Abstract
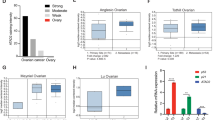
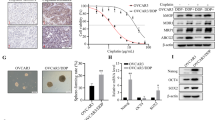
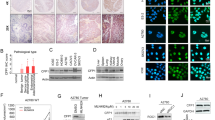
Ovarian cancer survival rates have stagnated in the last 20 years despite the development of novel chemotherapeutic agents. Modulators of gene expression, such as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, are among the new agents being used in clinical trials. Predictors of sensitivity to chemotherapy have remained elusive. In this study, we show that the expression of the transcriptional corepressor C-terminal binding protein-2 (CtBP2) is elevated in human ovarian tumors. Downregulation of CtBP2 expression in ovarian cancer cell lines using short-hairpin RNA strategy suppressed the growth rate and migration of the resultant cancer cells. The knockdown cell lines also showed upregulation of HDAC activity and increased sensitivity to selected HDAC inhibitors. Conversely, forced expression of wild-type CtBP2 in the knockdown cell lines reversed HDAC activity and partially rescued cellular sensitivity to the HDAC inhibitors. We propose that CtBP2 is an ovarian cancer oncogene that regulates gene expression program by modulating HDAC activity. CtBP2 expression may be a surrogate indicator of cellular sensitivity to HDAC inhibitors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altekruse S, Kosary C, Krapcho M, Neyman N, Aminou R, Waldron W et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2007. National Cancer Institue, Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010.
Tang L, Yang J, Ng SK, Rodriguez N, Choi PW, Vitonis A et al. Autoantibody profiling to identify biomarkers of key pathogenic pathways in mucinous ovarian cancer. Eur J Cancer 2010; 46: 170–179.
Katsanis N, Fisher EM . A novel C-terminal binding protein (CTBP2) is closely related to CTBP1, an adenovirus E1A-binding protein, and maps to human chromosome 21q21.3. Genomics 1998; 47: 294–299.
Boyd JM, Subramanian T, Schaeper U, La Regina M, Bayley S, Chinnadurai G . A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. EMBO J 1993; 12: 469–478.
Turner J, Crossley M . Cloning and characterization of mCtBP2, a co-repressor that associates with basic Kruppel-like factor and other mammalian transcriptional regulators. EMBO J 1998; 17: 5129–5140.
Chinnadurai G . Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2007; 39: 1593–1607.
Chinnadurai G . The transcriptional corepressor CtBP: a foe of multiple tumor suppressors. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 731–734.
Grooteclaes M, Deveraux Q, Hildebrand J, Zhang Q, Goodman RH, Frisch SM . C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003; 100: 4568–4573.
Grooteclaes ML, Frisch SM . Evidence for a function of CtBP in epithelial gene regulation and anoikis. Oncogene 2000; 19: 3823–3828.
Chinnadurai G . CtBP, an unconventional transcriptional corepressor in development and oncogenesis. Mol Cell 2002; 9: 213–224.
Sierra J, Yoshida T, Joazeiro CA, Jones KA . The APC tumor suppressor counteracts beta-catenin activation and H3K4 methylation at Wnt target genes. Genes Dev 2006; 20: 586–600.
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, Affar el B, Whetstine JR, Lan F et al. Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 2003; 422: 735–738.
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN, Kemp S, van Kuilenburg AB . Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J 2003; 370: 737–749.
Minucci S, Pelicci PG . Histone deacetylase inhibitors and the promise of epigenetic (and more) treatments for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 38–51.
Yoo CB, Jones PA . Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2006; 5: 37–50.
Glaser KB . HDAC inhibitors: clinical update and mechanism-based potential. Biochem Pharmacol 2007; 74: 659–671.
Lin X, Sun B, Liang M, Liang YY, Gast A, Hildebrand J et al. Opposed regulation of corepressor CtBP by SUMOylation and PDZ binding. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 1389–1396.
Zhao LJ, Subramanian T, Zhou Y, Chinnadurai G . Acetylation by p300 regulates nuclear localization and function of the transcriptional corepressor CtBP2. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 4183–4189.
Fang M, Li J, Blauwkamp T, Bhambhani C, Campbell N, Cadigan KM . C-terminal-binding protein directly activates and represses Wnt transcriptional targets in Drosophila. EMBO J 2006; 25: 2735–2745.
Hildebrand JD, Soriano P . Overlapping and unique roles for C-terminal binding protein 1 (CtBP1) and CtBP2 during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 5296–5307.
Hamada F, Bienz M . The APC tumor suppressor binds to C-terminal binding protein to divert nuclear beta-catenin from TCF. Dev Cell 2004; 7: 677–685.
Engers R, Gabbert HE . Mechanisms of tumor metastasis: cell biological aspects and clinical implications. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 2000; 126: 682–692.
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A . WNT and beta-catenin signalling: diseases and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 691–701.
Cuilliere-Dartigues P, El-Bchiri J, Krimi A, Buhard O, Fontanges P, Flejou JF et al. TCF-4 isoforms absent in TCF-4 mutated MSI-H colorectal cancer cells colocalize with nuclear CtBP and repress TCF-4-mediated transcription. Oncogene 2006; 25: 4441–4448.
Zhang CL, McKinsey TA, Lu JR, Olson EN . Association of COOH-terminal-binding protein (CtBP) and MEF2-interacting transcription repressor (MITR) contributes to transcriptional repression of the MEF2 transcription factor. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 35–39.
Khan N, Jeffers M, Kumar S, Hackett C, Boldog F, Khramtsov N et al. Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem J 2008; 409: 581–589.
Fournel M, Bonfils C, Hou Y, Yan PT, Trachy-Bourget MC, Kalita A et al. MGCD0103, a novel isotype-selective histone deacetylase inhibitor, has broad spectrum antitumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 759–768.
Huang KC, Park DC, Ng SK, Lee JY, Ni X, Ng WC et al. Selenium binding protein 1 in ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 2006; 118: 2433–2440.
Bradner JE, West N, Grachan ML, Greenberg EF, Haggarty SJ, Warnow T et al. Chemical phylogenetics of histone deacetylases. Nat Chem Biol 2010; 6: 238–243.
Acknowledgements
We thank critical reading of the manuscript by Professor YF Wong. We acknowledge the provision of belinostat, vorinostat, MGCD0103 from Selleck Inc. LB was supported by Ruth N White Gynecologic Oncology Research Fellowship. The Laboratory of Gynecologic Oncology was partly supported by Robert and Deborah First Fund, the Sperling Family Fund Foundation, Women’s Cancer Program and Gillette Center for Women’s Cancer from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Ovarian Cancer Research Foundation, Adler Foundation, Inc., and Friends of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barroilhet, L., Yang, J., Hasselblatt, K. et al. C-terminal binding protein-2 regulates response of epithelial ovarian cancer cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oncogene 32, 3896–3903 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.380
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.380
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Coordinate transcriptional regulation of ErbB2/3 by C-terminal binding protein 2 signals sensitivity to ErbB2 inhibition in pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Oncogenesis (2023)
-
Aldolase B attenuates clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression by inhibiting CtBP2
Frontiers of Medicine (2023)
-
CtBP1/2 differentially regulate genomic stability and DNA repair pathway in high-grade serous ovarian cancer cell
Oncogenesis (2021)
-
The transrepression and transactivation roles of CtBPs in the pathogenesis of different diseases
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2021)
-
Establishment of multifactor predictive models for the occurrence and progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
BMC Cancer (2020)