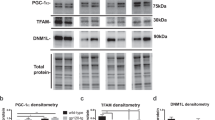
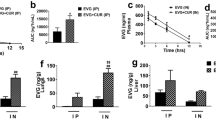
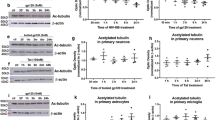
Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) infection in the central nervous system (CNS) may lead to neuronal loss and progressively deteriorating CNS function: HIV-1 gene products, especially gp120, induce free radical-mediated apoptosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), are among the potential mediators of these effects. Neurons readily form ROS after gp120 exposure, and so might be protected from ROS-mediated injury by antioxidant enzymes such as Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase (SOD1) and/or glutathione peroxidase (GPx1). Both enzymes detoxify oxygen free radicals. As they are highly efficient gene delivery vehicles for neurons, recombinant SV40-derived vectors were used for these studies. Cultured mature neurons derived from NT2 cells and primary fetal neurons were transduced with rSV40 vectors carrying human SOD1 and/or GPx1 cDNAs, then exposed to gp120. Apoptosis was measured by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Transduction efficiency of both neuron populations was >95%, as assayed by immunostaining. Transgene expression was also ascertained by Western blotting and direct assays of enzyme activity. Gp120 induced apoptosis in a high percentage of unprotected NT2-N. Transduction with SV(SOD1) and SV(GPx1) before gp120 challenge reduced neuronal apoptosis by >90%. Even greater protection was seen in cells treated with both vectors in sequence. Given singly or in combination, they protect neuronal cells from HIV-1-gp120 induced apoptosis. We tested whether rSV40 s can deliver antioxidant enzymes to the CNS in vivo: intracerebral injection of SV(SOD1) or SV(GPx1) into the caudate putamen of rat brain yielded excellent transgene expression in neurons. In vivo transduction using SV(SOD1) also protected neurons from subsequent gp120-induced apoptosis after injection of both into the caudate putamen of rat brain. Thus, SOD1 and GPx1 can be delivered by SV40 vectors in vitro or in vivo. This approach may merit consideration for therapies in HIV-1-induced encephalopathy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Major EO, Rausch D, Marra C, Clifford D . HIV-associated dementia. Science 2000; 288: 440–442.
Price RW, Brew B, Sidtis J, Rosenblum M, Scheck AC, Cleary P . The brain in AIDS: central nervous system HIV-1 infection and AIDS dementia complex. Science 1988; 239: 586–592.
Dore GJ, Hoy JF, Mallal SA, Li Y, Mijch AM, French MA et al. Trends in incidence of AIDS illnesses in Australia from 1983 to 1994: the Australian AIDS cohort. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol 1997; 16: 39–43.
Ferrando S, van Gorp W, McElhiney M, Goggin K, Sewell M, Rabkin J . Highly active antiretroviral treatment in HIV infection: benefits for neuropsychological function. AIDS 1998; 12: F65–F70.
Dore GJ, Correll PK, Li Y, Kaldor JM, Cooper DA, Brew BJ . Changes to AIDS dementia complex in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. AIDS 1999; 13: 1249–1253.
Ellis RJ, Deutsch R, Heaton RK, Marcotte TD, McCutchan JA, Nelson JA et al. Neurocognitive impairment is an independent risk factor for death in HIV infection. San Diego HIV Neurobehavioral Research Center Group. Arch Neurol 1997; 54: 416–424.
Cicala C, Arthos J, Rubbert A, Selig S, Wildt K, Cohen OJ et al. HIV-1 envelope induces activation of caspase-3 and cleavage of focal adhesion kinase in primary human CD4(+) T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 1178–1183.
Twu C, Liu NQ, Popik W, Bukrinsky M, Sayre J, Roberts J et al. Cardiomyocytes undergo apoptosis in human immunodeficiency virus cardiomyopathy through mitochondrion- and death receptor-controlled pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 14386–14391.
Catani MV, Corasaniti MT, Navarra M, Nistico G, Finazzi-Agro A, Melino G . gp120 induces cell death in human neuroblastoma cells through the CXCR4 and CCR5 chemokine receptors. J Neurochem 2000; 74: 2373–2379.
Garden GA, Guo W, Jayadev S, Tun C, Balcaitis S, Choi J et al. HIV associated neurodegeneration requires p53 in neurons and microglia. FASEB J 2004; 18: 1141–1143.
Xu Y, Kulkosky J, Acheampong E, Nunnari G, Sullivan J, Pomerantz RJ . HIV-1-mediated apoptosis of neuronal cells: Proximal molecular mechanisms of HIV-1-induced encephalopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 7070–7075.
Koenig S, Gendelman HE, Orenstein JM, Dal Canto MC, Pezeshkpour GH, Yungbluth M et al. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science 1986; 233: 1089–1093.
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Boyes BE, McGeer EG . Reactive microglia are positive for HLA-DR in the substantia nigra of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease brains. Neurology 1988; 38: 1285–1291.
Wahl SM, Allen JB, McCartney-Francis N, Morganti-Kossmann MC, Kossmann T, Ellingsworth L et al. Macrophage- and astrocyte-derived transforming growth factor beta as a mediator of central nervous system dysfunction in acquired immune deficiency syndrome. J Exp Med 1991; 173: 981–991.
Meucci O, Fatatis A, Simen AA, Bushell TJ, Gray PW, Miller RJ . Chemokines regulate hippocampal neuronal signaling and gp120 neurotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14500–14505.
Regulier EG, Reiss K, Khalili K, Amini S, Zagury JF, Katsikis PD et al. T-cell and neuronal apoptosis in HIV infection: implications for therapeutic intervention. Int Rev Immunol 2004; 23: 25–59.
Kaul M, Lipton SA . Chemokines and activated macrophages in HIV gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 8212–8216.
Kruman II, Nath A, Mattson MP . HIV-1 protein Tat induces apoptosis of hippocampal neurons by a mechanism involving caspase activation, calcium overload, and oxidative stress. Exp Neurol 1998; 154: 276–288.
Itoh K, Mehraein P, Weis S . Neuronal damage of the substantia nigra in HIV-1 infected brains. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2000; 99: 376–384.
Brooke S, Chan R, Howard S, Sapolsky R . Endocrine modulation of the neurotoxicity of gp120: implications for AIDS-related dementia complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 9457–9462.
Lipton SA, Choi YB, Pan ZH, Lei SZ, Chen HS, Sucher NJ et al. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 1993; 364: 626–632.
Brenneman DE, Westbrook GL, Fitzgerald SP, Ennist DL, Elkins KL, Ruff MR et al. Neuronal cell killing by the envelope protein of HIV and its prevention by vasoactive intestinal peptide. Nature 1988; 335: 639–642.
Lipton SA, Sucher NJ, Kaiser PK, Dreyer EB . Synergistic effects of HIV coat protein and NMDA receptor-mediated neurotoxicity. Neuron 1991; 7: 111–118.
Dreyer EB, Kaiser PK, Offermann JT, Lipton SA . HIV-1 coat protein neurotoxicity prevented by calcium channel antagonists. Science 1990; 248: 364–367.
Mollace V, Nottet HS, Clayette P, Turco MC, Muscoli C, Salvemini D et al. Oxidative stress and neuroAIDS: triggers, modulators and novel antioxidants. Trends Neurosci 2001; 24: 411–416.
Hensley K, Tabatabaie T, Stewart CA, Pye Q, Floyd RA . Nitric oxide and derived species as toxic agents in stroke, AIDS dementia, and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Chem Res Toxicol 1997; 10: 527–532.
Kimura T, Kameoka M, Ikuta K . Amplification of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic cells by HIV-1 infection. FEBS Lett 1993; 326: 232–236.
Coyle JT, Puttfarcken P . Oxidative stress, glutamate, and neurodegenerative disorders. Science 1993; 262: 689–695.
Treitinger A, Spada C, Verdi JC, Miranda AF, Oliveira OV, Silveira MV et al. Decreased antioxidant defence in individuals infected by the human immunodeficiency virus. Eur J Clin Invest 2000; 30: 454–459.
Piedimonte G, Guetard D, Magnani M, Corsi D, Picerno I, Spataro P et al. Oxidative protein damage and degradation in lymphocytes from patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Infect Dis 1997; 176: 655–664.
Aukrust P, Svardal AM, Muller F, Lunden B, Berge RK, Ueland PM et al. Increased levels of oxidized glutathione in CD4+ lymphocytes associated with disturbed intracellular redox balance in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Blood 1995; 86: 258–267.
Beckman JS, Koppenol WH . Nitric oxide, superoxide, and peroxynitrite: the good, the bad, and ugly. Am J Physiol 1996; 271: C1424–C1437.
Bonfoco E, Krainc D, Ankarcrona M, Nicotera P, Lipton SA . Apoptosis and necrosis: two distinct events induced, respectively, by mild and intense insults with N-methyl-D-aspartate or nitric oxide/superoxide in cortical cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 7162–7166.
Chao CC, Hu S, Peterson PK . Glia, cytokines, and neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Neurobiol 1995; 9: 189–205.
Owuor ED, Kong AN . Antioxidants and oxidants regulated signal transduction pathways. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64: 765–770.
Paolicchi A, Dominici S, Pieri L, Maellaro E, Pompella A . Glutathione catabolism as a signaling mechanism. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64: 1027–1035.
BouHamdan M, Duan LX, Pomerantz RJ, Strayer DS . Inhibition of HIV-1 by an anti-integrase single-chain variable fragment (SFv): delivery by SV40 provides durable protection against HIV-1 and does not require selection. Gene Therapy 1999; 6: 660–666.
Goldstein H, Pettoello-Mantovani M, Anderson CM, Cordelier P, Pomerantz RJ, Strayer DS . Gene therapy using a simian virus 40-derived vector inhibits the development of in vivo human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of severe combined immunodeficiency mice implanted with human fetal thymic and liver tissue. J Infect Dis 2002; 185: 1425–1430.
Strayer DS, Kondo R, Milano J, Duan LX . Use of SV40-based vectors to transduce foreign genes to normal human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Gene Therapy 1997; 4: 219–225.
Strayer DS, Zern MA . Gene delivery to the liver using simian virus 40-derived vectors. Semin Liver Dis 1999; 19: 71–81.
Strayer DS, Lamothe M, Wei D, Milano J, Kondo R . Generation of recombinant SV40 vectors for gene transfer. Methods Mol Biol 2001; 165: 103–117.
Kondo R, Feitelson MA, Strayer DS . Use of SV40 to immunize against hepatitis B surface antigen: implications for the use of SV40 for gene transduction and its use as an immunizing agent. Gene Therapy 1998; 5: 575–582.
Shi B, De Girolami U, He J, Wang S, Lorenzo A, Busciglio J et al. Apoptosis induced by HIV-1 infection of the central nervous system. J Clin Invest 1996; 98: 1979–1990.
Tabatabaie T, Stewart C, Pye Q, Kotake Y, Floyd RA . In vivo trapping of nitric oxide in the brain of neonatal rats treated with the HIV-1 envelope protein gp 120: protective effects of alpha-phenyl-tert-butylnitrone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 386–390.
Pleasure SJ, Page C, Lee VM . Pure, postmitotic, polarized human neurons derived from NTera 2 cells provide a system for expressing exogenous proteins in terminally differentiated neurons. J Neurosci 1992; 12: 1802–1815.
Busciglio J, Yeh J, Yankner BA . beta-Amyloid neurotoxicity in human cortical culture is not mediated by excitotoxins. J Neurochem 1993; 61: 1565–1568.
Jana A, Pahan K . Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 induces apoptosis in human primary neurons through redox-regulated activation of neutral sphingomyelinase. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 9531–9540.
Klein RS, Williams KC, Alvarez-Hernandez X, Westmoreland S, Force T, Lackner AA et al. Chemokine receptor expression and signaling in macaque and human fetal neurons and astrocytes: implications for the neuropathogenesis of AIDS. J Immunol 1999; 163: 1636–1646.
Boven LA, Gomes L, Hery C, Gray F, Verhoef J, Portegies P et al. Increased peroxynitrite activity in AIDS dementia complex: implications for the neuropathogenesis of HIV-1 infection. J Immunol 1999; 162: 4319–4327.
Shin HK, Lee JH, Kim CD, Kim YK, Hong JY, Hong KW . Prevention of impairment of cerebral blood flow autoregulation during acute stage of subarachnoid hemorrhage by gene transfer of Cu/Zn SOD-1 to cerebral vessels. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2003; 23: 111–120.
Watanabe Y, Chu Y, Andresen JJ, Nakane H, Faraci FM, Heistad DD . Gene transfer of extracellular superoxide dismutase reduces cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2003; 34: 434–440.
Ralph GS, Binley K, Wong LF, Azzouz M, Mazarakis ND . Gene therapy for neurodegenerative and ocular diseases using lentiviral vectors. Clin Sci (London) 2006; 110: 37–46.
Barkats M, Millecamps S, Abrioux P, Geoffroy MC, Mallet J . Overexpression of glutathione peroxidase increases the resistance of neuronal cells to Abeta-mediated neurotoxicity. J Neurochem 2000; 75: 1438–1446.
Ridet JL, Bensadoun JC, Deglon N, Aebischer P, Zurn AD . Lentivirus-mediated expression of glutathione peroxidase: neuroprotection in murine models of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Dis 2006; 21: 29–34.
Hoehn B, Yenari MA, Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK . Glutathione peroxidase overexpression inhibits cytochrome C release and proapoptotic mediators to protect neurons from experimental stroke. Stroke 2003; 34: 2489–2494.
Wang H, Cheng E, Brooke S, Chang P, Sapolsky R . Over-expression of antioxidant enzymes protects cultured hippocampal and cortical neurons from necrotic insults. J Neurochem 2003; 87: 1527–1534.
Chang P, Cheng E, Brooke S, Sapolsky R . Marked differences in the efficacy of post-insult gene therapy with catalase versus glutathione peroxidase. Brain Res 2005; 1063: 27–31.
Droge W, Holm E . Role of cysteine and glutathione in HIV infection and other diseases associated with muscle wasting and immunological dysfunction. FASEB J 1997; 11: 1077–1089.
Cordelier P, Van Bockstaele E, Calarota SA, Strayer DS . Inhibiting AIDS in the central nervous system: gene delivery to protect neurons from HIV. Mol Ther 2003; 7: 801–810.
Strayer DS . SV40 as an effective gene transfer vector in vivo. J Biol Chem 1996; 271: 24741–24746.
Strayer D, Branco F, Zern MA, Yam P, Calarota SA, Nichols CN et al. Durability of transgene expression and vector integration: recombinant SV40-derived gene therapy vectors. Mol Ther 2002; 6: 227–237.
Cordelier P, Calarota SA, Pomerantz RJ, Xiaoshan J, Strayer DS . Inhibition of HIV-1 in the central nervous system by IFN-alpha2 delivered by an SV40 vector. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2003; 23: 477–488.
Strayer DS, Akkina R, Bunnell BA, Dropulic B, Planelles V, Pomerantz RJ et al. Current status of gene therapy strategies to treat HIV/AIDS. Mol Ther 2005; 11: 823–842.
Strayer DS, Cordelier P, Kondo R, Liu B, Matskevich AA, McKee HJ et al. What they are, how they work and why they do what they do? The story of SV40-derived gene therapy vectors and what they have to offer. Curr Gene Ther 2005; 5: 151–165.
Sauter BV, Parashar B, Chowdhury NR, Kadakol A, Ilan Y, Singh H et al. A replication-deficient rSV40 mediates liver-directed gene transfer and a long-term amelioration of jaundice in gunn rats. Gastroenterology 2000; 119: 1348–1357.
Mitchell CB, Strayer D . Titering gene delivery vectors by QPCR: application to rSV40-derived vectors. Mol Ther 2005; 11: S69, Abstract#175.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH Grants MH70287, MH69122, AI48244, and AI41399. The authors appreciate the encouragement and advice of several colleagues in formulating and executing these studies: Drs Pierre Cordelier, Kathy Kopnisky, Roger J Pomerantz, Diane Rausch and Elena Marusich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, L., Louboutin, JP., Reyes, B. et al. Antioxidant enzyme gene delivery to protect from HIV-1 gp120-induced neuronal apoptosis. Gene Ther 13, 1645–1656 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302821
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302821
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The nature and nurture of cell heterogeneity: accounting for macrophage gene-environment interactions with single-cell RNA-Seq
BMC Genomics (2017)
-
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Promotes Mitochondrial Toxicity
Neurotoxicity Research (2017)
-
Intracisternal rSV40 administration provides effective pan-CNS transgene expression
Gene Therapy (2012)
-
Gene transfer to the rhesus monkey brain using SV40-derived vectors is durable and safe
Gene Therapy (2011)
-
Efficient CNS gene delivery by intravenous injection
Nature Methods (2010)