Abstract
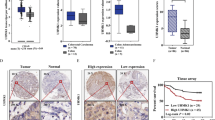
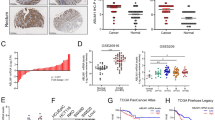
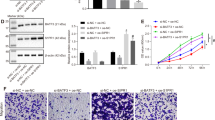
The LIM protein AJUBA is a scaffold protein participating in the regulation of cell adhesion, mitosis, DNA damage, cell differentiation, proliferation, migration and gene transcription. However, its roles in tumorigenesis and progression are poorly defined. Here, we report that AJUBA is highly expressed in colorectal cancer (CRC) and promotes CRC cell growth in culture and in xenografted mice via an inhibition of apoptosis. AJUBA represses the expression of IFIT2 gene, an interferon-stimulated gene and a known apoptosis inducer and tumour suppressor to mediate its resistance to apoptosis. Mechanistic investigations reveal that AJUBA specifically binds the FERM domain of JAK1 to dissociate JAK1 from the IFNγ recepter, resulting in an inhibition of STAT1 phosporylation and concomitantly its nuclear translocation. Clinically, the level of AJUBA in CRC specimens is negatively correlated with the levels of IFIT2 and pSTAT1. Collectively, these studies demonstrate that AJUBA can promote CRC growth via inhibiting apoptosis and serve as a target for the therapeutics and a marker for diagnosis of CRC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirota T, Kunitoku N, Sasayama T, Marumoto T, Zhang D, Nitta M et al. Aurora-A and an interacting activator, the LIM protein Ajuba, are required for mitotic commitment in human cells. Cell 2003; 114: 585–598.
Schimizzi GV, Longmore GD . Ajuba proteins. Curr Biol: CB 2015; 25: R445–R446.
Burglin TR, Affolter M . Homeodomain proteins: an update. Chromosoma 2016; 125: 497–521.
Langer EM, Feng Y, Zhaoyuan H, Rauscher FJ 3rd, Kroll KL, Longmore GD, Ajuba LIM . proteins are snail/slug corepressors required for neural crest development in Xenopus. Dev Cell 2008; 14: 424–436.
Goyal RK, Lin P, Kanungo J, Payne AS, Muslin AJ, Longmore GD . Ajuba, a novel LIM protein, interacts with Grb2, augments mitogen-activated protein kinase activity in fibroblasts, and promotes meiotic maturation of Xenopus oocytes in a Grb2- and Ras-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol 1999; 19: 4379–4389.
Pratt SJ, Epple H, Ward M, Feng Y, Braga VM, Longmore GD . The LIM protein Ajuba influences p130Cas localization and Rac1 activity during cell migration. J Cell Biol 2005; 168: 813–824.
Sun G, Irvine KD . Ajuba family proteins link JNK to Hippo signaling. Sci Signal 2013; 6: ra81.
Hou Z, Peng H, Ayyanathan K, Yan KP, Langer EM, Longmore GD et al. The LIM protein AJUBA recruits protein arginine methyltransferase 5 to mediate SNAIL-dependent transcriptional repression. Mol Cell Biol 2008; 28: 3198–3207.
Srichai MB, Konieczkowski M, Padiyar A, Konieczkowski DJ, Mukherjee A, Hayden PS et al. A WT1 co-regulator controls podocyte phenotype by shuttling between adhesion structures and nucleus. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 14398–14408.
Ayyanathan K, Peng H, Hou Z, Fredericks WJ, Goyal RK, Langer EM et al. The Ajuba LIM domain protein is a corepressor for SNAG domain mediated repression and participates in nucleocytoplasmic shuttling. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 9097–9106.
Darnell Jr JE, Kerr IM, Stark GR . Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994; 264: 1415–1421.
Mertens C, Darnell JE Jr . SnapShot: JAK-STAT signaling. Cell 2007; 131: 612.
Kotenko SV, Pestka S . Jak-Stat signal transduction pathway through the eyes of cytokine class II receptor complexes. Oncogene 2000; 19: 2557–2565.
Blouin CM, Lamaze C . Interferon gamma receptor: the beginning of the journey. Front Immunol 2013; 4: 267.
O’Connell D, Bouazza B, Kokalari B, Amrani Y, Khatib A, Ganther JD et al. IFN-gamma-induced JAK/STAT, but not NF-kappaB, signaling pathway is insensitive to glucocorticoid in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 2015; 309: L348–L359.
Reich NC . A death-promoting role for ISG54/IFIT2. J Interferon Cytokine Res: The Official Journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research 2013; 33: 199–205.
Stawowczyk M, Van Scoy S, Kumar KP, Reich NC . The interferon stimulated gene 54 promotes apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 7257–7266.
Zhou X, Michal JJ, Zhang L, Ding B, Lunney JK, Liu B et al. Interferon induced IFIT family genes in host antiviral defense. Int J Biol Sci 2013; 9: 200–208.
Tiwari M, Prasad S, Tripathi A, Pandey AN, Ali I, Singh AK et al. Apoptosis in mammalian oocytes: a review. Apoptosis: An International Journal on Programmed Cell Death 2015; 20: 1019–1025.
Quispel WT, Stegehuis-Kamp JA, Santos SJ, van Wengen A, Dompeling E, Egeler RM et al. Intact IFN-gammaR1 expression and function distinguishes Langerhans cell histiocytosis from mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease. J Clin Immunol 2014; 34: 84–93.
Krebs DL, Hilton DJ . SOCS: physiological suppressors of cytokine signaling. J Cell Sci 2000; 113 (Pt 16): 2813–2819.
Baetz A, Frey M, Heeg K, Dalpke AH . Suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins indirectly regulate toll-like receptor signaling in innate immune cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279: 54708–54715.
Qin H, Yeh WI, De Sarno P, Holdbrooks AT, Liu Y, Muldowney MT et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3/suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 (STAT3/SOCS3) axis in myeloid cells regulates neuroinflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 5004–5009.
Vlotides G, Sorensen AS, Kopp F, Zitzmann K, Cengic N, Brand S et al. SOCS-1 and SOCS-3 inhibit IFN-alpha-induced expression of the antiviral proteins 2,5-OAS and MxA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 320: 1007–1014.
Zhang JG, Farley A, Nicholson SE, Willson TA, Zugaro LM, Simpson RJ et al. The conserved SOCS box motif in suppressors of cytokine signaling binds to elongins B and C and may couple bound proteins to proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 2071–2076.
Bluyssen HA, Vlietstra RJ, Faber PW, Smit EM, Hagemeijer A, Trapman J . Structure, chromosome localization, and regulation of expression of the interferon-regulated mouse Ifi54/Ifi56 gene family. Genomics 1994; 24: 137–148.
Du LY, Cui YL, Chen EQ, Cheng X, Liu L, Tang H . Correlation between the suppressor of cytokine signaling-1 and 3 and hepatitis B virus: possible roles in the resistance to interferon treatment. Virol J 2014; 11: 51.
Gongora C, Mechti N . Interferon signaling pathways. Bulletin du cancer 1999; 86: 911–919.
Stark GR, Darnell JE Jr . The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity 2012; 36: 503–514.
Reich NC . STATs get their move on. Jak-Stat 2013; 2: e27080.
Decker T, Kovarik P, Meinke A . GAS elements: a few nucleotides with a major impact on cytokine-induced gene expression. J Interferon Cytokine Res: The Official Journal of the International Society for Interferon and Cytokine Research 1997; 17: 121–134.
Li Q, Peng H, Fan H, Zou X, Liu Q, Zhang Y et al. The LIM protein Ajuba promotes adipogenesis by enhancing PPARgamma and p300/CBP interaction. Cell Death Differe 2016; 23: 158–168.
Chen J, Xu H, Zou X, Wang J, Zhu Y, Chen H et al. Snail recruits Ring1B to mediate transcriptional repression and cell migration in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 2014; 74: 4353–4363.
Jia H, Cong Q, Chua JF, Liu H, Xia X, Zhang X et al. p57Kip2 is an unrecognized DNA damage response effector molecule that functions in tumor suppression and chemoresistance. Oncogene 2015; 34: 3568–3581.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Frank J Rauscher III for his critical reading and insightful suggestions, and Xinyu Hou for her technical support. This work was supported by the Ministry of Sciences & Technology of China (2013CB 910900); the National Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 81372309, 81402376, 31671415, 31601114, 81402177); Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (13JC1401302, 15410724200); Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. 201440426); and Science and Technology Commission of Changning District of Shanghai No. CNKW2014F01); and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015M570369).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, H., Song, L., Cong, Q. et al. The LIM protein AJUBA promotes colorectal cancer cell survival through suppression of JAK1/STAT1/IFIT2 network. Oncogene 36, 2655–2666 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.418
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.418
This article is cited by
-
The diagnostic/prognostic roles and biological function of the IFIT family members in acute myeloid leukemia
BMC Medical Genomics (2023)
-
Direct and indirect effects of IFN-α2b in malignancy treatment: not only an archer but also an arrow
Biomarker Research (2022)
-
IFNγ signaling integrity in colorectal cancer immunity and immunotherapy
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2022)
-
Nuclear translocation of Gasdermin D sensitizes colorectal cancer to chemotherapy in a pyroptosis-independent manner
Oncogene (2022)
-
Targeting cancer stem cell pathways for cancer therapy
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2020)