Abstract
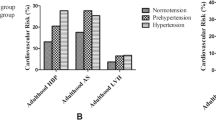
Blood pressure (BP) levels in the Finnish population are amongst the highest in the world, despite favourable changes at the national level in the past two decades. The study evaluates the familial aggregation of BP and the association of some environmental factors to the familial aggregation of BP as a primary epidemiological approach of the genetics of hypertension in a sample of families with young offspring from eastern Finland. Offspring aged 15 years were examined between 1996 and 1997 and their biological parents were examined between 1993 and 1994. A total of 224 children were invited, 184 families participated, from which 144 were included in the analysis with complete data. Systolic (SBP), diastolic (DBP) and mean (MAP) arterial BPs were the main outcome measurements. After the offspring’s gender and body mass index (BMI) and the parent’s age and BMI were controlled for, the mother/offspring correlation of SBP and the father/offspring correlation of MAP were statistically significant (r = 0.18, P = 0.039, n = 134 and r = 0.20, P = 0.048, n = 99, respectively). The additional adjustment for the parent’s education and family history of acute myocardial infarction did not change these results. There was a higher proportion of offspring in the highest quartile of SBP and MAP when the mother had a history of hypertension (OR = 3.4, 95% CI = 1.4–8.5, n = 139, and OR = 2.6, 95% CI = 1.0–6.5, n = 139, respectively). The study confirmed the familial aggregation of BP. The consistent BP association between the mother and the offspring may indicate the key role of the mother in the primary prevention of hypertension.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fuentes, R., Notkola, IL., Shemeikka, S. et al. Familial aggregation of blood pressure: a population-based family study in eastern Finland. J Hum Hypertens 14, 441–445 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001049
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001049
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Association of blood pressure and hypertension between parents and offspring: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Trans-ethnic meta-analysis identifies new loci associated with longitudinal blood pressure traits
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
The Relationship Between Psychosocial Status and Hypertensive Condition
Current Hypertension Reports (2018)
-
Controversies in epidemiology of intracranial aneurysms and SAH
Nature Reviews Neurology (2016)
-
Familial correlation and aggregation of body mass index and blood pressure in Chinese Han population
BMC Public Health (2013)