (2000).
Soisson, S.M., Nimnual, A.S., Uy, M., Bar-Sagi, D. & Kuriyan, J. Cell 95, 259–268 (1998).
Worthylake, D.K., Rossman, K.L. & Sondek, J. Nature 408, 682–688 (2000).
Abe, K. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10141–10149 (2000).
Abdul-Manan, N. et al. Nature 399, 379–383 (1999).
Mott, H.R. et al. Nature 399, 384–388 (1999).
Morreale, A. et al. Nature Struct. Biol. 7, 384–388 (2000).
Coso, O.A. et al. Cell 81, 1137–1146 (1995).
Clarke, N., Arenzana, N., Hai, T., Minden, A. & Prywes, R. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 1065–1073 (1998).
Minden, A., Lin, A., Claret, F.-X., Abo, A. & Karin, M. Cell 81, 1147–1157 (1995).
Khosravi-Far, R., Solski, P.A., Kinch, M.S., Burridge, K. & Der, C.J. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 6443–6453 (1995).
Qiu, R.-G., Chen, J., McCormick, F. & Symons, M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 11781–11785 (1995).
Karnoub, A.E., Der, C.J. & Campbell, S.L. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 2847–2857 (2001).
Mossessova, E., Gulbis, J.M. & Goldberg, J. Cell 92, 415–423 (1998).
Renault, L., Kuhlmann, J., Henkel, A. & Wittinghofer, A. Cell 105, 245–255 (2001).
Westwick, J.K. et al. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 1324–1335 (1997).
Benard, V., Bohl, B.P. & Bokoch, G.M. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 13198–13204 (1999).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Pham for Tiam1 and Intersectin DH/PH protein preparations, Q. Lambert and H. Mehta for cell culture preparations and M. Rand for figure preparation. This work was supported by NIH grants to C.J.D. and S.L.C. D.K.W. is supported by a grant from the American Cancer Society. J.S. acknowledges the support from the NIH and the Pew Charitable Trusts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karnoub, A., Worthylake, D., Rossman, K. et al. Molecular basis for Rac1 recognition by guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Nat Struct Mol Biol 8, 1037–1041 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb719
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb719
This article is cited by
-
Rac3 induces a molecular pathway triggering breast cancer cell aggressiveness: differences in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines
BMC Cancer (2013)
-
Structural insights into host GTPase isoform selection by a family of bacterial GEF mimics
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2009)
-
Crucial structural role for the PH and C1 domains of the Vav1 exchange factor
EMBO reports (2008)
-
Release of autoinhibition of ASEF by APC leads to CDC42 activation and tumor suppression
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2007)
-
Intersectin-1L nucleotide exchange factor regulates secretory granule exocytosis by activating Cdc42
The EMBO Journal (2006)