Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The pharmacokinetic characteristics of human leptin were examined in rhesus monkeys and in C57BL/6J mice fed a normal chow or a high-fat diet.
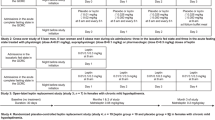
DESIGN: For the monkey study, in nine rhesus monkeys (body weight 12.4±2.4 kg; mean±s.d.), recombinant met-human leptin was injected intravenously or subcutaneously (1 mg/kg). For the mouse study, after 6 months of feeding C57BL/6J mice a high-fat diet (body weight 32.9±3.6 g; n=8) or a control diet (24.5±1.2 g; n=6), recombinant met-human leptin was administered intraperitoneally (10 μg/g). Blood samples were collected for leptin measurement at specific time points after leptin administration.
MEASUREMENTS: Plasma leptin concentrations were determined by radioimmunoassay and pharmacokinetic analysis was performed.
RESULTS: Disposition of human leptin in rhesus monkeys was biphasic following intravenous administration, with a terminal phase half-life of 96.4±16.5 min and clearance of 1.8±0.2 ml/min/kg. Subcutaneously administered leptin was absorbed slowly, perhaps by a zero-order process as leptin levels appeared to plateau and remained elevated throughout the 8 h sampling period. In C57BL/6J mice, the absorption and elimination of human leptin were both first-order following intraperitoneal administration. Pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ between normal-weight mice fed a chow diet and obese mice fed a high-fat diet. The elimination half-life was 47.0±26.4 min in mice fed a high-fat diet and 49.5±12.0 min in mice fed a control diet.
CONCLUSION: The kinetics of leptin in rhesus monkeys were biphasic and clearance was similar to values previously reported in humans. The estimated half-life was 96.4 min in rhesus monkeys and 49.5 min in normal weight mice. The was no difference in leptin kinetics between high-fat fed and control mice, suggesting that the increased baseline leptin levels in the obese mice are due to increased leptin production and secretion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM . Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue Nature 1994 372: 425–432.
Ahrén B, Larsson H, Wilhelmsson C, Näsman B, Olsson T . Regulation of circulating leptin in humans Endocrine 1997 7: 1–8.
Weigle DS, Duell PB, Connor WE, Steiner RA, Soules MR, Kuijper JL . Effect of fasting, refeeding, and dietary fat restriction on plasma leptin levels J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 561–565.
Dubuc GR, Phinney SD, Stern JS, Havel PJ . Changes of serum leptin and endocrine and metabolic parameters after 7 days of energy restriction in men and women Metabolism 1998 47: 429–434.
Keim NL, Stern JS, Havel PJ . Relation between circulating leptin concentrations and appetite during a prolonged, moderate energy deficit in women Am J Clin Nutr 1998 68: 794–801.
Blum WF . Leptin: the voice of the adipose tissue Horm Res 1997 48 (Suppl 4): 2–8.
Bray GA, York DA . Leptin and clinical medicine; a new piece in the puzzle of obesity J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1997 82: 2771–2776.
Dallongeville J, Fruchart JC, Auwerx J . Leptin, a pleiotropic hormone: physiology, pharmacology, and strategies for discovery of leptin modulators J Med Chem 1998 41: 5337–5352.
Havel PJ, Kasim-Karakas S, Mueller W, Johnson PR, Gingerich RL, Stern JS . Relationship of plasma leptin to plasma insulin and adiposity in normal weight and overweight women: effects of dietary fat content and sustained weight loss J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996 81: 4406–4413.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF . Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans New Engl J Med 1996 334: 292–2965.
Klein S, Coppack SW, Mohamed-Ali V, Landt M . Adipose tissue leptin production and plasma leptin kinetics in humans Diabetes 1996 45: 984–987.
Saad MF, Khan A, Sharma A, Michael R, Riad Gabriel MG, Boyadjian R, Jinagouda SD, Steil GM, Kamdar V . Physiological insulinemia acutely modulates plasma leptin Diabetes 1998 47: 544–549.
Havel PJ, Uriu Hare JY, Liu T, Stanhope KL . Stern JS, Keen CL, Ahrén B. Marked and rapid decreases of circulating leptin in streptozotocin diabetic rats: reversal by insulin Am J Physiol 1998 274: R1482–1491.
Mueller WM, Gregoire FM, Stanhope KL, Mobbs CV, Mizuno TM, Warden CH, Stern JS, Havel PJ . Evidence that glucose metabolism regulates leptin secretion from cultured rat adipocytes Endocrinology 1998 139: 551–558.
Larsson H, Elmståhl S, Ahrén B . Plasma leptin levels correlate to islet function independently of body fat in postmenopausal women Diabetes 1996 45: 1580–1584.
Ahrén B, Larsson H . Leptin—a regulator of islet function? Its plasma levels correlate to glucagon and insulin secretion in healthy women Metabolism 1997 46: 1477–1481.
Havel PJ, Townsend R, Chaump L, Teff K . High-fat meals reduce 24-h circulating leptin concentrations in women Diabetes 1999 48: 334–341.
Klein S, Coppack SW, Mohamed-Ali V, Landt M . Adipose tissue leptin production and plasma leptin kinetics in humans Diabetes 1996 45: 984–987.
Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros CS, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS . Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting Nature 1996 382: 250–252.
Van Heek M, Mullins DE, Wirth MA, Graziano MP, Fawzi AB, Comptons DS, France CF, Hoos LM, Casale RL, Syvertz EJ, Strader CD, Davis HR . The relationship of tissue localization, distribution and turnover to feeding after intraperitoneal 125I-leptin administration to ob/ob and db/db mice Horm Metab Res 1996 28: 653–658.
Vila R, Adan C, Rafecas I, Fernandez-Lopez JA, Remesar X, Alemany M . Plasma leptin turnover rates in lean and obese Zucker rats Endocrinology 1998 139: 4466–4469.
Ahrén B, Simonsson E, Scheurink AJW, Mulder H, Myrsén U, Sundler F . Dissociated insulinotropic sensitivity to glucose- and carbachol in high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in C57BL/6J mice Metabolism 1997 46: 97–106.
Ahrén B, Månsson S, Gingerich RL, Havel PJ . Regulation of plasma leptin in mice: influence of age, high-fat diet and fasting Am J Physiol 1997 273: R113–R120.
Ahrén B, Scheurink AJW . Marked hyperleptinemia after high-fat diet associated with severe glucose intolerance in mice Eur J Endocrinol 1998 139: 461–467.
Ahrén B . Plasma leptin and insulin in C547B1/6J mice on a high-fat diet: relation to subsequent changes in body weight Acta Physiol Scand 1999 165: 233–240.
Golub MS, Anderson JH . Adaptation of pregnant rhesus monkeys to short-term chair restraint Lab Anim Sci 1986 36: 507–511.
Ma ZA, Gingerich RL, Santiago JV, Klein S, Smith CH, Landt M . Radioimmunoassay of leptin in human plasma Clin Chem 1996 42: 942–946.
Gibaldi, Milo . Biopharmaceuticals and Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 4th ed Lea and Febiger: Malvern, PA 1991.
Cumin F, Baum HP, Levens N . Mechanism of leptin removal from the circulation by the kidney J Endocrinol 1997 155: 577–585.
Zeng J, Patterson BW, Klein S, Martin DR, Dagogo-Jack S, Kohrt WM, Miller SB, Landt M . Whole body leptin kinetics and renal metabolism in vivo Am J Physiol 1997 273: E1102–E1106.
Hill RA, Margetic S, Pegg GG, Gazzola C . Leptin: its pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998 22: 765–770.
Cumin F, Baum HP, de Gasparo M, Levens N . Removal of endogenous leptin from the circulation by the kidney Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1997 21: 495–504.
Meyer C, Robson D, Rackovsky N, Nadkarni V, Gerich J . Role of the kidney in human leptin metabolism Am J Physiol 1997 273: E903–E907.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr Landt for sharing his data, to Lilian Bengtsson and Lena Kvist for expert technical assistance and to Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, for providing the recombinant leptin for the experiments. The work was supported by grants from the Swedish Medical Research Council (grant no 14X-6834), Albert Påhlsson and Novo Nordic Foundations, Swedish Diabetes Association, Malmö University Hospital and the Faculty of Medicine, Lund University (BA), and NIH grants DK-50129 and DK-5747 and the American Diabetes Association (PJH). We would also like to thank Jenny Short, Sarah Davis, and Vanessa Bakula for their help in coordinating and conducting the primate studies and Dr Andrew G Hendrickx and the Venture Research Program (NIH RR-00169) of the California Regional Primate Research Center for supporting this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahrén, B., Baldwin, R. & Havel, P. Pharmacokinetics of human leptin in mice and rhesus monkeys. Int J Obes 24, 1579–1585 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801447
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0801447
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Animal models of obesity and diabetes mellitus
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2018)
-
Metreleptin: First Global Approval
Drugs (2013)
-
The potential role of glutamate in the current diabetes epidemic
Acta Diabetologica (2012)
-
Morbidly Obese are Ghrelin and Leptin Hyporesponders with Lesser Intragastric Balloon Treatment Efficiency
Obesity Surgery (2011)
-
Monitoring of stored and available fuel by the CNS: implications for obesity
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2003)