Abstract
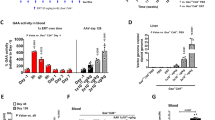
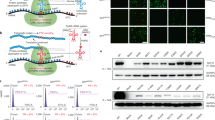
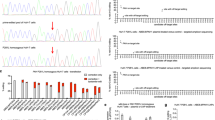
Treatment of many inherited liver enzyme deficiencies requires the removal of toxic intermediate metabolites from the blood of affected individuals. We propose that circulating toxins can be adequately cleared and disease phenotype influenced by enzyme expressed in tissues other than the liver. Phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) activity was constitutively expressed in skeletal and cardiac muscle of transgenic mice which carried the PAH cDNA under the transcriptional control of the mouse muscle creatine kinase promoter. Muscle PAH-expressing mice were bred to liver PAH-deficient, hyperphenylalaninemic mice to yield progeny that lack PAH activity in liver but express PAH in muscle. These mice exhibited hyperphenylalaninemia at baseline, but serum phenylalanine levels decreased significantly when the mice were supplemented with tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a required cofactor for PAH. This is the first demonstration that a liver-specific enzyme, when expressed in a heterologous tissue and supplied with necessary cofactors, can effectively clear toxic metabolites from the circulation of individuals with inherited enzyme deficiency. This result suggests that gene therapy targeted to heterologous tissues, such as muscle, will be effective in the treatment of selected inborn errors of metabolism.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harding, C., Wild, K., Chang, D. et al. Metabolic engineering as therapy for inborn errors of metabolism – development of mice with phenylalanine hydroxylase expression in muscle. Gene Ther 5, 677–683 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300653
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300653
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Pharmacologic inhibition of L‐tyrosine degradation ameliorates cerebral dopamine deficiency in murine phenylketonuria (PKU)
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2014)
-
Clinical therapeutics for phenylketonuria
Drug Delivery and Translational Research (2012)
-
Long‐term correction of murine phenylketonuria by viral gene transfer: liver versus muscle
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2010)
-
What we know that could influence future treatment of phenylketonuria
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2009)
-
Correction of Murine PKU Following AAV-mediated Intramuscular Expression of a Complete Phenylalanine Hydroxylating System
Molecular Therapy (2008)