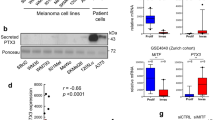
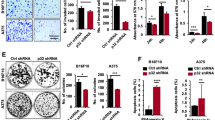
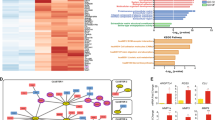
Abstract
Hallmarks of malignant melanoma are its propensity to metastasize and its resistance to treatment, giving patients with advanced disease a poor prognosis. The transition of melanoma from non-invasive radial growth phase (RGP) to invasive and metastatically competent vertical growth phase (VGP) is a major step in tumor progression, yet the mechanisms governing this transformation are unknown. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) is highly expressed by VGP melanomas, and is thought to contribute to melanoma progression by degrading type I collagen within the skin to facilitate melanoma invasion. Protease activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) is activated by MMP-1, and is also expressed by VGP melanomas. However, the effects of MMP-1 signaling through PAR-1 have not been examined in melanoma. Here, we demonstrate that an MMP-1/PAR-1 signaling axis exists in VGP melanoma, and is necessary for melanoma invasion. Introduction of MMP-1 into RGP melanoma cells induced gene expression associated with tumor progression and promoted invasion in vitro, and enhanced tumor growth and conferred metastatic capability in vivo. This study demonstrates that both the type I collagenase and PAR-1 activating functions of MMP-1 are required for melanoma progression, and suggests that MMP-1 may be a major contributor to the transformation of melanoma from non-invasive to malignant disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal A, Covic L, Sevigny LM, Kaneider NC, Lazarides K, Azabdaftari G et al. (2008). Targeting a metalloprotease-PAR1 signaling system with cell-penetrating pepducins inhibits angiogenesis, ascites, and progression of ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 7: 2746–2757.
Airola K, Karonen T, Vaalamo M, Lehti K, Lohi J, Kariniemi A-L et al. (1999). Expression of collagenase-1 and -3 and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and -3 correlates with the level of invasion in malignant melanomas. Br J Cancer 80: 733–743.
Arora P, Ricks TK, Trejo J . (2007). Protease-activated receptor signalling, endocytic sorting and dysregulation in cancer. J Cell Sci 120: 921–928.
Balch C, Soong S-J, Atkins M, Buzaid A, Thompson J . (2004). An evidence-based staging system for cutaneous melanoma. CA Cancer J Clin 54: 131–149.
Berwick M, Erdei E, Hay J . (2009). Melanoma epidemiology and public health. Dermatol Clin 27: 205–214.
Blackburn JS, Brinckerhoff CE . (2008). Matrix metalloproteinase-1 and thrombin differentially activate gene expression in endothelial cells via PAR-1 and promote angiogenesis. Am J Path 173: 1736–1746.
Blackburn JS, Rhodes CH, Coon CI, Brinckerhoff CE . (2007). RNA interference inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-1 prevents melanoma metastasis by reducing tumor collagenase activity and angiogenesis 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-1791. Cancer Res 67: 10849–10858.
Boire A, Covic L, Agarvai A, Jacques S, Sherifi S, Kuliopulos A . (2005). PAR1 is a matrix metalloproteinase-1 receptor that promotes invasion and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Cell 120: 303–313.
Breslow A . (1970). Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg 172: 902–908.
Clark W, Ainsworth A, Bernardino E, Yang C, Mihm C, Reed R . (1975). The developmental biology of primary human maligant melanomas. Semin Oncol 2: 83–103.
Curran S, Murray GI . (2000). Matrix metalloproteinases: molecular aspects of their roles in tumour invasion and metastasis. Eur J Cancer 36: 1621–1630.
Depasquale I, Thompson WD . (2008). Prognosis in human melanoma: PAR-1 expression is superior to other coagulation components and VEGF. Histopathology 52: 500–509.
Durko M, Navab R, Shibata H, Brodt P . (1998). Suppression of basement membrane type IV collagen degradation and cell invasion in human melanoma cells expressing an antisense RNA for MMP-1. Biochim Biophys Acta 1356: 271–280.
Even-Ram SC, Maoz M, Pokroy E, Reich R, Katz B-Z, Gutwein P et al. (2001). Tumor cell invasion is promoted by activation of protease activated receptor-1 in cooperation with the alpha vbeta 5 integrin. J Biol Chem 276: 10952–10962.
Fingleton B . (2006). Maxtrix metalloproteinases: roles in cancer and metastasis. Front Biosci 11: 479–491.
Gray-Schopfer V, Wellbrock C, Marais R . (2007). Melanoma biology and new targeted therapy. Nature 445: 851–857.
Haluska F, Ibrahim N . (2006). Therapeutic targets in melanoma: map kinase pathway. Curr Oncol Rep 8: 400–405.
Hofmann U, Houben R, Brocker E, Becker J . (2005). Role of matrix metalloproteinases in melanoma cell invasion. Biochimie 87: 307–314.
Hofmann U, Westphal J, van Muijen G, Ruiter D . (2000). Matrix metalloproteinases in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 115: 337–344.
Huntington JT, Shields JM, Der CJ, Wyatt CA, Benbow U, Slingluff CL et al. (2004). Overexpression of collagenase 1 (MMP-1) is mediated by the ERK pathway in invasive melanoma cells. J Bio Chem 279: 33168–33176.
Iida J, Wilhelmson KL, Price MA, Wilson CM, Pei D, Furcht LT et al. (2004). Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase promotes human melanoma invasion and growth. J Investig Dermatol 122: 167–176.
Ishii Y, Ogura T, Tatemichi M, Fujisawa H, Otsuka F, Esumi H . (2003). Induction of matrix metalloproteinase gene transcription by nitric oxide and mechanisms of MMP-1 gene induction in human melanoma cell lines. Int J Canc 103: 161–168.
Leiter U, Friedegund M, Shittek B, Garbe C . (2004). The natural course of cutaneous melanoma. J Surg Onc 86: 172–178.
Loffek S, Zigrino P, Angel P, Anwald B, Krieg T, Mauch C . (2005). High invasive melanoma cells induce matrix metalloproteinase-1 synthesis in fibroblasts by interleukin-1a and basic fibroblast growth factor-mediated mechansims. J Invest Dermatol 124: 638–645.
Ludeman MJ, Kataoka H, Srinivasan Y, Esmon NL, Esmon CT, Coughlin SR . (2005). PAR1 cleavage and signaling in response to activated protein C and thrombin. J Biol Chem 280: 13122–13128.
Macfarlane SR, Seatter MJ, Kanke T, Hunter GD, Plevin R . (2001). Proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacol Rev 53: 245–282.
Martin C, Mahon G, Klinger M, Kay R, Symons M, Der C et al. (2001). The thrombin receptor, PAR-1, causes transformation by activation of Rho-mediated signaling pathways. Oncogene 20: 1953–1963.
Massi D, Naldini A, Ardinghi C, Carraro F, Franchi A, Paglierani M et al. (2005). Expression of protease-activated receptors 1 and 2 in melanocytic nevi and malignant melanoma. Hum Pathol 36: 676–685.
Nierodzik ML, Chen K, Takeshita K, Li J-J, Huang Y-Q, Feng X-S et al. (1998). Protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) is required and rate-limiting for thrombin-enhanced experimental pulmonary metastasis. Blood 92: 3694–3700.
Nikkola J, Vihinen P, Vuoristo M-S, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P, Kahari V-M, Pyrhonen S . (2005). High serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-1 are associated with rapid progression in patients with metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 11: 5158–5166.
Ntayi C, Lorimier S, Berthier-Vergnes O, Hornebeck W, Bernard P . (2001). Cumulative influence of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and -2 in the migration of melanoma cells within three-dimensional type I collagen lattices. Exp Cell Res 270: 110–118.
Ornstein D, Zacharski L . (2001). Treatment of cancer with anticoagulants: rationale for treatment of melanoma. Int J Hematol 72: 157–161.
Petrella BL, Lohi J, Brinckerhoff CE . (2005). Identification of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase as a target of hypoxia-inducible factor-2a in von-Hippel-Lindau renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 24244: 1043–1052.
Rothhammer T, Braig S, Bosserhoff A-K . (2008). Bone morphogenetic proteins induce expression of metalloproteinases in melanoma cells and fibroblasts. Eur J Cancer 44: 2526–2534.
Salah Z, Maoz M, Pokroy E, Lotem M, Bar-Shavit R, Uziely B . (2007). Protease-activated receptor-1 (hPar1), a survival factor eliciting tumor progression. Mol Cancer Res 5: 229–240.
Suzuki K, Enghild J, Morodomi T, Salvesen G, Nagase H . (1990). Mechanisms of actvation of tissue procollagenase by matrix metalloproteinase-3 (stromelysin). Biochemistry 29: 10261–10270.
Tellez C, Bar-Eli M . (2003). Role and regulation of the thrombin receptor (PAR-1) in human melanoma. Oncogene 22: 3130–3137.
Tellez CS, Davis DW, Prieto VG, Gershenwald JE, Johnson MM, McCarty MF et al. (2006). Quantitative analysis of melanocytic tissue array reveals inverse correlation between activator protein-2[alpha] and protease-activated receptor-1 expression during melanoma progression. J Invest Dermatol 127: 387–393.
Ueda Y, Richmond A . (2006). NF-kappa B activation in melanoma. Pigment Cell Res 19: 112–124.
Villares GJ, Zigler M, Wang H, Melnikova VO, Wu H, Friedman R et al. (2008). Targeting melanoma growth and metastasis with systemic delivery of liposome-incorporated protease-activated receptor-1 small interfering RNA. Cancer Res 68: 9078–9086.
Wyatt CA, Geoghegan JC, Brinckerhoff CE . (2005). Short hairpin RNA-mediated inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in MDA-231 cells: effects on matrix destruction and tumor growth. Cancer Res 65: 11101–11108.
Acknowledgements
We thank Shaun Coughlin (University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA) for his generous gift of the AP–PAR-1 construct. This work was supported by NIH grants CA-77267 and AR-26599 (to CEB), NIH grant T32-AI07363 (to JSB) and the Prouty Pilot Grant by the Friends of the Norris Cotton Cancer Center (to CEB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blackburn, J., Liu, I., Coon, C. et al. A matrix metalloproteinase-1/protease activated receptor-1 signaling axis promotes melanoma invasion and metastasis. Oncogene 28, 4237–4248 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.272
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.272
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 as a Marker of Tonsil-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Assess Bone Marrow Cell Migration
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine (2023)
-
A KLK4 proteinase substrate capture approach to antagonize PAR1
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Olig2 regulates p53-mediated apoptosis, migration and invasion of melanoma cells
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The role of collagen in cancer: from bench to bedside
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
SOX9 is a dose-dependent metastatic fate determinant in melanoma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)