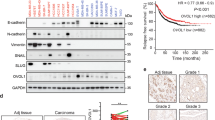
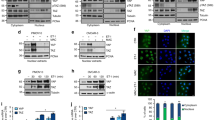
Abstract
Despite the fundamental pathophysiological importance of β-catenin in tumor progression, the mechanism underlying its final transcriptional output has been partially elucidated. Here, we report that β-arrestin-1 (β-arr1) is an epigenetic regulator of endothelin (ET)-1-induced β-catenin signaling in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). In response to ET A receptor (ETAR) activation by ET-1, β-arr1 increases its nuclear translocation and direct binding to β-catenin. This in turn enhanced β-catenin nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activity, which was prevented by expressing a mutant β-arr1 incapable of nuclear distribution. β-arr1–β-catenin interaction controls β-catenin target gene expressions, such as ET-1, Axin 2, Matrix metalloproteinase 2, and Cyclin D1, by promoting histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) dissociation and the recruitment of p300 acetyltransferase on these promoter genes, resulting in enhanced H3 and H4 histone acetylation, and gene transcription, required for cell migration, invasion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. These effects are abrogated by β-arr1 silencing or by mutant β-arr1, as well as by β-catenin or p300 silencing, confirming that nuclear β-arr1 forms a functional complex capable of regulating epigenetic changes in β-catenin-driven invasive behavior. In a murine orthotopic model of metastatic human EOC, silencing of β-arr1 or mutant β-arr1 expression, as well as ETAR blockade, inhibits metastasis. In human EOC tissues, β-arr1–β-catenin nuclear complexes are selectively enriched at β-catenin target gene promoters, correlating with tumor grade, confirming a direct in vivo β-arr1–β-catenin association at specific set of genes involved in EOC progression. Collectively, our study provides insights into how a β-arr1-mediated epigenetic mechanism controls β-catenin activity, unraveling new components required for its nuclear function in promoting metastasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson J, Bagnato A, Battistini B, Nisen P . The endothelin axis: emerging role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 110–116.
Rosanò L, Bagnato A . Convergent pathways link the endothelin A receptor to the beta-catenin: the beta-arrestin connection. Cell Cycle 2009; 8: 1462–1463.
Shenoy SK, Lefkowitz RJ . Seven-transmembrane receptor signalling through beta-arrestin. Sci STKE 2005; 308: cm10.
Luttrell LM, Roudabush FL, Choy EW, Miller WE, Field ME, Pierce KL et al. Activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by β-arrestin scaffolds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 2449–2454.
Rosanò L, Cianfrocca R, Masi S, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Biroccio A et al. Beta-arrestin links endothelin A receptor to beta-catenin signalling to induce ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 2806–2811.
Li TT, Alemayehu M, Aziziyeh AI, Pape C, Pampillo M, Postovit LM et al. Beta-arrestin/Ral signalling regulates lysophosphatidic acid-mediated migration and invasion of human breast tumor cells. Mol Cancer Res 2009; 7: 1064–1077.
Buchanan FG, Gorden DL, Matta P, Shi Q, Matrisian LM, DuBois RN . Role of beta-arrestin 1 in the metastatic progression of colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 1492–1497.
Tilley DG, Kim IM, Patel PA, Violin JD, Rockman HA . Beta-arrestin mediates beta 1-adrenergic receptor-epidermal growth factor receptor interaction and downstream signalling. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 20375–20386.
Chun KS, Lao HC, Trempus CS, Okada M, Langenbach R . The prostaglandin receptor EP2 activates multiple signalling pathways and beta-arrestin1 complex formation during mouse skin papilloma development. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: 1620–1627.
Dasgupta P, Rastogi S, Pillai S, Ordonez-Ercan D, Morris M, Haura E et al. Nicotine induces cell proliferation by β-arrestin–mediated activation of Src and Rb–Raf-1 pathways. J Clin Invest 2006; 116: 2208–2217.
Bonnans C, Flacelière M, Grillet F, Dantec C, Desvignes JP, Pannequin J et al. Essential requirement for β-arrestin2 in mouse intestinal tumors with elevated Wnt signalling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 3047–3052.
Ahn S, Kim J, Hara MR, Ren XR, Lefkowitz RJ . β-Arrestin-2 Mediates Anti-apoptotic signalling through regulation of BAD Phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 2009; 284: 8855–8865.
Xiao K, McClatchy DB, Shukla AK, Zhao Y, Chen M, Shenoy SK et al. Functional specialization of beta-arrestin interactions revealed by proteomic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 12011–12016.
Ma L, Pei G . Beta-arrestin signalling and regulation of transcription. J Cell Sci 2007; 120: 213–218.
Yue R, Kang J, Zhao C, Hu W, Tang Y, Liu X et al. Beta-arrestin1 regulates zebrafish hematopoiesis through binding to YY1 and relieving polycomb group repression. Cell 2009; 139: 535–546.
Parathath SR, Mainwaring LA, Fernandez LA, Guldal CG, Nahlé Z, Kenney AM . β-Arrestin-1 links mitogenic sonic hedgehog signalling to the cell cycle exit machinery in neural precursors. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 4013–4024.
Kang J, Shi Y, Xiang B, Qu B, Su W, Zhu M et al. A nuclear function of beta-arrestin1 in GPCR signalling: regulation of histone acetylation and gene transcription. Cell 2005; 123: 833–847.
Shi Y, Feng Y, Kang J, Liu C, Li Z, Li D et al. Critical regulation of CD4+ T cell survival and autoimmunity by beta-arrestin 1. Nat Immunol 2007; 8: 817–824.
Dasgupta P, Rizwani W, Pillai S, Davis R, Banerjee S, Hug K et al. β-ARR1-mediated regulation of E2F target genes in nicotine-induced growth of lung tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011; 103: 317–333.
Shenoy SK, Han S, Zhao YL, Hara MR, Oliver T, Cao Y et al. β-arrestin 1 mediates metastatic growth of breast cancer cells by facilitating HIF-1-dependent VEGF expression. Oncogene 2012; 31: 282–292.
Hoeppner CZ, Cheng N, Ye RD . Identification of a nuclear localization sequence in β-arrestin-1 and its functional implications. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 8932–8943.
Lefkowitz RJ, Shenoy SK . Transduction of receptor signals by beta-arrestins. Science 2005; 308: 512–517.
Clevers H . Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in development and disease. Cell 2006; 127: 469–480.
Kovacs JJ, Hara MR, Davenport CL, Kim J, Lefkowitz RJ . Arrestin development: emerging roles for β-arrestins in developmental signalling pathways. Dev Cell 2009; 17: 443–458.
Chen W, Hu LA, Semenov MV, Yanagawa S, Kikuchi A, Lefkowitz RJ et al. Beta-arrestin1 modulates lymphoid enhancer factor transcriptional activity through interaction with phosphorylated dishevelled proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 14889–14894.
Chen W, Ten Berge D, Brown J, Ahn S, Hu LA, Miller WE et al. Dishevelled 2 recruits beta-arrestin 2 to mediate Wnt5A-stimulated endocytosis of Frizzled 4. Science 2003; 301: 1391–1394.
Bryja V, Gradl D, Schambony A, Arenas E, Schulte G . Beta-arrestin is a necessary component of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 6690–6695.
Cianfrocca R, Rosanò L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Natali PG, Bagnato A . Beta-arrestin-1 mediates the endothelin-1-induced activation of Akt and integrin-linked kinase. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2010; 88: 796–801.
Scott MG, Le Rouzic E, Périanin A, Pierotti V, Enslen H, Benichou S et al. Differential nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of beta-arrestins. characterization of a leucine-rich nuclear export signal in beta-arrestin 2. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 37693–37701.
Wang P, Wu Y, Ge X, Ma L, Pei G . Subcellular localization of beta-arrestins is determined by their intact N domain and the nuclear export signal at the C terminus. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 11648–11653.
Yang M, He RL, Benovic JL, Ye RD . Beta-Arrestin1 interacts with the G-protein subunits beta1gamma2 and promotes beta1gamma2-dependent Akt signalling for NF-kappaB activation. Biochem J 2009; 417: 287–296.
Kim TH, Xiong H, Zhang Z, Ren B . Beta-catenin activates the growth factor endothelin-1 in colon cancer cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 597–604.
Sun P, Xiong H, Kim TH, Ren B, Zhang Z . Positive inter-regulation between beta-catenin/T cell factor-4 signalling and endothelin-1 signalling potentiates proliferation and survival of prostate cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol 2006; 69: 520–531.
Tetsu O, McCormick F . Beta-catenin regulates the expression of Cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature 1999; 398: 422–426.
Wu B, Crampton SP, Hughes CC . Wnt signalling induces matrix metalloproteinase expression and regulates T cell transmigration. Immunity 2007; 26: 227–239.
Billin AN, Thirlwell H, Ayer DE . Beta-catenin-histone deacetylase interactions regulate the transition of LEF1 from a transcriptional repressor to an activator. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 6882–6890.
Jin Q, Yu LR, Wang L, Zhang Z, Kasper LH, Lee JE et al. Distinct roles of GCN5/PCAF-mediated H3K9ac and CBP/p300-mediated H3K18/27ac in nuclear receptor transactivation. EMBO J 2011; 30: 249–262.
Rosanò L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra MR, Dedhar S, de Herreros AG et al. Endothelin-1 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 11649–11657.
Rosanò L, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Dedhar S, Nicotra MR, Natali PG et al. Integrin-linked kinase functions as a downstream mediator of endothelin-1 to promote invasive behavior in ovarian carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther 2006; 5: 833–842.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA . Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009; 139: 871–890.
Polyak K, Weinberg RA . Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states: acquisition of malignant and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 265–273.
Rosanò L, Cianfrocca R, Spinella F, Di Castro V, Nicotra MR, Lucidi A et al. Acquisition of chemoresistance and EMT phenotype is linked with activation of the endothelin A receptor pathway in ovarian carcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 2350–2360.
Bagnato A, Rosanò L . The endothelin axis in cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2008; 40: 1443–1451.
Bagnato A, Loizidou M, Pflug BR, Curwen J, Growcott J . Role of the endothelin axis and its antagonists in the treatment of cancer. Br J Pharmacol 2011; 163: 220–233.
Rosanò L, Varmi M, Salani D, Di Castro V, Spinella F, Natali PG et al. Endothelin-1 induces tumor proteinase activation and invasiveness of ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 8340–8346.
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge Valentina Caprara and Aldo Lupo for excellent technical assistance, Maria Vincenza Sarcone for secretarial assistance, Dr Maurizio Fanciulli for valuable comments, Dr Robert Lefkowitz (Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Duke University) for his insightful comments and for kindly providing β-arr1 expression vector; Dr Zhuohua Zhang (University of California San Diego School of Medicine, La Jolla, CA, USA) for ET-1 promoter reporter and its mutant control, and Dr Tania Merlino for the formal revision of the manuscript. This work was supported by the grant funded by the Associazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosanò, L., Cianfrocca, R., Tocci, P. et al. β-arrestin-1 is a nuclear transcriptional regulator of endothelin-1-induced β-catenin signaling. Oncogene 32, 5066–5077 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.527
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.527
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting tumor-stroma communication by blocking endothelin-1 receptors sensitizes high-grade serous ovarian cancer to PARP inhibition
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Targeting the Endothelin-1 pathway to reduce invasion and chemoresistance in gallbladder cancer cells
Cancer Cell International (2023)
-
Systems analysis identifies endothelin 1 axis blockade for enhancing the anti-tumor effect of multikinase inhibitor
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
YAP and endothelin-1 signaling: an emerging alliance in cancer
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)
-
Nuclear βArrestin1 regulates androgen receptor function in castration resistant prostate cancer
Oncogene (2021)