Abstract
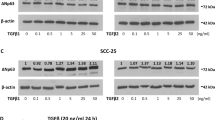
In the present study we analyzed the regulation of the two isoforms of the RhoA-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor Net1 by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in keratinocytes. We report that short-term TGF-β treatment selectively induced Net1 isoform2 (Net1A) but not Net1 isoform1. This led to upregulation of cytoplasmic Net1A protein levels that were necessary for TGF-β-mediated RhoA activation. Smad signaling and the MAPK/ERK kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway were involved in Net1A upregulation by TGF-β. Interestingly, long-term TGF-β treatment resulted in Net1 mRNA downregulation and Net1A protein degradation by the proteasome. Furthermore, we identified the microRNA miR-24 as a novel post-transcriptional regulator of Net1A expression. Silencing of Net1A resulted in disruption of E-cadherin- and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1)-mediated junctions, as well as expression of the transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin, Slug and the mesenchymal markers N-cadherin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) and fibronectin, indicating that late TGF-β-induced downregulation of Net1A is involved in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Finally, miR-24 was found to be implicated in the regulation of the EMT program in response to TGF-β and was shown to be directly involved in the TGF-β-induced breast cancer cell invasiveness through Net1A regulation. Our results emphasize the importance of Net1 isoform2 in the short- and long-term TGF-β-mediated regulation of EMT.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baum B, Georgiou M . (2011). Dynamics of adherens junctions in epithelial establishment, maintenance, and remodeling. J Cell Biol 192: 907–917.
Carr HS, Cai C, Keinanen K, Frost JA . (2009). Interaction of the RhoA exchange factor Net1 with discs large homolog 1 protects it from proteasome-mediated degradation and potentiates Net1 activity. J Biol Chem 284: 24269–24280.
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ . (2007). Differentiation plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and disease. Nat Cell Biol 9: 1000–1004.
Fujii M, Takeda K, Imamura T, Aoki H, Sampath TK, Enomoto S et al. (1999). Roles of bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors and Smad proteins in osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation. Mol Biol Cell 10: 3801–3813.
Garcia-Mata R, Burridge K . (2007). Catching a GEF by its tail. Trends Cell Biol 17: 36–43.
Garcia-Mata R, Dubash AD, Sharek L, Carr HS, Frost JA, Burridge K . (2007). The nuclear RhoA exchange factor Net1 interacts with proteins of the Dlg family, affects their localization, and influences their tumor suppressor activity. Mol Cell Biol 27: 8683–8697.
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G et al. (2008). The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 10: 593–601.
Ikushima H, Miyazono K . (2010). TGFbeta signalling: a complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer 10: 415–424.
Inoue Y, Imamura T . (2008). Regulation of TGF-beta family signaling by E3 ubiquitin ligases. Cancer Sci 99: 2107–2112.
Izzi L, Attisano L . (2004). Regulation of the TGFbeta signalling pathway by ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Oncogene 23: 2071–2078.
Javelaud D, Mauviel A . (2005). Crosstalk mechanisms between the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways and Smad signaling downstream of TGF-beta: implications for carcinogenesis. Oncogene 24: 5742–5750.
Kardassis D, Murphy C, Fotsis T, Moustakas A, Stournaras C . (2009). Control of transforming growth factor beta signal transduction by small GTPases. FEBS J 276: 2947–2965.
Kong W, Yang H, He L, Zhao JJ, Coppola D, Dalton WS et al. (2008). MicroRNA-155 is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA. Mol Cell Biol 28: 6773–6784.
Kurisaki K, Kurisaki A, Valcourt U, Terentiev AA, Pardali K, Ten Dijke P et al. (2003). Nuclear factor YY1 inhibits transforming growth factor beta- and bone morphogenetic protein-induced cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4494–4510.
Lal A, Navarro F, Maher CA, Maliszewski LE, Yan N, O'Day E et al. (2009). miR-24 Inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to “seedless” 3′UTR microRNA recognition elements. Mol Cell 35: 610–625.
Lee J, Moon HJ, Lee JM, Joo CK . (2010). Smad3 regulates Rho signaling via NET1 in the TGF-{beta}-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 285: 26618–26627.
Lin SC, Liu CJ, Lin JA, Chiang WF, Hung PS, Chang KW . (2011). miR-24 up-regulation in oral carcinoma: positive association from clinical and in vitro analysis. Oral Oncol 46: 204–208.
Massague J . (2008). TGFbeta in cancer. Cell 134: 215–230.
Moustakas A, Heldin CH . (2005). Non-Smad TGF-beta signals. J Cell Sci 118: 3573–3584.
Moustakas A, Heldin CH . (2008). Dynamic control of TGF-beta signaling and its links to the cytoskeleton. FEBS Lett 582: 2051–2065.
Moustakas A, Heldin CH . (2009). The regulation of TGFbeta signal transduction. Development 136: 3699–3714.
Nakaya Y, Sukowati EW, Wu Y, Sheng G . (2008). RhoA and microtubule dynamics control cell-basement membrane interaction in EMT during gastrulation. Nat Cell Biol 10: 765–775.
Pardali K, Moustakas A . (2007). Actions of TGF-beta as tumor suppressor and pro-metastatic factor in human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1775: 21–62.
Piek E, Moustakas A, Kurisaki A, Heldin CH, ten Dijke P . (1999). TGF-(beta) type I receptor/ALK-5 and Smad proteins mediate epithelial to mesenchymal transdifferentiation in NMuMG breast epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 112 (Pt 24): 4557–4568.
Qin H, Carr HS, Wu X, Muallem D, Tran NH, Frost JA . (2005). Characterization of the biochemical and transforming properties of the neuroepithelial transforming protein 1. J Biol Chem 280: 7603–7613.
Qin W, Shi Y, Zhao B, Yao C, Jin L, Ma J et al. (2010). miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting the open reading frame (ORF) region of FAF1 in cancer cells. PLoS One 5: e9429.
Rajasekaran SA, Palmer LG, Moon SY, Peralta Soler A, Apodaca GL, Harper JF et al. (2001). Na,K-ATPase activity is required for formation of tight junctions, desmosomes, and induction of polarity in epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 12: 3717–3732.
Rossman KL, Der CJ, Sondek J . (2005). GEF means go: turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6: 167–180.
Sahai E, Marshall CJ . (2002). ROCK and Dia have opposing effects on adherens junctions downstream of Rho. Nat Cell Biol 4: 408–415.
Schmidt A, Hall A . (2002). The Rho exchange factor Net1 is regulated by nuclear sequestration. J Biol Chem 277: 14581–14588.
Shen X, Li J, Hu PP, Waddell D, Zhang J, Wang XF . (2001). The activity of guanine exchange factor NET1 is essential for transforming growth factor-beta-mediated stress fiber formation. J Biol Chem 276: 15362–15368.
Shi Y, Massague J . (2003). Mechanisms of TGF-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. Cell 113: 685–700.
Shirakihara T, Horiguchi K, Miyazawa K, Ehata S, Shibata T, Morita I et al. (2011). TGF-beta regulates isoform switching of FGF receptors and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J 30: 783–795.
Sun F, Wang J, Pan Q, Yu Y, Zhang Y, Wan Y et al. (2009). Characterization of function and regulation of miR-24-1 and miR-31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 380: 660–665.
Sun Q, Zhang Y, Yang G, Chen X, Cao G, Wang J et al. (2008). Transforming growth factor-beta-regulated miR-24 promotes skeletal muscle differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 36: 2690–2699.
Vaezi A, Bauer C, Vasioukhin V, Fuchs E . (2002). Actin cable dynamics and Rho/Rock orchestrate a polarized cytoskeletal architecture in the early steps of assembling a stratified epithelium. Dev Cell 3: 367–381.
Vardouli L, Moustakas A, Stournaras C . (2005). LIM-kinase 2 and cofilin phosphorylation mediate actin cytoskeleton reorganization induced by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem 280: 11448–11457.
Vardouli L, Vasilaki E, Papadimitriou E, Kardassis D, Stournaras C . (2008). A novel mechanism of TGFbeta-induced actin reorganization mediated by Smad proteins and Rho GTPases. FEBS J 275: 4074–4087.
Vasilaki E, Papadimitriou E, Tajadura V, Ridley AJ, Stournaras C, Kardassis D . (2010). Transcriptional regulation of the small GTPase RhoB gene by TGF{beta}-induced signaling pathways. FASEB J 24: 891–905.
Wang HR, Zhang Y, Ozdamar B, Ogunjimi AA, Alexandrova E, Thomsen GH et al. (2003). Regulation of cell polarity and protrusion formation by targeting RhoA for degradation. Science 302: 1775–1779.
Wang Q, Huang Z, Xue H, Jin C, Ju XL, Han JD et al. (2008). MicroRNA miR-24 inhibits erythropoiesis by targeting activin type I receptor ALK4. Blood 111: 588–595.
Xie L, Wang T, Yu S, Chen X, Wang L, Qian X et al. (2011). Cell-free miR-24 and miR-30d, potential diagnostic biomarkers in malignant effusions. Clin Biochem 44: 216–220.
Zaidi SK, Dowdy CR, van Wijnen AJ, Lian JB, Raza A, Stein JL et al. (2009). Altered Runx1 subnuclear targeting enhances myeloid cell proliferation and blocks differentiation by activating a miR-24/MKP-7/MAPK network. Cancer Res 69: 8249–8255.
Zhang YE . (2009). Non-Smad pathways in TGF-beta signaling. Cell Res 19: 128–139.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the PENED program of the Greek Secretariat for Research and Technology (Grant no. PENED03-688). We thank Dr EA Papakonstanti for valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papadimitriou, E., Vasilaki, E., Vorvis, C. et al. Differential regulation of the two RhoA-specific GEF isoforms Net1/Net1A by TGF-β and miR-24: role in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 31, 2862–2875 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.457
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.457
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition process during embryo implantation
Cell and Tissue Research (2022)
-
Connecting sex differences, estrogen signaling, and microRNAs in cardiac fibrosis
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Vav proteins maintain epithelial traits in breast cancer cells using miR-200c-dependent and independent mechanisms
Oncogene (2019)
-
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of the genes encoding the small GTPases RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC: implications for the pathogenesis of human diseases
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2018)
-
Crosstalk between TGF-β signaling and miRNAs in breast cancer metastasis
Tumor Biology (2016)