Abstract
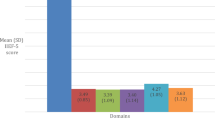
The association between hypogonadism, quality of life (QoL), and erectile dysfunction (ED) among the middle-aged and aged male in Taiwan is evaluated. A total of 680 study subjects aged ⩾40 years old were recruited from Northern (n=276), Middle (n=238), and Southern (n=202) Taiwan, respectively. ED was diagnosed by score of International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF-5). Taiwan version questionnaire for QoL includes domain 1 (physical domain), domain 2 (psychological domain), domain 3 (social relationship domain), and domain 4 (environmental domain) was used to measure QoL. Blood hormones, including FSH, LH, Prolactin, SHBG, total testosterone (TT), calculated free testosterone (cFT), and bioavailable testosterone (Bio-T), were determined. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate crude and multivariate-adjusted odds ratio of risk factors and its 95% confidence interval. A significantly inverse association between concentration of serum cFT and Bio-T, and severity of ED was observed. Scores of QoL of Domain 1–4 were significantly decreased with the increament of severity of ED. Significant correlations were found between IIEF scores and four domains of QoL, respectively. After adjustment for age, cFT and Bio-T, study subjects with ED (IIEF⩽21) would have significantly high risk of low level of QoL in four domains. In conclusion, a significant association between low levels of serum calculated cFT, Bio-T, and severity of ED was found. In addition, abnormal erectile function significantly associated with low level of QoL in four domains.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jardin A, Wagner G, Khoury S, Giuliano I, Padma-Nathan H, Rosen R (eds). Erectile dysfunction. First International Consultation on Erectile Dysfunction, Paris, 1–3 July 1999. Health Publications Ltd.: Plymouth 2000.
Wespes E, Amar E, Hatzichristou D, Montorsi F, Pryor J, Vardi Y . Guidelines on erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2002; 41: 1–5.
Wein AJ, van Arsdalen K . Drug-induced male sexual dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am 1988; 15: 23–31.
Araujo AB, Durante R, Feldman HA, Goldstein I, McKinlay JB . The relationship between depressive sympotoms and male erectile dysfunction: cross-sectional results from the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. Psychosom Med 1998; 60: 458–465.
Salonia A, Briganti A, Deho F, Naspro R, Scapaticci E, Scattoni V et al Pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction. Int J Androl 2003; 26: 129–136.
Burris AS, Banks SM, Carter CS, Davidson JM, Sherins RJ . A long-term prospective study of the physiologic and behavioural effects of hormone replacement in untreated hypogonadal men. J Androl 1992; 13: 297–304.
Feldman HA, Longcope C, Derby CA, Johannes CB, Araujo AB, Coviello AD et al Age trends in the level of serum testosterone and other hormones in middle-aged men: longitudinal results from the Massachusetts Male Aging study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002; 87: 589–598.
Vermeulen A . Androgens in the aging male. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991a; 73: 221–224.
Ahn AS, Park CM, Lee SW . The clinical relevance of sex hormone levels and sexual activity in the aging male. BJU Int 2000; 89: 526–530.
Schipper H, Clinch JJ, Olweny CLM . Quality of life studies: definitions and conceptual issues. In: Spilker B (ed). Quality of Life and Pharmacoeconomics in Clinical Trials. Lippen-cott-Raven: Philadelphia, PA, 1996, pp 11–23.
Stewart AL, Greenfield S, Hays RD, Wells K, Rogers WH, Berry SD et al. Functional status and well-being of patients with chronic conditions. Results from the Medical Outcomes Study. JAMA 1989; 262: 907–913.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A . The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology 1997; 49: 822–830.
Morley JE, Charlton E, Patrick P, Kaiser FE, Cadeau P, McCready D et al Validation of a screening questionnaire for androgen deficiency in aging male. Metabolism 2000; 49: 1239–1242.
The WHOQOL Group. Development of the World Health Organization WHOQOL-BREF quality of life assessment. Psychol Med 1998; 28: 551–558.
The WHOQOL-Taiwan Group. Introduction to the development of the WHOQOL-Taiwan version. Chin J Public Health (Taipei) 2000; 19: 315–324.
Morales A, Buvat J, Gooren LJ, Guay AT, Kaufma JM, Tan HM et al Endocrine aspects of sexual dysfunction in men. J Sexual Med 2004; 1: 69–81.
Feldman HA, Goldstein I, Hatzichristou DG, Krane RJ, McKinlay JB . Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 1994; 151: 54–61.
Francois G, Marie CM, Anne T, Caroline R, Michel M, Patrick T . Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in France: results of an epidemiological survey of a representative sample of 1004 men. Eur Urol 2002; 42: 382–389.
Kongkanand A, Thai erectile dysfunction epidemiological study group. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Thailand. Int J Androl 2000; 23: 77–80.
Chen K, Wu C, Chiang H . Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in Taiwanese males: a statistical analysis of 5939 urological patients. New Taipei J Med 2001; 3: 239–244.
Sanchez-cruz JJ, Cabrera-Leon A, Martin-Morales A, Fernandez A, Burgos R, Rejas J . Male erectile dysfunction and health-related quality of life. Eur Urol 2003; 44: 245–253.
Althof SE, Cappelleri JC, Shpilsky A, Stecher V, Diuguid C, Sweeney M et al Treatment responsiveness of the self-esteem and relationship questionnaire in erectile dysfunction. Urology 2003; 61: 888–892.
Mak R, Backer G, Kornitzer M, Meyer J . Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction in a population-based study in Belgium. Eur Urol 2002; 41: 132–138.
Moreira EJ, Lobo C, Diament A, Nicolosi A, Glasser DB . Incidence of erectile dysfunction in men 40 to 69 years old: results from a population-based cohort study in Brazil. Uology 2003; 61: 431–436.
Mirone V, Imbimbo C, Bortolotti A, Cintio ED, Colli E, Landoni M . Cigarette smoking as risk factor for erectile dysfunction: results from an Italian epidemiological study. Eur Urol 2002; 41: 294–297.
Okulate G, Olayinka O, Dogunro AS . Erectile dysfunction: prevalence and relationship to depression, alcohol abuse and panic disorder. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2003; 25: 209–213.
Tsujimura A, Matsumiya K, Matsuoka Y, Takahashi T, Koga M, Iwasa A . Bioavailable testosterone with age and erectile dysfunction. J Urol 2003; 170: 2345–2347.
Morales A, Lunenfeld B . Investigation, treatment and monitoring of late-onset hypoganadism in males. Official recommendations of the International Society for the Study of the Aging Male. Aging Male 2002; 5: 74–86.
Derouet H, Lehmann J, Stamm B, Luhl C, Romer D, Georg T . Age dependent secretion of LH and ACTH in healthy men and patients with erectile dysfunction. Eur Urol 2002; 41: 144–154.
Acknowledgements
This study is in part financially supported by the Taiwanese Association of Andrology. With a collective collaboration, Drs HS Chiang, CR Yang, HC Wu, TL Wu, and SP Huang contributed to collect part of study subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A
Appendix A
WHOQOL-BREF: Taiwanese-adapted version
- Q1:
-
How would you rate your quality of life?
- Q2:
-
How satisfied are you with your health?
- Q3:
-
To what extent do you feel that physical pain prevents you from doing what you need to do?
- Q4:
-
How much medical treatment do you need to function in your daily life?
- Q5:
-
How much do you enjoy life?
- Q6:
-
To what extent do you feel your life to be meaningful?
- Q7:
-
How well are you able to concentrate?
- Q8:
-
How safe do you feel in your daily life?
- Q9:
-
How healthy is your physical environment?
- Q10:
-
Do you have enough energy for everyday life?
- Q11:
-
Are you able to accept your bodily appearance?
- Q12:
-
Do you have enough money to meet your needs?
- Q13:
-
How available to you is the information that you need in your day-to-day life?
- Q14:
-
To what extent do you have the opportunity for leisure activities?
- Q15:
-
How well are you able to get around?
- Q16:
-
How satisfied are you with your sleep?
- Q17:
-
How satisfied are you with your ability to perform your daily living activities?
- Q18:
-
How satisfied are you with your capacity for work?
- Q19:
-
How satisfied are you with yourself?
- Q20:
-
How satisfied are you with your personal relationships?
- Q21:
-
How satisfied are you with your sex life?
- Q22:
-
How satisfied are you with the support you get from your friends?
- Q23:
-
How satisfied are you with the conditions of your living place?
- Q24:
-
How satisfied are you with your access to health services?
- Q25:
-
How satisfied are you with your transport?
- Q26:
-
How often do you have negative feelings such as a blue mood, despair, anxiety, or depression?
- Q27:
-
Do you feel respected by others? (additional questionnaire for Taiwan version)
- Q28:
-
Are you usually able to get the things you like to eat? (additional questionnaire for Taiwan version)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hwang, T., Lo, HC., Tsai, TF. et al. Association among hypogonadism, quality of life and erectile dysfunction in middle-aged and aged male in Taiwan. Int J Impot Res 19, 69–75 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901480
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3901480
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A comparison of sexual desire in opiate-dependent men receiving methadone and buprenorphine maintenance treatment
Annals of General Psychiatry (2019)
-
Effect of long-acting testosterone undecanoate treatment on quality of life in men with testosterone deficiency syndrome: a double blind randomized controlled trial
Asian Journal of Andrology (2012)
-
Influence of serum testosterone on urinary continence and sexual activity in patients undergoing radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2010)
-
The relationship of serum and salivary cortisol levels to male sexual dysfunction as measured by the International Index of Erectile Function
International Journal of Impotence Research (2009)