Abstract
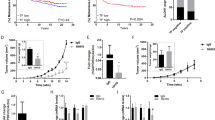
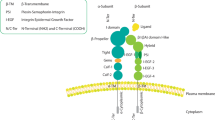
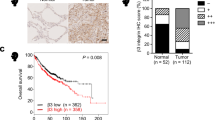
The integrin α9β1 binds a number of extracellular matrix components to mediate cell adhesion, migration and tissue invasion. Although expressed in a variety of normal human cells including endothelium, it is also expressed in cancer cells. We have previously shown that α9β1 binds VEGF-A to facilitate angiogenesis, an important component of the tumor microenvironment. As α9β1 induces accelerated cancer cell migration, we wished to determine what role it played in cancer growth and metastasis. In this study, we show that α9β1 expression induces molecular changes consistent with epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In addition, we found that α9β1 forms a tri-partite protein complex with β-catenin and E-cadherin, which dissociates following integrin activation and subsequent src and β-catenin phosphorylation. These findings were consistent in cells in which: α9β1 was exogenously over-expressed, or when its expression was suppressed in cancer cells endogenously expressing α9β1. These in vitro results are biologically significant as α9β1-expressing cancer cells induce greater tumor growth and metastases in mice as compared to the cells without α9β1 expression or when integrin expression is suppressed. Furthermore, integrin α9β1 is expressed in primary human small cell lung cancer and patients having a high expression of α9β1 demonstrated significantly worse long-term survival compared with patients with low α9β1 expression. These findings highlight a novel mechanism of integrin α9β1 function in human cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Radisky DC . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Sci 2005; 118: 4325–4326.
Voulgari A, Pintzas A . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: mechanisms, markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006; 1796: 75–90.
Kim KK, Wei Y, Szekeres C, Kugler MC, Wolters PJ, Hill ML et al. Epithelial cell alpha3beta1 integrin links beta-catenin and Smad signaling to promote myofibroblast formation and pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 213–224.
Guarino M, Rubino B, Ballabio G . The role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology. Pathology 2007; 39: 305–318.
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S, Hu GF . Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in metastasis. Cancer Res 2009; 69: 7135–7139.
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D, Monfar M, Baulida J et al. The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol 2000; 2: 84–89.
Jung H, Lee KP, Park SJ, Park JH, Jang YS, Choi SY et al. TMPRSS4 promotes invasion, migration and metastasis of human tumor cells by facilitating an epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2008; 27: 2635–2647.
Hynes RO . Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002; 110: 673–687.
Takada Y, Ye X, Simon S . The integrins. Genome Biol 2007; 8: 215.
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA . Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2010; 10: 9–22.
Singh P, Chen C, Pal-Ghosh S, Stepp MA, Sheppard D, Van De Water L . Loss of integrin alpha9beta1 results in defects in proliferation, causing poor re-epithelialization during cutaneous wound healing. J Invest Dermatol 2009; 129: 217–228.
Rathinam R, Alahari SK . Important role of integrins in the cancer biology. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2010; 29: 223–237.
Bates RC, Bellovin DI, Brown C, Maynard E, Wu B, Kawakatsu H et al. Transcriptional activation of integrin beta6 during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition defines a novel prognostic indicator of aggressive colon carcinoma. J Clin Invest 2005; 115: 339–347.
Kim Y, Kugler MC, Wei Y, Kim KK, Li X, Brumwell AN et al. Integrin alpha3beta1-dependent beta-catenin phosphorylation links epithelial Smad signaling to cell contacts. J Cell Biol 2009; 184: 309–322.
Maschler S, Wirl G, Spring H, Bredow DV, Sordat I, Beug H et al. Tumor cell invasiveness correlates with changes in integrin expression and localization. Oncogene 2005; 24: 2032–2041.
Chattopadhyay N, Wang Z, Ashman LK, Brady-Kalnay SM, Kreidberg JA . alpha3beta1 integrin-CD151, a component of the cadherin-catenin complex, regulates PTPmu expression and cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 2003; 163: 1351–1362.
Timoshenko AV, Rastogi S, Lala PK . Migration-promoting role of VEGF-C and VEGF-C binding receptors in human breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 2007; 97: 1090–1098.
Brown MC, Staniszewska I, Lazarovici P, Tuszynski GP, Del Valle L, Marcinkiewicz C . Regulatory effect of nerve growth factor in alpha9beta1 integrin-dependent progression of glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2008; 10: 968–980.
Lydolph MC, Morgan-Fisher M, Hoye AM, Couchman JR, Wewer UM, Yoneda A . Alpha9beta1 integrin in melanoma cells can signal different adhesion states for migration and anchorage. Exp Cell Res 2009; 315: 3312–3324.
Huang XZ, Wu JF, Ferrando R, Lee JH, Wang YL, Farese Jr RV et al. Fatal bilateral chylothorax in mice lacking the integrin alpha9beta1. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 5208–5215.
Kajiya K, Hirakawa S, Ma B, Drinnenberg I, Detmar M . Hepatocyte growth factor promotes lymphatic vessel formation and function. EMBO J 2005; 24: 2885–2895.
Vlahakis NE, Young BA, Atakilit A, Sheppard D . The lymphangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF-C and -D are ligands for the integrin alpha9beta1. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 4544–4552.
Bazigou E, Xie S, Chen C, Weston A, Miura N, Sorokin L et al. Integrin-alpha9 is required for fibronectin matrix assembly during lymphatic valve morphogenesis. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 175–186.
Vlahakis NE, Young BA, Atakilit A, Hawkridge AE, Issaka RB, Boudreau N et al. Integrin alpha9beta1 directly binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-A and contributes to VEGF-A-induced angiogenesis. J Biol Chem 2007; 282: 15187–15196.
Oommen S, Gupta SK, Vlahakis NE . Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) induces endothelial and cancer cell migration through direct binding to integrin {alpha}9{beta}1: identification of a specific {alpha}9{beta}1 binding site. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 1083–1092.
Wheeler DL, Iida M, Dunn EF . The role of Src in solid tumors. Oncologist 2009; 14: 667–678.
Aleshin A, Finn RS . SRC: a century of science brought to the clinic. Neoplasia 2010; 12: 599–607.
Gupta SK, Vlahakis NE . Integrin alpha9beta1 mediates enhanced cell migration through nitric oxide synthase activity regulated by Src tyrosine kinase. J Cell Sci 2009; 122: 2043–2054.
Nam JS, Ino Y, Sakamoto M, Hirohashi S . Src family kinase inhibitor PP2 restores the E-cadherin/catenin cell adhesion system in human cancer cells and reduces cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 2430–2436.
Logan CY, Nusse R . The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2004; 20: 781–810.
Moon RT, Kohn AD, De Ferrari GV, Kaykas A . WNT and beta-catenin signaling: disease and therapies. Nat Rev Genet 2004; 5: 691–701.
Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A, Aaronson SA . Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nature Cell Biology 2001; 3: 683–686.
Borok Z . Role for alpha3 integrin in EMT and pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest 2009; 119: 7–10.
Alphonso A, Alahari SK . Stromal cells and integrins: conforming to the needs of the tumor microenvironment. Neoplasia 2009; 11: 1264–1271.
Kim S, Kang HY, Nam EH, Choi MS, Zhao XF, Hong CS et al. TMPRSS4 induces invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition through upregulation of integrin alpha5 and its signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis 2010; 31: 597–606.
Song L, Morris M, Bagui T, Lee FY, Jove R, Haura EB . Dasatinib (BMS-354825) selectively induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells dependent on epidermal growth factor receptor signaling for survival. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 5542–5548.
Allen MD, Vaziri R, Green M, Chelala C, Brentnall AR, Dreger S et al. Clinical and functional significance of alpha9beta1 integrin expression in breast cancer: a novel cell-surface marker of the basal phenotype that promotes tumour cell invasion. J Pathol 2011; 223: 646–658.
Hibi K, Yamakawa K, Ueda R, Horio Y, Murata Y, Tamari M et al. Aberrant upregulation of a novel integrin alpha subunit gene at 3p21.3 in small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 1994; 9: 611–619.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Dean Sheppard (UCSF, CA), Debabrata Mukhopadhyay and Edward Leof (Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA) for helpful discussions; Mark A. Schroeder for help with animal studies; Aaron Bungam for the lung tissue registry. This work was supported by NHLBI Research Grant K08HL076455-05 and Mayo Foundation Research Grants to NEV.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Oommen, S., Aubry, MC. et al. Integrin α9β1 promotes malignant tumor growth and metastasis by potentiating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 32, 141–150 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.41
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.41
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Integrin alpha9 emerges as a key therapeutic target to reduce metastasis in rhabdomyosarcoma and neuroblastoma
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Integrins regulate stemness in solid tumor: an emerging therapeutic target
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
A prognostic index based on an eleven gene signature to predict systemic recurrences in colorectal cancer
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2019)
-
Twist1 promotes breast cancer invasion and metastasis by silencing Foxa1 expression
Oncogene (2017)
-
Calreticulin promotes EGF-induced EMT in pancreatic cancer cells via Integrin/EGFR-ERK/MAPK signaling pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2017)