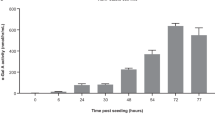
Abstract
The deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase (G6Pase) underlies life-threatening hypoglycemia and growth retardation in glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD-Ia). An adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector encoding G6Pase was pseudotyped as AAV8 and administered to 2-week-old GSD-Ia mice (n=9). Median survival was prolonged to 7 months following vector administration, in contrast to untreated GSD-Ia mice that survived for only 2 weeks. Although GSD-Ia mice were initially growth-retarded, treated mice increased fourfold in weight to normal size. Blood glucose was partially corrected by 2 weeks following treatment, whereas blood cholesterol normalized. Glucose-6-phosphatase activity was partially corrected to 25% of the normal level at 7 months of age in treated mice, and blood glucose during fasting remained lower in treated, affected mice than in normal mice. Glycogen storage was partially corrected in the liver by 2 weeks following treatment, but reaccumulated to pre-treatment levels by 7 months old (m.o.). Vector genome DNA decreased between 3 days and 3 weeks in the liver following vector administration, mainly through the loss of single-stranded genomes; however, double-stranded vector genomes were more stable. Although CD8+ lymphocytic infiltrates were present in the liver, partial biochemical correction was sustained at 7 m.o. The development of efficacious AAV vector-mediated gene therapy could significantly reduce the impact of long-term complications in GSD-Ia, including hypoglycemia, hyperlipidemia and growth failure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Chen Y-T . Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds). The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill: New York, 2001, pp 1521–1551.
Talente GM, Coleman RA, Alter C, Baker L, Brown BI, Cannon RA et al. Glycogen storage disease in adults. Ann Intern Med 1994; 120: 218–226.
Kishnani P, Bengur AR, Chen YT . Pulmonary hypertension in glycogen storage disease type I. J Inherit Metab Dis 1996; 19: 213–216.
Lei KJ, Chen H, Pan CJ, Ward JM, Mosinger Jr B, Lee EJ et al. Glucose-6-phosphatase dependent substrate transport in the glycogen storage disease type-1a mouse. Nat Genet 1996; 13: 203–209.
Zingone A, Hiraiwa H, Pan CJ, Lin B, Chen H, Ward JM et al. Correction of glycogen storage disease type 1a in a mouse model by gene therapy. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 828–832.
Sun MS, Pan CJ, Shieh JJ, Ghosh A, Chen LY, Mansfield BC et al. Sustained hepatic and renal glucose-6-phosphatase expression corrects glycogen storage disease type Ia in mice. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 11: 2155–2164.
Beaty RM, Jackson M, Peterson D, Bird A, Brown T, Benjamin Jr DK et al. Delivery of glucose-6-phosphatase in a canine model for glycogen storage disease, type Ia, with adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors. Gene Therapy 2002; 9: 1015–1022.
Trinh KY, O'Doherty RM, Anderson P, Lange AJ, Newgard CB . Perturbation of fuel homeostasis caused by overexpression of the glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit in liver of normal rats. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 31615–31620.
Keller KM, Schutz M, Podskarbi T, Bindl L, Lentze MJ, Shin YS . A new mutation of the glucose-6-phosphatase gene in a 4-year-old girl with oligosymptomatic glycogen storage disease type 1a. J Pediatr 1998; 132: 360–361.
Gao GP, Alvira MR, Wang L, Calcedo R, Johnston J, Wilson JM . Novel adeno-associated viruses from rhesus monkeys as vectors for human gene therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 11854–11859.
Nakai H, Fuess S, Storm TA, Muramatsu S, Nara Y, Kay MA . Unrestricted hepatocyte transduction with adeno-associated virus serotype 8 vectors in mice. J Virol 2005; 79: 214–224.
Sun B, Zhang H, Franco LM, Young SP, Schneider A, Bird A et al. Efficacy of an adeno-associated virus 8-pseudotyped vector in glycogen storage disease type II. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 57–65.
Ghosh A, Allamarvdasht M, Pan CJ, Sun MS, Mansfield BC, Byrne BJ et al. Long-term correction of murine glycogen storage disease type Ia by recombinant adeno-associated virus-1-mediated gene transfer. Gene Therapy 2006; 13: 321–329.
Kishnani PS, Faulkner E, VanCamp S, Jackson M, Brown T, Boney A et al. Canine model and genomic structural organization of glycogen storage disease type Ia (GSD Ia). Vet Pathol 2001; 38: 83–91.
Sokal EM, Lopez-Silvarrey A, Buts JP, Otte JB . Orthotopic liver transplantation for type I glycogenosis unresponsive to medical therapy. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1993; 16: 465–467.
Kirschner BS, Baker AL, Thorp FK . Growth in adulthood after liver transplantation for glycogen storage disease type I. Gastroenterology 1991; 101: 238–241.
Selby R, Starzl TE, Yunis E, Todo S, Tzakis AG, Brown BI et al. Liver transplantation for type I and type IV glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr 1993; 152 (Suppl 1): S71–S76.
Malatack JJ, Finegold DN, Iwatsuki S, Shaw Jr BW, Gartner JC, Zitelli BJ et al. Liver transplantation for type I glycogen storage disease. Lancet 1983; 1: 1073–1075.
Faivre L, Houssin D, Valayer J, Brouard J, Hadchouel M, Bernard O . Long-term outcome of liver transplantation in patients with glycogen storage disease type Ia. J Inherit Metab Dis 1999; 22: 723–732.
Matern D, Starzl TE, Arnaout W, Barnard J, Bynon JS, Dhawan A et al. Liver transplantation for glycogen storage disease types I, III, and IV. Eur J Pediatr 1999; 158 (Suppl 2): S43–S48.
Chen YT, Scheinman JI, Park HK, Coleman RA, Roe CR . Amelioration of proximal renal tubular dysfunction in type I glycogen storage disease with dietary therapy. N Engl J Med 1990; 323: 590–593.
Chen YT . Type I glycogen storage disease: kidney involvement, pathogenesis and its treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 1991; 5: 71–76.
Sriram G, Martinez JA, Mccabe ERB, Liao JC, Dipple KM . Single-gene disorders: what role could moonlighting enzymes play? Am J Hum Genet 2005; 76: 911–924.
Sirover MA . New nuclear functions of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in mammalian cells. J Cell Biochem 2005; 95: 45–52.
Shashidharan P, Chalmers-Redman RME, Carlile GW, Rodic V, Gurvich N, Yuen T et al. Nuclear translocation of GAPDH-GFP fusion protein during apoptosis. Neuroreport 1999; 10: 1149–1153.
Sirover MA . New insights into an old protein: the functional diversity of mammalian glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta-Prot Struct Mol Enzymol 1999; 1432: 159–184.
Damodaran TV, Bird A, Schneider A, Chen YT, Koeberl DD . Genomics of glycogen storage disease type I a (GSD-Ia): global gene expression analysis in glucose-treated and untreated glucose-6-phosphatase knock-out mice. American Society of Human Genetics 55th Annual Meeting 2005, (Abstr. 1442).
Franco LM, Krishnamurthy V, Bali D, Weinstein DA, Arn P, Clary B et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma in glycogen storage disease type Ia: a case series. J Inherit Metab Dis 2005; 28: 153–162.
Song S, Lu Y, Choi YK, Han Y, Tang Q, Zhao G et al. DNA-dependent PK inhibits adeno-associated virus DNA integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 2112–2116.
Franco LM, Sun B, Yang X, Bird A, Zhang H, Schneider A et al. Evasion of immune responses to introduced human acid alpha-glucosidase by liver-restricted expression in glycogen storage disease type II. Mol Ther 2005; 12: 876–884.
Davidoff AM, Gray JT, Ng CYC, Zhang YB, Zhou JF, Spence Y et al. Comparison of the ability of adeno-associated viral vectors pseudotyped with serotype 2, 5, and 8 capsid proteins to mediate efficient transduction of the liver in murine and nonhuman primate models. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 875–888.
Sun B, Zhang H, Franco LM, Brown T, Bird A, Schneider A et al. Correction of glycogen storage disease type II by an adeno-associated virus vector containing a muscle-specific promoter. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 889–898.
Muzyczka N . Use of adeno-associated virus as a general transduction vector for mammalian cells. Microbiol Immunol 1992; 158: 98–129.
Halbert CL, Standaert TA, Aitken ML, Alexander IE, Russell DW, Miller AD . Transduction by adeno-associated virus vectors in the rabbit airway: efficiency, persistence, and readministration. J Virol 1997; 71: 5932–5941.
Xiao W, Chirmule N, Berta SC, McCullough B, Gao G, Wilson JM . Gene therapy vectors based on adeno-associated virus type 1. J Virol 1999; 73: 3994–4003.
Wolfsdorf JI, Crigler Jr JF . Effect of continuous glucose therapy begun in infancy on the long-term clinical course of patients with type I glycogen storage disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999; 29: 136–143.
Brix AE, Howerth EW, McConkie-Rosell A, Peterson D, Egnor D, Wells MR et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ia in two littermate Maltese puppies. Vet Pathol 1995; 32: 460–465.
Chalmers RA, Lawson AM . Organic Acids in Man. Chapman and Hall: New York, 1982.
Overbergh L, Valckx D, Waer M, Mathieu C . Quantification of murine cytokine mRNAs using real time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. Cytokine 1999; 11: 305–312.
Acknowledgements
DDK was supported by the Children's Fund for GSD Research, the Association for Glycogen Storage Disease and P01 HL059314-08. DDK and YTC were supported by the Muscular Dystrophy Association and Genzyme Corporation. DKB received support from HD-044799-01. The AAV8 packaging plasmid, p5E18-VD 2/8, was provided courtesy of Dr James M Wilson at the University of Pennsylvania (Philadelphia, PA, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koeberl, D., Sun, B., Damodaran, T. et al. Early, sustained efficacy of adeno-associated virus vector-mediated gene therapy in glycogen storage disease type Ia. Gene Ther 13, 1281–1289 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302774
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302774
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Long‐term complications of glycogen storage disease type Ia in the canine model treated with gene replacement therapy
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2018)
-
Hepatic mitochondrial dysfunction is a feature of Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia (GSDIa)
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
In Vivo Zinc Finger Nuclease-mediated Targeted Integration of a Glucose-6-phosphatase Transgene Promotes Survival in Mice With Glycogen Storage Disease Type IA
Molecular Therapy (2016)
-
Large animal models and new therapies for glycogen storage disease
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2015)
-
Rescue administration of a helper-dependent adenovirus vector with long-term efficacy in dogs with glycogen storage disease type Ia
Gene Therapy (2012)