Abstract
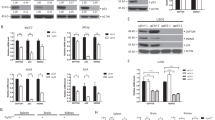
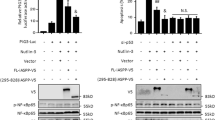
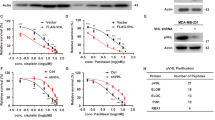
Inhibitor of differentiation-1 (Id-1) has been accepted as a putative oncogene to promote oncogenic processes through inactivation of tumor suppressors and activation of growth promoting pathways. Here, we show that Id-1 activates the Akt pathway by inhibition of phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) transcription through downregulation of p53. Id-1 negatively regulated both p53 and PTEN at the transcriptional level. In promoter assay with serial deletion and chromatin immunoprecipitation assay, the binding of p53 to the PTEN promoter was reduced by Id-1, suggesting that Id-1 regulates PTEN transcription through its p53 modulation. This led to Akt phosphorylation at Ser473 and the activation of the Akt-mediated canonical Wnt signaling pathway. The glycogen synthase kinase-3β phosphorylation at Ser9, stabilization and nuclear localization of β-catenin, T-cell factor (TCF)/lymphoid enhancer factor transactivation activity and cyclin D1 expression were enhanced by Id-1. On the other hand, Akt-mediated p27Kip1 phosphorylation at Thr157 and its cytosolic localization were also increased in Id-1 overexpressing MCF7 cells. In conclusion, our results disclose Id-1 as a novel PTEN inhibitor that could activate the Akt pathway and its downstream effectors, the Wnt/TCF pathway and p27Kip1 phosphorylation and suggest that the oncogenic function of Id-1 may be partly attributed to its PTEN inhibition in human breast carcinogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H . (1990). The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix–loop–helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 61: 49–59.
Blanco-Aparicio C, Renner O, Leal JF, Carnero A . (2007). PTEN, more than the AKT pathway. Carcinogenesis 28: 1379–1386.
Chung TW, Lee YC, Ko JH, Kim CH . (2003). Hepatitis B virus X protein modulates the expression of PTEN by inhibiting the function of p53, a transcriptional activator in liver cells. Cancer Res 63: 3453–3458.
Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW . (2006). Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 6: 184–192.
Jang KS, Han HX, Paik SS, Brown PH, Kong G . (2006). Id-1 overexpression in invasive ductal carcinoma cells is significantly associated with intratumoral microvessel density in ER-negative/node-positive breast cancer. Cancer Lett 244: 203–210.
Kim H, Chung H, Kim HJ, Lee JY, Oh MY, Kim Y et al. (2007a). Id-1 regulates Bcl-2 and Bax expression through p53 and NF-kappaB in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 112: 287–296.
Kim HJ, Chung H, Yoo YG, Kim H, Lee JY, Lee MO et al. (2007b). Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 activates vascular endothelial growth factor through enhancing the stability and activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol Cancer Res 5: 321–329.
Korinek V, Barker N, Morin PJ, van Wichen D, de Weger R, Kinzler KW et al. (1997). Constitutive transcriptional activation by a beta-catenin–Tcf complex in APC−/− colon carcinoma. Science 275: 1784–1787.
Li B, Cheung PY, Wang X, Tsao SW, Ling MT, Wong YC et al. (2007). Id-1 activation of PI3K/Akt/NFkappaB signaling pathway and its significance in promoting survival of esophageal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 28: 2313–2320.
Ling MT, Wang X, Zhang X, Wong YC . (2006). The multiple roles of Id-1 in cancer progression. Differentiation 74: 481–487.
Mayo LD, Dixon JE, Durden DL, Tonks NK, Donner DB . (2002). PTEN protects p53 from Mdm2 and sensitizes cancer cells to chemotherapy. J Biol Chem 277: 5484–5489.
Nelson WJ, Nusse R . (2004). Convergence of Wnt, beta-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science 303: 1483–1487.
Shin I, Yakes FM, Rojo F, Shin NY, Bakin AV, Baselga J et al. (2002). PKB/Akt mediates cell-cycle progression by phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) at threonine 157 and modulation of its cellular localization. Nat Med 8: 1145–1152.
Stambolic V, MacPherson D, Sas D, Lin Y, Snow B, Jang Y et al. (2001). Regulation of PTEN transcription by p53. Mol Cell 8: 317–325.
Swarbrick A, Akerfeldt MC, Lee CS, Sergio CM, Caldon CE, Hunter LJ et al. (2005). Regulation of cyclin expression and cell cycle progression in breast epithelial cells by the helix–loop–helix protein Id1. Oncogene 24: 381–389.
van Noort M, Meeldijk J, van der Zee R, Destree O, Clevers H . (2002). Wnt signaling controls the phosphorylation status of beta-catenin. J Biol Chem 277: 17901–17905.
Vikhanskaya F, Lee MK, Mazzoletti M, Broggini M, Sabapathy K . (2007). Cancer-derived p53 mutants suppress p53-target gene expression—potential mechanism for gain of function of mutant p53. Nucleic Acids Res 35: 2093–2104.
Virolle T, Adamson ED, Baron V, Birle D, Mercola D, Mustelin T et al. (2001). The Egr-1 transcription factor directly activates PTEN during irradiation-induced signalling. Nat Cell Biol 3: 1124–1128.
Wang J, Ouyang W, Li J, Wei L, Ma Q, Zhang Z et al. (2005). Loss of tumor suppressor p53 decreases PTEN expression and enhances signaling pathways leading to activation of activator protein 1 and nuclear factor kappaB induced by UV radiation. Cancer Res 65: 6601–6611.
Yoo YG, Oh SH, Park ES, Cho H, Lee N, Park H et al. (2003). Hepatitis B virus X protein enhances transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 278: 39076–39084.
Yook JI, Li XY, Ota I, Hu C, Kim HS, Kim NH et al. (2006). A Wnt-Axin2-GSK3beta cascade regulates Snail1 activity in breast cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1398–1406.
Zhang X, Ling MT, Wang Q, Lau CK, Leung SC, Lee TK et al. (2007). Identification of a novel inhibitor of differentiation-1 (ID-1) binding partner, caveolin-1, and its role in epithelial–mesenchymal transition and resistance to apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 282: 33284–33294.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2007-314-E00041) funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, JY., Kang, MB., Jang, SH. et al. Id-1 activates Akt-mediated Wnt signaling and p27Kip1 phosphorylation through PTEN inhibition. Oncogene 28, 824–831 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.451
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.451
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Inducible TgfbR1 and Pten deletion in a model of tongue carcinogenesis and chemoprevention
Cancer Gene Therapy (2023)
-
Signaling pathways and targeted therapies in lung squamous cell carcinoma: mechanisms and clinical trials
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
The functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor: new modes and prospects
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2018)
-
Chronic myeloid leukaemia cells require the bone morphogenic protein pathway for cell cycle progression and self-renewal
Cell Death & Disease (2018)
-
Id-1 promotes migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells through activating NF-κB signaling pathway
Journal of Biomedical Science (2017)