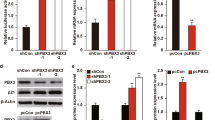
Abstract
Galectin-3 (Gal-3) is a multifunctional protein involved in cancer through regulation of cell adhesion, cell growth, apoptosis and metastasis, while p21 (Cip1/WAF1) is a negative regulator of the cell cycle, involved in apoptosis, transcription, DNA repair and metastasis. The results presented here demonstrate for the first time that the level of Gal-3 protein is associated with the level of p21 protein expression in human prostate cancer cells and the effects of Gal-3 on cell growth and apoptosis were reversed by modulating p21 expression level. Furthermore, Gal-3 regulates p21 expression at the post-translational level by stabilizing p21 protein via the carbohydrate-recognition domain. This is the first report suggesting a molecular function not yet described for Gal-3 as the regulator of p21 protein stability. This study provides a unique insight into the relationship of these two molecules during prostate cancer progression, and may provide a novel therapeutic target.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barondes SH, Cooper DN, Gitt MA, Leffler H . Galectins. Structure and function of a large family of animal lectins. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 20807–20810.
Feilchenfeldt J, Totsch M, Sheu SY, Robert J, Spiliopoulos A, Frilling A et al. Expression of galectin-3 in normal and malignant thyroid tissue by quantitative PCR and immunohistochemistry. Mod Pathol 2003; 16: 1117–1123.
Puglisi F, Minisini AM, Barbone F, Intersimone D, Aprile G, Puppin C et al. Galectin-3 expression in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Lett 2004; 212: 233–239.
Idikio H . Galectin-3 expression in human breast carcinoma: correlation with cancer histologic grade. Int J Oncol 1998; 12: 1287–1290.
Merseburger AS, Kramer MW, Hennenlotter J, Simon P, Knapp J, Hartmann JT et al. Involvement of decreased Galectin-3 expression in the pathogenesis and progression of prostate cancer. Prostate 2008; 68: 72–77.
Wang Y, Nangia-Makker P, Tait L, Balan V, Hogan V, Pienta KJ et al. Regulation of prostate cancer progression by galectin-3. Am J Pathol 2009; 174: 1515–1523.
Lin HM, Moon BK, Yu F, Kim HR . Galectin-3 mediates genistein-induced G(2)/M arrest and inhibits apoptosis. Carcinogenesis 2000; 21: 1941–1945.
Yang LP, Jiang S, Liu JQ, Miao XY, Yang ZL . Association of immunostaining of galectin-3 and sambucus nigra agglutinin with invasion, metastasis and poor progression of gallbladder adenocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology (e-pub ahead of print 12 April 2012; doi:10.5754/hge12129).
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ . The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 1993; 75: 805–816.
Brugarolas J, Moberg K, Boyd SD, Taya Y, Jacks T, Lees JA . Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by p21 is necessary for retinoblastoma protein-mediated G1 arrest after gamma-irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 1002–1007.
Garner E, Raj K . Protective mechanisms of p53-p21-pRb proteins against DNA damage-induced cell death. Cell Cycle 2008; 7: 277–282.
Coqueret O . New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol 2003; 13: 65–70.
Podust VN, Podust LM, Goubin F, Ducommun B, Hubscher U . Mechanism of inhibition of proliferating cell nuclear antigen-dependent DNA synthesis by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. Biochemistry 1995; 34: 8869–8875.
Streetly MJ, Maharaj L, Joel S, Schey SA, Gribben JG, Cotter FE . GCS-100, a novel galectin-3 antagonist, modulates MCL-1, NOXA, and cell cycle to induce myeloma cell death. Blood 2010; 115: 3939–3948.
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M et al. Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 1995; 376: 37–43.
Califice S, Castronovo V, Van Den Brule F . Galectin-3 and cancer (Review). Int J Oncol 2004; 25: 983–992.
Bartolazzi A, D'Alessandria C, Parisella MG, Signore A, Del Prete F, Lavra L et al. Thyroid cancer imaging in vivo by targeting the anti-apoptotic molecule galectin-3. PLoS One 2008; 3: e3768.
Iacovazzi PA, Notarnicola M, Caruso MG, Guerra V, Frisullo S, Altomare DF . Serum levels of galectin-3 and its ligand 90k/mac-2bp in colorectal cancer patients. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 2010; 32: 160–164.
Nangia-Makker P, Sarvis R, Visscher DW, Bailey-Penrod J, Raz A, Sarkar FH . Galectin-3 and L1 retrotransposons in human breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1998; 49: 171–183.
Brustmann H . Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in serous ovarian carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study with galectin-3 and cyclin D1 and outcome. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2008; 27: 380–389.
Ellerhorst JA, Stephens LC, Nguyen T, Xu XC . Effects of galectin-3 expression on growth and tumorigenicity of the prostate cancer cell line LNCaP. Prostate 2002; 50: 64–70.
Wang Y, Nangia-Makker P, Balan V, Hogan V, Raz A . Calpain activation through galectin-3 inhibition sensitizes prostate cancer cells to cisplatin treatment. Cell Death Dis 2010; 1: e101.
Abbas T, Dutta A . p21 in cancer: intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer 2009; 9: 400–414.
Suzuki A, Tsutomi Y, Miura M, Akahane K . Caspase 3 inactivation to suppress Fas-mediated apoptosis: identification of binding domain with p21 and ILP and inactivation machinery by p21. Oncogene 1999; 18: 1239–1244.
Le HV, Minn AJ, Massague J . Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors uncouple cell cycle progression from mitochondrial apoptotic functions in DNA-damaged cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 32018–32025.
Stivala LA, Cazzalini O, Prosperi E . The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21CDKN1A as a target of anti-cancer drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2012; 12: 85–96.
Caffo O, Doglioni C, Veronese S, Bonzanini M, Marchetti A, Buttitta F et al. Prognostic value of p21(WAF1) and p53 expression in breast carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study in 261 patients with long-term follow-up. Clin Cancer Res 1996; 2: 1591–1599.
Anttila MA, Kosma VM, Hongxiu J, Puolakka J, Juhola M, Saarikoski S et al. p21/WAF1 expression as related to p53, cell proliferation and prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer 1999; 79: 1870–1878.
Ogawa M, Onoda N, Maeda K, Kato Y, Nakata B, Kang SM et al. A combination analysis of p53 and p21 in gastric carcinoma as a strong indicator for prognosis. Int J Mol Med 2001; 7: 479–483.
Baretton GB, Klenk U, Diebold J, Schmeller N, Lohrs U . Proliferation- and apoptosis-associated factors in advanced prostatic carcinomas before and after androgen deprivation therapy: prognostic significance of p21/WAF1/CIP1 expression. Br J Cancer 1999; 80: 546–555.
Kim HR, Lin HM, Biliran H, Raz A . Cell cycle arrest and inhibition of anoikis by galectin-3 in human breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 4148–4154.
Waldman T, Lengauer C, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B . Uncoupling of S phase and mitosis induced by anticancer agents in cells lacking p21. Nature 1996; 381: 713–716.
Kraljevic Pavelic S, Cacev T, Kralj M . A dual role of p21waf1/cip1 gene in apoptosis of HEp-2 treated with cisplatin or methotrexate. Cancer Gene Ther 2008; 15: 576–590.
Blagosklonny MV . Are p27 and p21 cytoplasmic oncoproteins? Cell Cycle 2002; 1: 391–393.
Lee EW, Lee MS, Camus S, Ghim J, Yang MR, Oh W et al. Differential regulation of p53 and p21 by MKRN1 E3 ligase controls cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Embo J 2009; 28: 2100–2113.
Gan L, Wang J, Xu H, Yang X . Resistance to docetaxel-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by p38/p53/p21 signaling. Prostate 2011; 71: 1158–1166.
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993; 75: 817–825.
Parker SB, Eichele G, Zhang P, Rawls A, Sands AT, Bradley A et al. p53-independent expression of p21Cip1 in muscle and other terminally differentiating cells. Science 1995; 267: 1024–1027.
Bornstein G, Bloom J, Sitry-Shevah D, Nakayama K, Pagano M, Hershko A . Role of the SCFSkp2 ubiquitin ligase in the degradation of p21Cip1 in S phase. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 25752–25757.
Sheaff RJ, Singer JD, Swanger J, Smitherman M, Roberts JM, Clurman BE . Proteasomal turnover of p21Cip1 does not require p21Cip1 ubiquitination. Mol Cell 2000; 5: 403–410.
Amador V, Ge S, Santamaria PG, Guardavaccaro D, Pagano M . APC/C(Cdc20) controls the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of p21 in prometaphase. Mol Cell 2007; 27: 462–473.
Kim Y, Starostina NG, Kipreos ET . The CRL4Cdt2 ubiquitin ligase targets the degradation of p21Cip1 to control replication licensing. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 2507–2519.
Touitou R, Richardson J, Bose S, Nakanishi M, Rivett J, Allday MJ . A degradation signal located in the C-terminus of p21WAF1/CIP1 is a binding site for the C8 alpha-subunit of the 20S proteasome. EMBO J 2001; 20: 2367–2375.
Gong J, Ammanamanchi S, Ko TC, Brattain MG . Transforming growth factor beta 1 increases the stability of p21/WAF1/CIP1 protein and inhibits CDK2 kinase activity in human colon carcinoma FET cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 3340–3346.
Beck SE, Jung BH, Del Rosario E, Gomez J, Carethers JM . BMP-induced growth suppression in colon cancer cells is mediated by p21WAF1 stabilization and modulated by RAS/ERK. Cell Signal 2007; 19: 1465–1472.
Balan V, Nangia-Makker P, Kho DH, Wang Y, Raz A . Tyrosine-phosphorylated galectin-3 protein is resistant to prostate-specific antigen (PSA) cleavage. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 5192–5198.
Roy A, Kucukural A, Zhang Y . I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat Protoc 2010; 5: 725–738.
Seetharaman J, Kanigsberg A, Slaaby R, Leffler H, Barondes SH, Rini JM . X-ray crystal structure of the human galectin-3 carbohydrate recognition domain at 2.1-A resolution. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 13047–13052.
Schneidman-Duhovny D, Inbar Y, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ . PatchDock and SymmDock: servers for rigid and symmetric docking. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: W363–W367.
Mashiach E, Schneidman-Duhovny D, Andrusier N, Nussinov R, Wolfson HJ . FireDock: a web server for fast interaction refinement in molecular docking. Nucleic Acids Res 2008; 36: W229–W232.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Reuben Lotan for providing Gal-3-transfected LNCaP clones. This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R37CA46120-19 (A Raz) and the American Cancer Society grant 11-053-01-IRG (V Balan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Balan, V., Kho, D. et al. Galectin-3 regulates p21 stability in human prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 32, 5058–5065 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.528
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.528
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Novel fusion protein PK5-RL-Gal-3C inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma via anti-angiogenesis and cytotoxicity
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Monocarboxylate transporter-1 promotes osteoblast differentiation via suppression of p53, a negative regulator of osteoblast differentiation
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Galectin-3 is associated with a poor prognosis in primary hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Ablation of galectin-3 induces p27KIP1-dependent premature senescence without oncogenic stress
Cell Death & Differentiation (2014)