Abstract
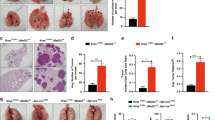
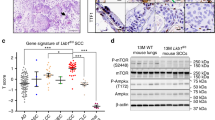
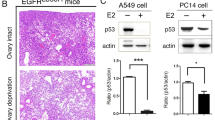
Smoking is the most important risk factor for both lung cancer (LC) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of myeloid cell nuclear factor-κB in the regulation of tumor cell growth signaling. We subjected mice lacking myeloid RelA/p65 (relaΔ−/−) to a metastatic LC model. Cigarette smoke (CS) exposure significantly increased the proliferation of Lewis lung carcinoma cell tumors in wild-type mice. In CS-exposed relaΔ−/− mice, the tumor growth was largely inhibited. Transcriptome and pathway analysis of cancer tissue revealed a fundamental impact of myeloid cells on various growth signaling pathways, including the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. In conclusion, myeloid RelA/p65 is necessary to link smoke-induced inflammation with LC growth and has a role in the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in tumor cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes PJ . Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med 2000; 343: 269–280.
Papi A, Casoni G, Caramori G, Guzzinati I, Boschetto P, Ravenna F et al. COPD increases the risk of squamous histological subtype in smokers who develop non-small cell lung carcinoma. Thorax 2004; 59: 679–681.
Young RP, Hopkins RJ, Christmas T, Black PN, Metcalf P, Gamble GD . COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history. Eur Respir J 2009; 34: 380–386.
Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Harris CC . Radical causes of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 276–285.
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, Park JM, Li ZW, Egan LJ et al. IKKbeta links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated cancer. Cell 2004; 118: 285–296.
Karin M, Greten FR . NF-kappaB: linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 749–759.
Takahashi H, Ogata H, Nishigaki R, Broide DH, Karin M . Tobacco smoke promotes lung tumorigenesis by triggering IKKbeta- and JNK1-dependent inflammation. Cancer Cell 2010; 17: 89–97.
Balkwill F . Tumor necrosis factor or tumor promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2002; 13: 135–141.
Kim S, Takahashi H, Lin WW, Descargues P, Grivennikov S, Kim Y et al. Carcinoma-produced factors activate myeloid cells through TLR2 to stimulate metastasis. Nature 2009; 457: 102–106.
Luo JL, Maeda S, Hsu LC, Yagita H, Karin M . Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts inflammation- induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell 2004; 6: 297–305.
Algul H, Treiber M, Lesina M, Nakhai H, Saur D, Geisler F et al. Pancreas-specific RelA/p65 truncation increases susceptibility of acini to inflammation-associated cell death following cerulein pancreatitis. J Clin Invest 2007; 117: 1490–1501.
Hess C, Herr C, Beisswenger C, Zakharkina T, Schmid RM, Bals R . Myeloid RelA regulates pulmonary host defense networks. Eur Respir J 2010; 35: 343–352.
Oguma K, Oshima H, Aoki M, Uchio R, Naka K, Nakamura S et al. Activated macrophages promote Wnt signalling through tumour necrosis factor-alpha in gastric tumour cells. EMBO J 2008; 27: 1671–1681.
Reya T, Clevers H . Wnt signalling in stem cells and cancer. Nature 2005; 434: 843–850.
Berschneider B, Königshoff M . WNT1 inducible signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1): a novel mediator linking development and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2011; 43: 306–309.
Kaler P, Godasi BN, Augenlicht L, Klampfer L . The NF-kappaB/AKT-dependent Induction of Wnt Signaling in Colon Cancer Cells by Macrophages and IL-1beta. Cancer Microenviron 2009; 2: 69–80.
Sharma M, Chuang WW, Sun Z . Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt stimulates androgen pathway through GSK3beta inhibition and nuclear beta-catenin accumulation. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 30935–30941.
Walser T, Cui X, Yanagawa J, Lee JM, Heinrich E, Lee G et al. Smoking and lung cancer: the role of inflammation. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2008; 5: 811–815.
Punturieri A, Szabo E, Croxton TL, Shapiro SD, Dubinett SM . Lung cancer and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: needs and opportunities for integrated research. J Natl Cancer Inst 2009; 101: 554–559.
Stathopoulos GT, Sherrill TP, Han W, Sadikot RT, Yull FE, Blackwell TS et al. Host nuclear factor-kappaB activation potentiates lung cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer Res 2008; 6: 364–371.
Zhu BQ, Heeschen C, Sievers RE, Karliner JS, Parmley WW, Glantz SA et al. Second hand smoke stimulates tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Cell 2003; 4: 191–196.
Moghaddam SJ, Li H, Cho SN, Dishop MK, Wistuba II, Ji L et al. Promotion of lung carcinogenesis by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease-like airway inflammation in a K-ras-induced mouse model. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2009; 40: 443–453.
Zaynagetdinov R, Sherrill TP, Polosukhin VV, Han W, Ausborn JA, McLoed AG et al. A critical role for macrophages in promotion of urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis. J Immunol 2011; 187: 5703–5711.
Grivennikov SI, Karin M . Inflammatory cytokines in cancer: tumour necrosis factor and interleukin 6 take the stage. Ann Rheum Dis 2011; 70 (Suppl 1): i104–i108.
Murdoch C, Muthana M, Coffelt SB, Lewis CE . The role of myeloid cells in the promotion of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 618–631.
Takanami I, Takeuchi K, Kodaira S . Tumor-associated macrophage infiltration in pulmonary adenocarcinoma: association with angiogenesis and poor prognosis. Oncology 1999; 57: 138–142.
Chen JJ, Lin YC, Yao PL, Yuan A, Chen HY, Shun CT et al. Tumor-associated macrophages: the double-edged sword in cancer progression. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 953–964.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M . Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010; 140: 883–899.
Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch R, Amit S, Kasem S et al. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004; 431: 461–466.
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS, Ghosh S . Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol 2011; 12: 695–708.
Perkins ND . The diverse and complex roles of NF-kappaB subunits in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 121–132.
Hu MC, Hung MC . Role of IkappaB kinase in tumorigenesis. Future Oncol 2005; 1: 67–78.
Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, Yang JY et al. IkappaB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 2004; 117: 225–237.
Waterfield MR, Zhang M, Norman LP, Sun SC . NF-kappaB1/p105 regulates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated MAP kinase signaling by governing the stability and function of the Tpl2 kinase. Mol Cell 2003; 11: 685–694.
Green CE, Liu T, Montel V, Hsiao G, Lester RD, Subramaniam S et al. Chemoattractant signaling between tumor cells and macrophages regulates cancer cell migration, metastasis and neovascularization. PLoS One 2009; 4: e6713.
Yao PL, Lin YC, Wang CH, Huang YC, Liao WY, Wang SS et al. Autocrine and paracrine regulation of interleukin-8 expression in lung cancer cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2005; 32: 540–547.
Tennis M, Van SM, Winn RA . Role of the wnt signaling pathway and lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2007; 2: 889–892.
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Dasari V, Sidhu SS, Mengistab A, Finkbeiner W, Gallup M et al. Wnt and Hedgehog are critical mediators of cigarette smoke-induced lung cancer. PLoS One 2006; 1: e93.
Xu X, Sun PL, Li JZ, Jheon S, Lee CT, Chung JH . Aberrant Wnt1/beta-catenin expression is an independent poor prognostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. J Thorac Oncol 2011; 6: 716–724.
Clausen BE, Burkhardt C, Reith W, Renkawitz R, Forster I . Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysMcre mice. Transgenic Res 1999; 8: 265–277.
Li X, Magenheimer BS, Xia S, Johnson T, Wallace DP, Calvet JP et al. A tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated pathway promoting autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nat Med 2008; 14: 863–868.
Alalwani SM, Sierigk J, Herr C, Pinkenburg O, Gallo R, Vogelmeier C et al. The antimicrobial peptide LL-37 modulates the inflammatory and host defense response of human neutrophils. Eur J Immunol 2010; 40: 1118–1126.
Irizarry RA, Bolstad BM, Collin F, Cope LM, Hobbs B, Speed TP . Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic Acids Res 2003; 31: e15.
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S et al. Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 2004; 5: R80.
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Hirakawa M . KEGG for representation and analysis of molecular networks involving diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 2010; 38 (Database issue): D355–D360.
The Gene Ontology Consortium, The Gene Ontology: enhancements for 2011. Nucleic Acids Res 2011; 40: D559–D564.
Backes C, Keller A, Kuentzer J, Kneissl B, Comtesse N, Elnakady YA et al. GeneTrail—advanced gene set enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2007; 35 (Web Server issue): W186–W192.
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N, Golani I . Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav Brain Res 2001; 125: 279–284.
Koczulla R, von Degenfeld G, Kupatt C, Krotz F, Zahler S, Gloe T et al. An angiogenic role for the human peptide antibiotic LL-37/hCAP-18. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 1665–1672.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG Ba 1641/12), the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (FKZ 01GI0881-0888), and the LOEWE-Schwerpunkt ‘Tumor and Inflammation’ of the state of Hesse to RB. We thank Thomas Damm, Andreas Kamyschnikow and Anja Honecker for excellent technical support. We thank Professor Ingrid Förster for making the LysMcre animal available for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Beisswenger, C., Herr, C. et al. Myeloid cell RelA/p65 promotes lung cancer proliferation through Wnt/β-catenin signaling in murine and human tumor cells. Oncogene 33, 1239–1248 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.75
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.75
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Kruppel-like factor 13 inhibits cell proliferation of gastric cancer by inducing autophagic degradation of β-catenin
Discover Oncology (2022)
-
FERMT3 mediates cigarette smoke-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition through Wnt/β-catenin signaling
Respiratory Research (2021)
-
Targeted inhibition of endothelial calpain delays wound healing by reducing inflammation and angiogenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2020)
-
Sox17 is required for endothelial regeneration following inflammation-induced vascular injury
Nature Communications (2019)
-
IL-17C-mediated innate inflammation decreases the response to PD-1 blockade in a model of Kras-driven lung cancer
Scientific Reports (2019)