Abstract
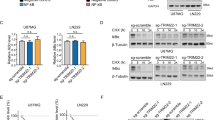
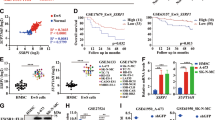
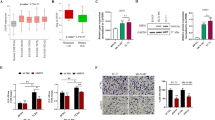
Although radiotherapy improves survival in patients, glioblastoma multiformes (GBMs) tend to relapse with augmented tumor migration and invasion even after ionizing radiation (IR). Aberrant nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 (Stat3) activation and interaction have been suggested in several human tumors. However, possible NF-κB/Stat3 interaction and the role of Stat3 in maintenance of NF-κB nuclear retention in GBM still remain unknown. Stat3 and NF-κB (p65) physically interact with one another in the nucleus in glioma tumors. Most importantly, glutathione S-transferase pull-down assays identified that Stat3 binds to the p65 transactivation domain and is present in the NF-κB DNA-binding complex. Irradiation significantly elevated nuclear phospho-p65/phospho-Stat3 interaction in correlation with increased intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and soluble-ICAM-1 levels, migration and invasion in human glioma xenograft cell lines 4910 and 5310. Chromatin immunopreicipitation and promoter luciferase activity assays confirmed the critical role of adjacent NF-κB (+399) and Stat3 (+479) binding motifs in the proximal intron-1 in elevating IR-induced ICAM-1 expression. Specific inhibition of Stat3 or NF-κB with Stat3.siRNA or JSH-23 severely inhibited IR-induced p65 recruitment onto ICAM-1 intron-1 and suppressed migratory properties in both the cell lines. On the other hand, Stat3C- or IR-induced Stat3 promoter recruitment was significantly decreased in p65-knockdown cells, thereby suggesting the reciprocal regulation between p65 and Stat3. We also observed a significant increase in NF-κB enrichment on ICAM-1 intron-1 and ICAM-1 transactivation in Stat3C overexpressing cells. In in vivo orthotopic experiments, suppression of tumor growth in Stat3.si+IR-treated mice was associated with the inhibition of IR-induced p-p65/p-Stat3 nuclear colocalization and ICAM-1 levels. To our knowledge, this is the first study showing the crucial role of NF-κB/Stat3 nuclear association in IR-induced ICAM-1 regulation and implies that targeting NF-κB/Stat3 interaction may have future therapeutic significance in glioma treatment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fine HA, Dear KB, Loeffler JS, Black PM, Canellos GP . Meta-analysis of radiation therapy with and without adjuvant chemotherapy for malignant gliomas in adults. Cancer 1993; 71: 2585–2597.
Louis DN . Molecular pathology of malignant gliomas. Annu Rev Pathol 2006; 1: 97–117.
Rao JS . Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 489–501.
Wild-Bode C, Weller M, Rimner A, Dichgans J, Wick W . Sublethal irradiation promotes migration and invasiveness of glioma cells: implications for radiotherapy of human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2744–2750.
Kargiotis O, Geka A, Rao JS, Kyritsis AP . Effects of irradiation on tumor cell survival, invasion and angiogenesis. J Neurooncol 2010; 100: 323–338.
Li T, Zeng ZC, Wang L, Qiu SJ, Zhou JW, Zhi XT et al. Radiation enhances long-term metastasis potential of residual hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice through TMPRSS4-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Gene Ther 2011; 18: 617–626.
Karin M, Greten FR . NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 749–759.
Lowe JM, Cha H, Yang Q, Fornace AJ . Nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) is a novel positive transcriptional regulator of the oncogenic Wip1 phosphatase. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 5249–5257.
Naugler WE, Karin M . NF-kappaB and cancer-identifying targets and mechanisms. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2008; 18: 19–26.
Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 2008; 132: 344–362.
Magne N, Toillon RA, Bottero V, Didelot C, Houtte PV, Gerard JP et al. NF-kappaB modulation and ionizing radiation: mechanisms and future directions for cancer treatment. Cancer Lett 2006; 231: 158–168.
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 695–708.
Chen LF, Fischle W, Verdin E, Greene WC . Duration of nuclear NF-kappaB action regulated by reversible acetylation. Science 2001; 293: 1653–1657.
Ghizzoni M, Haisma HJ, Maarsingh H, Dekker FJ . Histone acetyltransferases are crucial regulators in NF-kappaB mediated inflammation. Drug Discov Today 2011; 16: 504–511.
Chen LF, Greene WC . Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2004; 5: 392–401.
Brantley EC, Benveniste EN . Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3: a molecular hub for signaling pathways in gliomas. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 675–684.
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C et al. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999; 98: 295–303.
Lee H, Herrmann A, Deng JH, Kujawski M, Niu G, Li Z et al. Persistently activated Stat3 maintains constitutive NF-kappaB activity in tumors. Cancer Cell 2009; 15: 283–293.
Roland CL . Harken AH, Sarr MG, Barnett CC, Jr. ICAM-1 expression determines malignant potential of cancer. Surgery 2007; 141: 705–707.
Maenpaa A, Kovanen PE, Paetau A, Jaaskelainen J, Timonen T . Lymphocyte adhesion molecule ligands and extracellular matrix proteins in gliomas and normal brain: expression of VCAM-1 in gliomas. Acta Neuropathol 1997; 94: 216–225.
Burim RV, Teixeira SA, Colli BO, Peria FM, Tirapelli LF, Marie SK et al. ICAM-1 (Lys469Glu) and PECAM-1 (Leu125Val) polymorphisms in diffuse astrocytomas. Clin Exp Med 2009; 9: 157–163.
Berens ME, Giese A . ‘...those left behind.’ Biology and oncology of invasive glioma cells. Neoplasia 1999; 1: 208–219.
Voraberger G, Schafer R, Stratowa C . Cloning of the human gene for intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and analysis of its 5'-regulatory region. Induction by cytokines and phorbol ester. J Immunol 1991; 147: 2777–2786.
Ledebur HC, Parks TP . Transcriptional regulation of the intercellular adhesion molecule-1 gene by inflammatory cytokines in human endothelial cells. Essential roles of a variant NF-kappa B site and p65 homodimers. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 933–943.
Xue J, Thippegowda PB, Hu G, Bachmaier K, Christman JW, Malik AB et al. NF-kappaB regulates thrombin-induced ICAM-1 gene expression in cooperation with NFAT by binding to the intronic NF-kappaB site in the ICAM-1 gene. Physiol Genomics 2009; 38: 42–53.
Lam LT, Wright G, Davis RE, Lenz G, Farinha P, Dang L et al. Cooperative signaling through the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 and nuclear factor-{kappa}B pathways in subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2008; 111: 3701–3713.
Atkinson GP, Nozell SE, Benveniste ET . NF-kappaB and STAT3 signaling in glioma: targets for future therapies. Expert Rev Neurother 2010; 10: 575–586.
Bollrath J, Greten FR . IKK/NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis. EMBO Rep 2009; 10: 1314–1319.
Grivennikov SI, Karin M . Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2010; 21: 11–19.
Lee H, Deng J, Xin H, Liu Y, Pardoll D, Yu H . A requirement of STAT3 DNA binding precludes Th-1 immunostimulatory gene expression by NF-kappaB in tumors. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 3772–3780.
Jang HD, Yoon K, Shin YJ, Kim J, Lee SY . PIAS3 suppresses NF-kappaB-mediated transcription by interacting with the p65/RelA subunit. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 24873–24880.
Strebovsky J, Walker P, Lang R, Dalpke AH . Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) limits NFkappaB signaling by decreasing p65 stability within the cell nucleus. FASEB J 2011; 25: 863–874.
Benezra M, Chevallier N, Morrison DJ, MacLachlan TK, el-Deiry WS, Licht JD . BRCA1 augments transcription by the NF-kappaB transcription factor by binding to the Rel domain of the p65/RelA subunit. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 26333–26341.
Dutta J, Fan G, Gelinas C . CAPERalpha is a novel Rel-TAD-interacting factor that inhibits lymphocyte transformation by the potent Rel/NF-kappaB oncoprotein v-Rel. J Virol 2008; 82: 10792–10802.
Liu S, Wu LC, Pang J, Santhanam R, Schwind S, Wu YZ et al. Sp1/NFkappaB/HDAC/miR-29b regulatory network in KIT-driven myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 333–347.
Liu S, Liu Z, Xie Z, Pang J, Yu J, Lehmann E et al. Bortezomib induces DNA hypomethylation and silenced gene transcription by interfering with Sp1/NF-kappaB-dependent DNA methyltransferase activity in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 2364–2373.
Han SS, Yun H, Son DJ, Tompkins VS, Peng L, Chung ST et al. NF-kappaB/STAT3/PI3K signaling crosstalk in iMyc E mu B lymphoma. Mol Cancer 2010; 9: 97.
Surh YJ, Bode AM, Dong Z . Breaking the NF-kappaB and STAT3 alliance inhibits inflammation and pancreatic tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2010; 3: 1379–1381.
He G, Yu GY, Temkin V, Ogata H, Kuntzen C, Sakurai T et al. Hepatocyte IKKbeta/NF-kappaB inhibits tumor promotion and progression by preventing oxidative stress-driven STAT3 activation. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 286–297.
He G, Karin M . NF-kappaB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res 2011; 21: 159–168.
Squarize CH, Castilho RM, Sriuranpong V, Pinto DS, Gutkind JS . Molecular cross-talk between the NFkappaB and STAT3 signaling pathways in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 2006; 8: 733–746.
McDonald MW, Shu HK, Curran WJ, Crocker IR . Pattern of failure after limited margin radiotherapy and temozolomide for glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2011; 79: 130–136.
Anwar KN, Fazal F, Malik AB, Rahman A . RhoA/Rho-associated kinase pathway selectively regulates thrombin-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in endothelial cells via activation of I kappa B kinase beta and phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J Immunol 2004; 173: 6965–6972.
Roebuck KA . Oxidant stress regulation of IL-8 and ICAM-1 gene expression: differential activation and binding of the transcription factors AP-1 and NF-kappaB (review). Int J Mol Med 1999; 4: 223–230.
Roy J, Audette M, Tremblay MJ . Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) gene expression in human T cells is regulated by phosphotyrosyl phosphatase activity. Involvement of NF-kappaB, Ets, and palindromic interferon-gamma-responsive element-binding sites. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 14553–14561.
Rahman A, True AL, Anwar KN, Ye RD, Voyno-Yasenetskaya TA, Malik AB . Galpha(q) and Gbetagamma regulate PAR-1 signaling of thrombin-induced NF-kappaB activation and ICAM-1 transcription in endothelial cells. Circ Res 2002; 91: 398–405.
Giannini C, Sarkaria JN, Saito A, Uhm JH, Galanis E, Carlson BL et al. Patient tumor EGFR and PDGFRA gene amplifications retained in an invasive intracranial xenograft model of glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro-oncol 2005; 7: 164–176.
Kesanakurti D, Sareddy GR, Babu PP, Kirti PB . Mustard NPR1, a mammalian IkappaB homologue inhibits NF-kappaB activation in human GBM cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 390: 427–433.
Kesanakurti D, Chetty C, Dinh DH, Gujrati M, Rao JS . Role of MMP-2 in the regulation of IL-6/Stat3 survival signaling via interaction with α5β1 integrin in glioma. Oncogene (e-pub ahead of print 20 February 2012; doi:10.1038/onc.2012.52).
Badiga AV, Chetty C, Kesanakurti D, Are D, Gujrati M, Klopfenstein JD et al. MMP-2 siRNA inhibits radiation-enhanced invasiveness in glioma cells. PLoS One 2011; 6: e20614.
Kesanakurti D, Chetty C, Bhoopathi P, Lakka SS, Gorantla B, Tsung AJ et al. Suppression of MMP-2 attenuates TNF-alpha induced NF-kappaB activation and leads to JNK mediated cell death in glioma. PLoS One 2011; 6: e19341.
Acknowledgements
We thank Noorjehan Ali for technical assistance, Shelle Abraham for manuscript preparation, Diana Meister and Sushma Jasti for manuscript review. This research was supported by award NS64535-01A2 (to JSR) from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kesanakurti, D., Chetty, C., Rajasekhar Maddirela, D. et al. Essential role of cooperative NF-κB and Stat3 recruitment to ICAM-1 intronic consensus elements in the regulation of radiation-induced invasion and migration in glioma. Oncogene 32, 5144–5155 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.546
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.546
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeting TRAF3IP2, Compared to Rab27, is More Effective in Suppressing the Development and Metastasis of Breast Cancer
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
A Prognostic Signature for Lower Grade Gliomas Based on Expression of Long Non-Coding RNAs
Molecular Neurobiology (2019)
-
YM155 decreases radiation-induced invasion and reverses epithelial–mesenchymal transition by targeting STAT3 in glioblastoma
Journal of Translational Medicine (2018)
-
Cooperative STAT/NF-κB signaling regulates lymphoma metabolic reprogramming and aberrant GOT2 expression
Nature Communications (2018)
-
A novel interaction of PAK4 with PPARγ to regulate Nox1 and radiation-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in glioma
Oncogene (2017)