Abstract
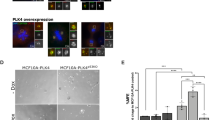
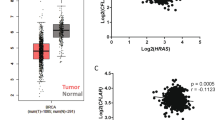
The ability of breast cancer cells to resist anoikis, apoptosis caused by detachment of the non-malignant epithelial cells from the extracellular matrix (ECM), is thought to be critical for breast tumor growth, invasion and metastasis. ErbB2, an oncoprotein that is often overproduced in breast tumors, can block breast cancer cell anoikis via mechanisms that are understood only in part. In an effort to understand them better we found that detachment of the non-malignant human breast epithelial cells from the ECM upregulates a protein Perp in these cells. Perp is a component of the desmosomes, multiprotein complexes involved in cell-to-cell adhesion. Perp can cause apoptosis via unknown mechanisms. We demonstrated that Perp upregulation by cell detachment is driven by detachment-induced loss of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). We also found that Perp knockdown by RNA interference (RNAi) rescues detached cells from death which indicates that Perp contributes to their anoikis. We observed that ErbB2, when overexpressed in detached breast epithelial cells, causes Perp downregulation. Furthermore, ErbB2-directed RNAi or treatment with lapatinib, an ErbB2/EGFR small-molecule inhibitor used for breast cancer therapy, upregulated Perp in ErbB2-positive human breast and ovarian carcinoma cells. We established that ErbB2 downregulates Perp by activating an ErbB2 effector protein kinase Mek that blocks detachment-induced EGFR loss in a manner that requires the presence of a signaling protein Sprouty-2. Finally, we observed that restoration of the wild-type Perp levels in ErbB2-overproducing breast epithelial cells increases their anoikis susceptibility and blocks their clonogenicity in the absence of adhesion to the ECM. In summary, we have identified a novel mechanism of ErbB2-mediated mechanism of anoikis resistance of ErbB2-overproducing breast epithelial cells. This mechanism allows such cells to grow without adhesion to the ECM and is driven by ErbB2-induced activation of Mek, subsequent EGFR upregulation and further EGFR-dependent Perp loss.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosen K, Coll ML, Li A, Filmus J . Transforming growth factor-alpha prevents detachment-induced inhibition of c-Src kinase activity, Bcl-XL down-regulation, and apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 37273–37279.
Rosen K, Shi W, Calabretta B, Filmus J . Cell detachment triggers p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent overexpression of Fas ligand. A novel mechanism of anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 46123–46130.
Vachon PH, Harnois C, Grenier A, Dufour G, Bouchard V, Han J et al. Differentiation state-selective roles of p38 isoforms in human intestinal epithelial cell anoikis. Gastroenterology 2002; 123: 1980–1991.
Liu Z, Li H, Wu X, Yoo BH, Yan SR, Stadnyk AW et al. Detachment-induced upregulation of XIAP and cIAP2 delays anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 2006; 25: 7680–7690.
Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Erdos V, Huang SN, Filmus J, Kerbel RS . Massive programmed cell death in intestinal epithelial cells induced by three-dimensional growth conditions: suppression by mutant c-H-ras oncogene expression. J Cell Biol 1995; 131: 1587–1598.
Frisch SM, Francis H . Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 1994; 124: 619–626.
Ljubimov AV, Bartek J, Couchman JR, Kapuller LL, Veselov VV, Kovarik J et al. Distribution of individual components of basement membrane in human colon polyps and adenocarcinomas as revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Int J Cancer 1992; 50: 562–566.
Douma S, Van Laar T, Zevenhoven J, Meuwissen R, Van Garderen E, Peeper DS . Suppression of anoikis and induction of metastasis by the neurotrophic receptor TrkB. Nature 2004; 430: 1034–1039.
Berezovskaya O, Schimmer AD, Glinskii AB, Pinilla C, Hoffman RM, Reed JC et al. Increased expression of apoptosis inhibitor protein XIAP contributes to anoikis resistance of circulating human prostate cancer metastasis precursor cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 2378–2386.
Freedman VH, Shin SI . Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell 1974; 3: 355–359.
Lim KH, Baines AT, Fiordalisi JJ, Shipitsin M, Feig LA, Cox AD et al. Activation of RalA is critical for Ras-induced tumorigenesis of human cells. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 533–545.
Haenssen KK, Caldwell SA, Shahriari KS, Jackson SR, Whelan KA, Klein-Szanto AJ et al. ErbB2 requires integrin alpha5 for anoikis resistance via Src regulation of receptor activity in human mammary epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 2010; 123: 1373–1382.
Reginato MJ, Mills KR, Paulus JK, Lynch DK, Sgroi DC, Debnath J et al. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat Cell Biol 2003; 5: 733–740.
Liu Z, Li H, Derouet M, Filmus J, LaCasse EC, Korneluk RG et al. ras Oncogene triggers up-regulation of cIAP2 and XIAP in intestinal epithelial cells: epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent and -independent mechanisms of ras-induced transformation. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 37383–37392.
Yoo BH, Wang Y, Erdogan M, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Corcos L et al. Oncogenic ras-induced down-regulation of pro-apoptotic protease caspase-2 is required for malignant transformation of intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 38894–38903.
Rosen K, Rak J, Jin J, Kerbel RS, Newman MJ, Filmus J . Downregulation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bak is required for the ras-induced transformation of intestinal epithelial cells. Curr Biol 1998; 8: 1331–1334.
Rosen K, Rak J, Leung T, Dean NM, Kerbel RS, Filmus J . Activated Ras prevents downregulation of Bcl-X(L) triggered by detachment from the extracellular matrix. A mechanism of Ras-induced resistance to anoikis in intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 2000; 149: 447–456.
Liu Z, Li H, Derouet M, Berezkin A, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S et al. Oncogenic Ras inhibits anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells by preventing the release of a mitochondrial pro-apoptotic protein Omi/HtrA2 into the cytoplasm. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 14738–14747.
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE . EphA2: a determinant of malignant cellular behavior and a potential therapeutic target in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2004; 23: 1448–1456.
Scotlandi K, Maini C, Manara MC, Benini S, Serra M, Cerisano V et al. Effectiveness of insulin-like growth factor I receptor antisense strategy against Ewing's sarcoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther 2002; 9: 296–307.
Frankel A, Rosen K, Filmus J, Kerbel RS . Induction of anoikis and suppression of human ovarian tumor growth in vivo by down-regulation of Bcl-X(L). Cancer Res 2001; 61: 4837–4841.
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE . CEACAM6 gene silencing impairs anoikis resistance and in vivo metastatic ability of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 465–473.
Jiang K, Sun J, Cheng J, Djeu JY, Wei S, Sebti S . Akt mediates Ras downregulation of RhoB, a suppressor of transformation, invasion, and metastasis. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: 5565–5576.
Derouet M, Wu X, May L, Hoon YB, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S et al. Acquisition of anoikis resistance promotes the emergence of oncogenic K-ras mutations in colorectal cancer cells and stimulates their tumorigenicity in vivo. Neoplasia 2007; 9: 536–545.
Jacks T, Weinberg RA . Taking the study of cancer cell survival to a new dimension. Cell 2002; 111: 923–925.
Frisch SM, Screaton RA . Anoikis mechanisms. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2001; 13: 555–562.
Schmelzle T, Mailleux AA, Overholtzer M, Carroll JS, Solimini NL, Lightcap ES et al. Functional role and oncogene-regulated expression of the BH3-only factor Bmf in mammary epithelial anoikis and morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 3787–3792.
Debnath J, Mills KR, Collins NL, Reginato MJ, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS . The role of apoptosis in creating and maintaining luminal space within normal and oncogene-expressing mammary acini. Cell 2002; 111: 29–40.
Debnath J, Brugge JS . Modelling glandular epithelial cancers in three-dimensional cultures. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 675–688.
Gudjonsson T, Ronnov-Jessen L, Villadsen R, Rank F, Bissell MJ, Petersen OW . Normal and tumor-derived myoepithelial cells differ in their ability to interact with luminal breast epithelial cells for polarity and basement membrane deposition. J Cell Sci 2002; 115: 39–50.
Weaver VM, Lelievre S, Lakins JN, Chrenek MA, Jones JC, Giancotti F et al. beta4 integrin-dependent formation of polarized three-dimensional architecture confers resistance to apoptosis in normal and malignant mammary epithelium. Cancer Cell 2002; 2: 205–216.
Muschler J, Streuli CH . Cell-matrix interactions in mammary gland development and breast cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2010; 2: a003202.
Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, Holt JA, Wong SG, Keith DE et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science 1989; 244: 707–712.
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA, Hynes NE . The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in development and cancer. EMBO J 2000; 19: 3159–3167.
Harari D, Yarden Y . Molecular mechanisms underlying ErbB2/HER2 action in breast cancer. Oncogene 2000; 19: 6102–6114.
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX . Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001; 2: 127–137.
Dusek RL, Bascom JL, Vogel H, Baron S, Borowsky AD, Bissell MJ et al. Deficiency of the p53/p63 target Perp alters mammary gland homeostasis and promotes cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2012; 14: R65.
Soule HD, Maloney TM, Wolman SR, Peterson WD Jr, Brenz R, McGrath CM et al. Isolation and characterization of a spontaneously immortalized human breast epithelial cell line, MCF-10. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 6075–6086.
Guadamillas MC, Cerezo A, Del Pozo MA . Overcoming anoikis—pathways to anchorage-independent growth in cancer. J Cell Sci 2011; 124: 3189–3197.
Attardi LD, Reczek EE, Cosmas C, Demicco EG, McCurrach ME, Lowe SW et al. PERP, an apoptosis-associated target of p53, is a novel member of the PMP-22/gas3 family. Genes Dev 2000; 14: 704–718.
Ihrie RA, Marques MR, Nguyen BT, Horner JS, Papazoglu C, Bronson RT et al. Perp is a p63-regulated gene essential for epithelial integrity. Cell 2005; 120: 843–856.
Ihrie RA, Attardi LD . A new Perp in the lineup: linking p63 and desmosomal adhesion. Cell Cycle 2005; 4: 873–876.
Ihrie RA, Reczek E, Horner JS, Khachatrian L, Sage J, Jacks T et al. Perp is a mediator of p53-dependent apoptosis in diverse cell types. Curr Biol 2003; 13: 1985–1990.
Rusnak DW, Lackey K, Affleck K, Wood ER, Alligood KJ, Rhodes N et al. The effects of the novel, reversible epidermal growth factor receptor/ErbB-2 tyrosine kinase inhibitor, GW2016, on the growth of human normal and tumor-derived cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther 2001; 1: 85–94.
O'Brien NA, Browne BC, Chow L, Wang Y, Ginther C, Arboleda J et al. Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT signaling confers resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib. Mol Cancer Ther 2010; 9: 1489–1502.
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxter L, Strzepek T, Costello D, Crowley P et al. The expression patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67 and AR by immmunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines. Breast Cancer (Auckl) 2010; 4: 35–41.
Wilken JA, Webster KT, Maihle NJ . Trastuzumab sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to EGFR-targeted therapeutics. J Ovarian Res 2010; 3: 7.
Santen RJ, Song RX, McPherson R, Kumar R, Adam L, Jeng MH et al. The role of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2002; 80: 239–256.
Kolch W . Meaningful relationships: the regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem J 2000; 351 (Pt 2): 289–305.
Alessi DR, Cuenda A, Cohen P, Dudley DT, Saltiel AR . PD 098059 is a specific inhibitor of the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 27489–27494.
Schulze A, Lehmann K, Jefferies HB, McMahon M, Downward J . Analysis of the transcriptional program induced by Raf in epithelial cells. Genes Dev 2001; 15: 981–994.
Goc A, Sabbineni H, Abdalla M, Somanath PR . p70 S6-kinase mediates the cooperation between Akt1 and Mek1 pathways in fibroblast-mediated extracellular matrix remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015; 1853: 1626–1635.
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF . A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 5241–5248.
Grassian AR, Schafer ZT, Brugge JS . ErbB2 stabilizes epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression via Erk and Sprouty2 in extracellular matrix-detached cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 79–90.
Roepstorff K, Grovdal L, Grandal M, Lerdrup M, van Deurs B . Endocytic downregulation of ErbB receptors: mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Histochem Cell Bio 2008; 129: 563–578.
Jost M, Huggett TM, Kari C, Rodeck U . Matrix-independent survival of human keratinocytes through an EGF receptor/MAPK-kinase-dependent pathway. Mol Biol Cell 2001; 12: 1519–1527.
Beaudry VG, Jiang D, Dusek RL, Park EJ, Knezevich S, Ridd K et al. Loss of the p53/p63 regulated desmosomal protein Perp promotes tumorigenesis. PLoS Genet 2010; 6: e1001168.
Kong CS, Cao H, Kwok S, Nguyen CM, Jordan RC, Beaudry VG et al. Loss of the p53/p63 target PERP is an early event in oral carcinogenesis and correlates with higher rate of local relapse. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2013; 115: 95–103.
Xia W, Lau YK, Zhang HZ, Liu AR, Li L, Kiyokawa N et al. Strong correlation between c-erbB-2 overexpression and overall survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 1997; 3: 3–9.
Khan AJ, King BL, Smith BD, Smith GL, DiGiovanna MP, Carter D et al. Characterization of the HER-2/neu oncogene by immunohistochemical and fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 540–548.
Baselga J, Bradbury I, Eidtmann H, Di Cosimo S, de Azambuja E, Aura C et al. Lapatinib with trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer (NeoALTTO): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012; 379: 633–640.
Recondo G, Canton ED, de la Vega M, Greco M, Recondo G, Valsecchi ME . Therapeutic options for HER-2 positive breast cancer: perspectives and future directions. World J Clin Oncol 2014; 5: 440–454.
Yoo BH, Berezkin A, Wang Y, Zagryazhskaya A, Rosen KV . Tumor suppressor protein kinase Chk2 is a mediator of anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. Int J Cancer 2012; 131: 357–366.
McDonald JH . Handbook of Biological Statistics 3rd edn Sparky House Publishing: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2014.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation (CBCF) Atlantic Region operating grant (R13 F14) awarded to KR. Contribution of GD was supported by the CBCF Atlantic Region operating grant (R14 F09). BY was a recipient of the IWK Health Centre Research Associateship. DC was a recipient of a CIBC Graduate Scholarship in Medical Research from the Beatrice Hunter Cancer Research Institute. We are grateful to Drs P Lee and A Stadnyk for the materials provided for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, I., Yoo, B., Masson, O. et al. ErbB2-dependent downregulation of a pro-apoptotic protein Perp is required for oncogenic transformation of breast epithelial cells. Oncogene 35, 5759–5769 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.109
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.109
This article is cited by
-
ErbB2/Her2-dependent downregulation of a cell death-promoting protein BLNK in breast cancer cells is required for 3D breast tumor growth
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Tumor levels of the mediators of ErbB2-driven anoikis resistance correlate with breast cancer relapse in patients receiving trastuzumab-based therapies
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021)
-
Trastuzumab-induced upregulation of a protein set in extracellular vesicles emitted by ErbB2-positive breast cancer cells correlates with their trastuzumab sensitivity
Breast Cancer Research (2020)
-
Upregulation of METTL14 mediates the elevation of PERP mRNA N6 adenosine methylation promoting the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer
Molecular Cancer (2020)
-
Identification of gene co-expression modules and hub genes associated with lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid cancer
Endocrine (2019)