Abstract
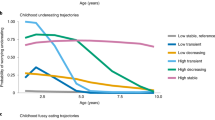
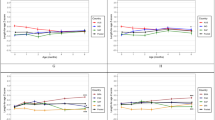
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the ability of maternally-rated infant temperament to predict fatness and activity patterns in early childhood. DESIGN: Longitudinal investigation of infants studied at 12 weeks and followed up at 2–3.5 y of age. SUBJECTS: Thirty healthy full-term infants from the general population. MEASUREMENTS: Body composition, behavioural activity and temperament at 12 weeks; anthropometry, body composition, diet and behavioural activity at follow-up. RESULTS: Infant temperament predicted later behaviour and fatness. Easily soothable infants had leaner childhood skinfold thicknesses (P<0.02) and were more active in childhood (P<0.025). Infant distress was also related to childhood diet composition. CONCLUSIONS: Infant temperament can predict later body composition and behaviour. Both energy intake and energy expenditure may be mechanisms by which the relationship develops.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wells, J., Stanley, M., Laidlaw, A. et al. Investigation of the relationship between infant temperament and later body composition. Int J Obes 21, 400–406 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800420
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0800420
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Protocol for iGrow (Infant Growth and Development Study): biopsychosocial predictors of childhood obesity risk at 2 years
BMC Public Health (2020)
-
Infant temperament and parent use of food to soothe predict change in weight-for-length across infancy: early risk factors for childhood obesity
International Journal of Obesity (2018)
-
Prenatal, birth and early life predictors of sedentary behavior in young people: a systematic review
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity (2016)
-
Obese parents – obese children? Psychological-psychiatric risk factors of parental behavior and experience for the development of obesity in children aged 0–3: study protocol
BMC Public Health (2013)
-
Joint Effects of Child Temperament and Maternal Sensitivity on the Development of Childhood Obesity
Maternal and Child Health Journal (2011)