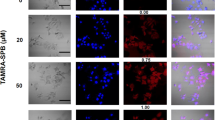
Abstract
Using our model to grow superficial human bladder cancer in the mouse bladder, we have found that the polyamide compound, Syn3, when injected intravesically for 1 hour at 1 mg/mL on two consecutive days, markedly increases rAd-β-gal intravesical gene transfer and expression. This enhanced transgene expression was much greater than obtain by the use of 22% ethanol, which had previously been shown to increase intravesical adenoviral gene transfer, whereas little or no gene expression was seen with exposure to only rAd-β-gal. β-Galactosidase staining was seen in virtually every normal urothelial and superficial tumor cell present, including tumors that express little or no coxsackie–adenovirus receptors when Syn3 was present. High adenoviral-mediated gene transfer was also documented in the pig bladder using Syn3 in a similar protocol. Therefore, Syn3 may overcome the limitations of adequate intravesical adenoviral-mediated gene transfer and, when combined with an appropriate adenoviral-mediated gene, could offer an effective approach to the treatment of superficial bladder cancer and perhaps even genetically altered precursor lesions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dalbagni G, Herr HW . Current use and questions concerning intravesical bladder cancer for superficial bladder cancer Urol Clin North Am 2000 27: 37–146
Herr HW . Tumor progression and survival in patients with T1G3 bladder tumors: 15 years outcome Br J Urol 1997 80: 762–765
Herr HW . Tumor progression and survival of patients with high grade, noninvasive papillary (TaG3) tumors: 15 year outcome J Urol 2000 163: 60–61
Watanabe T, Shinohara N, Sazawa A et al. An improved intravesical model using human bladder cancer cell lines to optimize gene and other therapies Cancer Gene Ther 2000 7: 1575–1580
Lilly JD, Parsons CL . Bladder surface glycosaminoglycans is a human epithelial permeability barrier Surg Gynecol Obstet 1990 171: 493–496
Nickel JC . Relative efficacy of various exogenous glycosaminoglycans in providing a bladder surface permeability barrier J Urol 1998 160: 612–614
Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G et al. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5 Science 1997 275: 1320–1323
Li Y, Pong RC, Bergelson JM et al. Loss of adenoviral receptor expression in human bladder cancer cells: a potential impact on the efficacy of gene therapy Cancer Res 1997 59: 325–330
Connor RJ, Engler H, Machemer T et al. Identification of polyamides that enhance adenovirus-mediated gene expression in the urothelium Gene Ther 2001 8: 41–48
Czerniak B, Li L, Chaturvedi V, Johnston DA, Benedict WF . Genetic modeling of urinary bladder carcinogenesis Genes, Chromosomes Cancer 2000 27: 392–402
Engler H, Anderson SC, Machemer T et al. Ethanol improves adenovirus-mediated gene transfer and expression to the bladder epithelium of rodents Urology 1999 53: 1049–1053
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the Retina Research Foundation and Tobacco Settlement Funds as appropriated by the Texas State Legislature. It was also supported by the Bladder SPORE Grant, the MD Anderson Core Grant CA16672 from the NCI, and a grant from the American Foundation of Urological Disease. We also thank P Ihnat and L Wichey-Lakshmanan for providing Syn3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, M., Rosser, C., Zhou, JH. et al. Syn3 provides high levels of intravesical adenoviral-mediated gene transfer for gene therapy of genetically altered urothelium and superficial bladder cancer. Cancer Gene Ther 9, 687–691 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700488
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700488
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Nadofaragene firadenovec in high-risk Bacillus Calmette Guérin unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a profile of its use
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives (2024)
-
Recurrence mechanisms of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer — a clinical perspective
Nature Reviews Urology (2022)
-
Effectiveness of two different dose administration regimens of an IL-15 superagonist complex (ALT-803) in an orthotopic bladder cancer mouse model
Journal of Translational Medicine (2019)
-
The development of interferon-based gene therapy for BCG unresponsive bladder cancer: from bench to bedside
World Journal of Urology (2019)
-
Current Clinical Trials in Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Current Urology Reports (2018)