Abstract
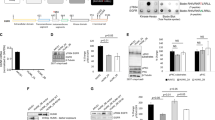
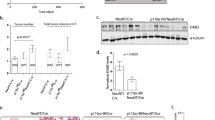
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases, particularly ErbB2, has an important role in the genesis of breast cancer. ErbB2 kinase activity promotes Ras-mediated stimulation of downstream protein kinase cascades, including the Ras/Raf-1/MAPK/ERK kinase (Mek)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (Erk) pathway, leading to tumor cell growth and migration. Signaling through the Ras–Erk pathway can be influenced by p21-activated kinase-1 (Pak1), an effector of the Rho family GTPases Rac and Cdc42. In this study, we asked if ErbB2 expression correlates with Pak1 and Erk activity in human breast cancer specimens, and if Pak1 signaling is required for ErbB2 transformation in a three-dimensional (3D) in vitro setting and in xenografts. We found a correlation between ErbB2 expression and activation of Pak in estrogen receptor-positive human breast tumor samples and observed that in 3D cultures, activation of Rac–Pak1 pathway by ErbB2 homodimers induced growth factor-independent proliferation and promoted disruption of 3D mammary acinar-like structures through activation of the Erk and Akt pathways. Further, we found that inhibition of Pak1 by small molecules compromised activation of Erk and Akt, resulting in reversion of the malignant phenotype and restoration of normal acinar architecture. Finally, ErbB2-amplified breast cancer cells expressing a specific Pak inhibitor showed delayed tumor formation and downregulation of Erk and Akt signaling in vivo. These data imply that the Rac–Pak pathway is vital to ErbB2-mediated transformation and that Pak inhibitors represent plausible drug targets in breast cancers in which ErbB2 signaling is activated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
constitutive active
- DN:
-
dominant negative
- ER:
-
estrogen receptor
- GST:
-
glutathione-S-transferase
- Pak:
-
p21-activated kinase
- PBD:
-
p21-binding domain
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
- PID:
-
Pak inhibitor domain
- rBM:
-
reconstituted basement membrane
- RTK:
-
receptor protein tyrosine kinase
- 3D:
-
three-dimensional
- TMA:
-
tissue microarray
References
Amundadottir LT, Leder P . (1998). Signal transduction pathways activated and required for mammary carcinogenesis in response to specific oncogenes. Oncogene 16: 737–746.
Arias-Romero LE, Chernoff J . (2008). A tale of two Paks. Biol Cell 100: 97–108.
Beeser A, Jaffer ZM, Hofmann C, Chernoff J . (2005). Role of group A p21-activated kinases in activation of extracellular-regulated kinase by growth factors. J Biol Chem 280: 36609–36615.
Bokoch GM . (2003). Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem 72: 743–781.
Deacon SW, Beeser A, Fukui JA, Rennefahrt UE, Myers C, Chernoff J et al. (2008). An isoform-selective, small-molecule inhibitor targets the autoregulatory mechanism of p21-activated kinase. Chem Biol 15: 322–331.
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J . (2009). Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28: 51–63.
Eblen ST, Slack JK, Weber MJ, Catling AD . (2002). Rac-PAK signaling stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation by regulating formation of MEKI-ERK complexes. Mol Cell Biol 22: 6023–6033.
Frost JA, Steen H, Shapiro P, Lewis T, Ahn N, Shaw PE et al. (1997). Cross-cascade activation of ERKs and ternary complex factors by Rho family proteins. EMBO J 16: 6426–6438.
Jaffer ZM, Chernoff J . (2002). p21-activated kinases: three more join the Pak. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 34: 713–717.
Maksimoska J, Feng L, Harms K, Yi C, Kissil J, Marmorstein R et al. (2008). Targeting Large Kinase Active Site with Rigid, Bulky Octahedral Ruthenium Complexes. J Am Chem Soc 130: 15764–15765.
Gao Y, Dickerson JB, Guo F, Zheng J, Zheng Y. (2004). Rational design and characterization of a Rac GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 7618–7623.
Hardy S, Kitamura M, Harris-Stansil T, Dai Y, Phipps ML . (1997). Construction of adenovirus vectors through Cre-lox recombination. J Virol 71: 1842–1849.
Higuchi M, Onishi K, Kikuchii C, Gotoh Y . (2008). Scaffolding function of PAK in the PDK1-Akt pathway. Nat Cell Biol 10: 1356–1364.
Hofmann C, Shepelev M, Chernoff J . (2004). The genetics of Pak. J Cell Sci 117: 4343–4354.
Holm C, Rayala S, Jirstrom K, Stal O, Kumar R, Landberg G. (2006). Association between Pak1 expression and subcellular localization and tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 98: 671–680.
Hynes NE, MacDonald G . (2009). ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol 21: 177–184.
Karunagaran D, Tzahar E, Beerli RR, Chen X, Graus-Porta D, Ratzkin BJ et al. (1996). ErbB-2 is a common auxiliary subunit of NDF and EGF receptors: implications for breast cancer. EMBO J 15: 254–264.
Kinsella TM, Nolan GP . (1996). Episomal vectors rapidly and stably produce high-titer recombinant retrovirus. Hum Gene Ther 7: 1405–1413.
Li Q, Mullins SR, Sloane BF, Mattingly RR . (2008). p21-Activated kinase 1 coordinates aberrant cell survival and pericellular proteolysis in a three-dimensional culture model for premalignant progression of human breast cancer. Neoplasia 10: 314–329.
Lightcap CM, Kari G, Arias-Romero LE, Chernoff J, Rodeck U, Williams JC . (2009). Interaction with LC8 is required for Pak1 nuclear import and is indispensable for zebrafish development. PLoS One 4: e6025.
Maksimoska J, Feng L, Harms K, Yi C, Kissil J, Marmorstein R et al. (2008). Targeting large kinase active site with rigid, bulky octahedral ruthenium complexes. J Am Chem Soc 130: 15764–15765.
Mao K, Kobayashi S, Jaffer ZM, Huang Y, Volden P, Chernoff J et al. (2008). Regulation of Akt/PKB activity by P21-activated kinase in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44: 429–434.
Menard RE, Mattingly RR . (2003). Cell surface receptors activate p21-activated kinase 1 via multiple Ras and PI3-kinase-dependent pathways. Cell Signal 15: 1099–1109.
Muthuswamy SK, Li D, Lelievre S, Bissell MJ, Brugge JS . (2001). ErbB2, but not ErbB1, reinitiates proliferation and induces luminal repopulation in epithelial acini. Nat Cell Biol 3: 785–792.
Porchia LM, Guerra M, Wang YC, Zhang Y, Espinosa AV, Shinohara M et al. (2007). OSU03012, a celecoxib derivative, directly targets p21 activated kinase. Mol Pharmacol 72: 1124–1131.
Rayala SK, Molli PR, Kumar R . (2006). Nuclear p21-activated kinase 1 in breast cancer packs off tamoxifen sensitivity. Cancer Res 66: 5985–5988.
Schnelzer A, Prechtel D, Knaus U, Dehne K, Gerhard M, Graeff H et al. (2000). Rac1 in human breast cancer: overexpression, mutation analysis, and characterization of a new isoform, Rac1b. Oncogene 19: 3013–3020.
Shalaby MR, Shepard HM, Presta L, Rodrigues ML, Beverley PC, Feldmann M et al. (1992). Development of humanized bispecific antibodies reactive with cytotoxic lymphocytes and tumor cells overexpressing the HER2 protooncogene. J Exp Med 175: 217–225.
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H et al. (2004). Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96: 926–935.
Soule HD, Maloney TM, Wolman SR, Peterson WDJ, Brenz R, McGrath CM et al. (1990). Isolation and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res 50: 6075–6086.
Srinivasan S, Wang F, Glavas S, Ott A, Hofmann F, Aktories K et al. (2003). Rac and Cdc42 play distinct roles in regulating PI(3,4,5)P3 and polarity during neutrophil chemotaxis. J Cell Biol 160: 3375–3385.
Treeck O, Diedrich K, Ortmann O . (2003). The activation of an extracellular signal-regulated kinase by oestradiol interferes with the effects of trastuzumab on HER2 signalling in endometrial adenocarcinoma cell lines. Eur J Cancer 39: 1302–1309.
Viaud J, Peterson JR . (2009). An allosteric kinase inhibitor binds the p21-activated kinase autoregulatory domain covalently. Mol Cancer Ther 8: 2559–2565.
Wang RA, Zhang H, Balasenthil S, Medina D, Kumar R . (2005). PAK1 hyperactivation is sufficient for mammary gland tumor formation. Oncogene 25: 2931–2936.
Wang SE, Shin I, Wu FY, Friedman DB, Arteaga CL . (2006). HER2/Neu (ErbB2) signaling to Rac1-Pak1 is temporally and spatially modulated by transforming growth factor beta. Cancer Res 66: 9591–9600.
Weigelt B, Lo AT, Park CC, Gray JW, Bissell MJ . (2009). HER2 signaling pathway activation and response of breast cancer cells to HER2-targeting agents is dependent strongly on the 3D microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res Treat 122: 35–43.
Zhan L, Xiang B, Muthuswamy SK . (2006). Controlled activation of ErbB1/ErbB2 heterodimers promote invasion of three-dimensional organized epithelia in an ErbB1-dependent manner: implications for progression of ErbB2-overexpressing tumors. Cancer Res 66: 5201–5208.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dan Kalman (Emory University School of Medicine) and Ariad Pharmaceuticals, for their gifts of pAd-lox vectors and AP1510, respectively, and Fang Zhu, of the FCCC Biostatistics Facility, for statistical analysis of TMA and xengraft data. This work was supported by grants from the NIH to JC (R01 CA58836) and SM (R01 CA098830) and to the Fox Chase Cancer Center (P30 CA006927), as well as by an appropriation from the state of Pennsylvania.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arias-Romero, L., Villamar-Cruz, O., Pacheco, A. et al. A Rac–Pak signaling pathway is essential for ErbB2-mediated transformation of human breast epithelial cancer cells. Oncogene 29, 5839–5849 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.318
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.318
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nucleocytoplasmic transport of active HER2 causes fractional escape from the DCIS-like state
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic implications and functional exploration of PAK gene family in human cancer
Cancer Cell International (2022)
-
p21-activated kinases as viable therapeutic targets for the treatment of high-risk Ewing sarcoma
Oncogene (2021)
-
Molecular and Transcriptional Signatures for ErbB2-Induced Invasion
Current Pharmacology Reports (2019)
-
Inhibitors of the p21 Activated Kinases
Current Pharmacology Reports (2018)