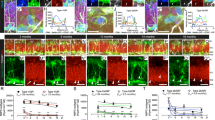
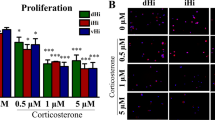
Abstract
An important question arising from previous observations in vivo is whether glucocorticoids can directly influence neuronal survival in the hippocampus. To this end, a primary postnatal hippocampal culture system containing mature neurons and expressing both glucocorticoid (GR) and mineralocorticoid (MR) receptors was developed. Results show that the GR agonist dexamethasone (DEX) targets neurons (microtubule-associated protein 2-positive cells) for death through apoptosis. GR-mediated cell death was counteracted by the MR agonist aldosterone (ALDO). Antagonism of MR with spironolactone ([7α-(acetylthio)-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21 carbolactone] (SPIRO)) causes a dose-dependent increase in neuronal apoptosis in the absence of DEX, indicating that nanomolar levels of corticosterone present in the culture medium, which are sufficient to activate MR, can mask the apoptotic response to DEX. Indeed, both SPIRO and another MR antagonist, oxprenoate potassium ((7α,17α)-17-hydroxy-3-oxo-7-propylpregn-4-ene-21-carboxylic acid, potassium salt (RU28318)), accentuated DEX-induced apoptosis. These results demonstrate that GRs can act directly to induce hippocampal neuronal death and that demonstration of their full apoptotic potency depends on abolition of survival-promoting actions mediated by MR.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E, Oitzl MS, Joels M . Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease. Endocr Rev 1998; 19: 269–301.
Gold PW, Chrousos GP . Organization of the stress system and its dysregulation in melancholic and atypical depression: high vs low CRH/NE states. Mol Psychiatry 2002; 7: 254–275.
Holsboer F . The corticosteroid receptor hypothesis of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000; 23: 477–501.
Reagan LP, McEwen BS . Controversies surrounding glucocorticoid-mediated cell death in the hippocampus. J Chem Neuroanat 1997; 13: 149–167.
Sapolsky RM . Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2000; 57: 925–935.
Lupien SJ, Nair NP, Briere S, Maheu F, Tu MT, Lemay M et al. Increased cortisol levels and impaired cognition in human aging: implication for depression and dementia in later life. Rev Neurosci 1999; 10: 117–139.
Sheline YI . 3D MRI studies of neuroanatomic changes in unipolar major depression: the role of stress and medical comorbidity. Biol Psychiatry 2000; 48: 791–800.
Starkman MN, Giordani B, Gebarski SS, Berent S, Schork MA, Schteingart DE . Decrease in cortisol reverses human hippocampal atrophy following treatment of Cushing's disease. Biol Psychiatry 1999; 46: 1595–1602.
Schubert MI, Kalisch K, Sotiropoulos I, Catania C, Sousa N, Almeida OFX et al. In vivo MR assessment of hippocampal volume and neurochemical changes in rats with altered corticosteroid milieu. Proc Int Soc Mag Res Med 2004; 12: 1445.
Magarinos AM, McEwen BS . Experimental diabetes in rats causes hippocampal dendritic and synaptic reorganization and increased glucocorticoid reactivity to stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 11056–11061.
Sousa N, Paula-Barbosa MM, Almeida OFX . Ligand and subfield specificity of corticoid-induced neuronal loss in the rat hippocampal formation. Neuroscience 1999; 89: 1079–1087.
Sousa N, Almeida OFX . Corticosteroids: sculptors of the hippocampal formation. Rev Neurosci 2002; 13: 59–84.
Almeida OFX, Condé GL, Crochemore C, Demeneix BA, Fischer D, Hassan AHS et al. Subtle shifts in the ratio between pro- and antiapoptotic molecules after activation of corticosteroid receptors decide neuronal fate. FASEB J 2000; 14: 779–790.
Hassan AHS, von Rosenstiel P, Patchev VK, Holsboer F, Almeida OFX . Exacerbation of apoptosis in the dentate gyrus of the aged rat by dexamethasone and the protective role of corticosterone. Exp Neurol 1996; 140: 43–52.
Fuchs E, Gould E . Mini-review: in vivo neurogenesis in the adult brain: regulation and functional implications. Eur J Neurosci 2000; 12: 2211–2214.
Reul JM, Gesing A, Droste S, Stec IS, Weber A, Bachmann C et al. The brain mineralocorticoid receptor: greedy for ligand, mysterious in function. Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 405: 235–249.
de Kloet ER, Oitzl MS, Joels M . Stress and cognition: are corticosteroids good or bad guys? Trends Neurosci 1999; 22: 422–426.
Sloviter RS, Dean E, Neubort S . Electron microscopic analysis of adrenalectomy-induced hippocampal granule cell degeneration in the rat: apoptosis in the adult central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 1993; 330: 324–336.
Sloviter RS, Sollas AL, Neubort S . Hippocampal dentate granule cell degeneration after adrenalectomy in the rat is not reversed by dexamethasone. Brain Res 1995; 682: 227–230.
Sousa N, Madeira MD, Paula-Barbosa MM . Corticosterone replacement restores normal morphological features to the hippocampal dendrites, axons and synapses of adrenalectomized rats. J Neurocytol 1999; 28: 541–558.
Hellbach S, Gartner P, Deicke J, Fischer D, Hassan AHS, Almeida OFX . Inherent glucocorticoid response potential of isolated hypothalamic neuroendocrine neurons. FASEB J 1998; 12: 199–207.
Liposits Z, Merchenthaler I, Wetsel WC, Reid JJ, Mellon PL, Weiner RI et al. Morphological characterization of immortalized hypothalamic neurons synthesizing luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone. Endocrinology 1991; 129: 1575–1583.
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA . Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 1992; 119: 493–501.
Beamen-Hall CM, Wainer BH, Eves E, Bohn MC . Expression of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in an immortalized hippocampal neuronal cell line. Brain Res 1996; 726: 141–152.
Crochemore C, Michaelidis TM, Fischer D, Loeffler JP, Almeida OFX . Enhancement of p53 activity and inhibition of neural cell proliferation by glucocorticoid receptor activation. FASEB J 2002; 16: 761–770.
Lucassen PJ, Vollmann-Honsdorf GK, Gleisberg M, Czeh B, De Kloet ER, Fuchs E . Chronic psychosocial stress differentially affects apoptosis in hippocampal subregions and cortex of the adult tree shrew. Eur J Neurosci 2001; 14: 161–166.
Elliott EM, Mattson MP, Vanderklish P, Lynch G, Chang I, Sapolsky RM . Corticosterone exacerbates kainate-induced alterations in hippocampal tau immunoreactivity and spectrin proteolysis in vivo. J Neurochem 1993; 61: 57–67.
Behl C, Lezoualc'h F, Trapp T, Widmann M, Skutella T, Holsboer F . Glucocorticoids enhance oxidative stress-induced cell death in hippocampal neurons in vitro. Endocrinology 1997; 138: 101–106.
Lu J, Sousa N, Almeida OFX . Paracrine regulation of proliferation in hippocampal and granule cells. 34th Annual Meeting of the Society of Neuroscience 2004, San Diego, CA (abstract 382.15).
Rosenfeld P, van Eekelen JA, Levine S, de Kloet ER . Ontogeny of corticosteroid receptors in the brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1993; 13: 295–319.
Vázquez DM . Stress and the developing limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1998; 23: 663–700.
Pearce D, Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Fejes-Toth G . Determinants of subnuclear organization of mineralocorticoid receptor characterized through analysis of wild type and mutant receptors. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 1451–1456.
Coirini H, Magarinos AM, De Nicola AF, Rainbow TC, McEwen BS . Further studies of brain aldosterone binding sites employing new mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor markers in vitro. Brain Res 1985; 361: 212–216.
Kim PJ, Cole MA, Kalman BA, Spencer RL . Evaluation of RU28318 and RU40555 as selective mineralocorticoid receptor and glucocorticoid receptor antagonists, respectively: receptor measures and functional studies. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 1998; 67: 213–222.
Alzamora R, Michea L, Marusic ET . Role of 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in nongenomic aldosterone effects in human arteries. Hypertension 2000; 35: 1099–1104.
Haynes LE, Griffiths MR, Hyde RE, Barber DJ, Mitchell IJ . Dexamethasone induces limited apoptosis and extensive sublethal damage to specific subregions of the striatum and hippocampus: implications for mood disorders. Neuroscience 2001; 104: 57–69.
Haynes LE, Lendon CL, Barber DJ, Mitchell IJ . 17-Beta-oestradiol attenuates dexamethasone-induced lethal and sublethal neuronal damage in the striatum and hippocampus. Neuroscience 2003; 120: 799–806.
Lu J, Goula D, Sousa N, Almeida OFX . Ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptor mediation of glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in hippocampal cells and the neuroprotective role of synaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Neuroscience 2003; 121: 123–131.
Sousa N, Madeira MD, Paula-Barbosa MM . Structural alterations of the hippocampal formation of adrenalectomized rats: an unbiased stereological study. J Neurocytol 1997; 26: 423–438.
Jaarsma D, Postema F, Korf J . Time course and distribution of neuronal degeneration in the dentate gyrus of rat after adrenalectomy: a silver impregnation study. Hippocampus 1992; 2: 143–150.
Hu Z, Yuri K, Ozawa H, Lu H, Kawata M . The in vivo time course for elimination of adrenalectomy-induced apoptotic profiles from the granule cell layer of the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 1997; 17: 3981–3989.
Welberg LA, Seckl JR . Prenatal stress, glucocorticoids and the programming of the brain. J Neuroendocrinol 2001; 13: 113–128.
Sousa N, Almeida OFX, Holsboer F, Paula-Barbosa MM, Madeira MD . Maintenance of hippocampal cell numbers in young and aged rats submitted to chronic unpredictable stress. Comparison with the effects of corticosterone treatment. Stress 1998; 2: 237.
Cameron HA, Woolley CS, Gould E . Adrenal steroid receptor immunoreactivity in cells born in the adult rat dentate gyrus. Brain Res 1993; 611: 342–346.
Reul JM, Gesing A, Droste S, Stec IS, Weber A, Bachmann C et al. The brain mineralocorticoid receptor: greedy for ligand, mysterious in function. Eur J Pharmacol 2000; 405: 235–249.
Woolley CS, Gould E, Sakai RR, Spencer RL, McEwen BS . Effects of aldosterone or RU28362 treatment on adrenalectomy-induced cell death in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Brain Res 1991; 554: 312–315.
Hornsby CD, Grootendorst J, de Kloet ER . Dexamethasone does not prevent seven-day ADX-induced apoptosis in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Stress 1996; 1: 51–64.
Nirde P, Terouanne B, Gallais N, Sultan C, Auzou G . Antimineralocorticoid 11beta-substituted spirolactones exhibit androgen receptor agonistic activity: a structure function study. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 59: 1307–1313.
Obradovic D, Tirard M, Nemethy Z, Hirsch O, Gronemeyer H, Almeida OFX . DAXX, FLASH, and FAF-1 modulate mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transcription in hippocampal cells—toward a basis for the opposite actions elicited by two nuclear receptors? Mol Pharmacol 2004; 65: 761–769.
Tirard M, Jasbinsek J, Almeida OFX, Michaelidis TM . The manifold actions of the protein inhibitor of activated STAT proteins on the transcriptional activity of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptors in neural cells. J Mol Endocrinol 2004; 32: 825–841.
Sousa N, Lukoyanov NV, Madeira MD, Almeida OF, Paula-Barbosa MM . Reorganization of the morphology of hippocampal neurites and synapses after stress-induced damage correlates with behavioral improvement. Neuroscience 2000; 97: 253–266.
Sapolsky RM, Meaney MJ . Maturation of the adrenocortical stress response: neuroendocrine control mechanisms and the stress hyporesponsive period. Brain Res 1986; 396: 64–76.
Acknowledgements
We thank Rosa Buric, Julia Deicke and Dieter Fischer for technical assistance. CC, JL, and YW were supported by fellowships from the Max Planck Society. The work was partly supported by the German Academic Exchange Service/Magyar Ösztöndij Bizottság (DAAD 323-PPP Ungarn), Acções Integradas Luso-Alemãs (DAAD-CRUP-ICCTI 314/Al-p-dr) and the European Commission (QLG3-CT-2000-00844).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crochemore, C., Lu, J., Wu, Y. et al. Direct targeting of hippocampal neurons for apoptosis by glucocorticoids is reversible by mineralocorticoid receptor activation. Mol Psychiatry 10, 790–798 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001679
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001679
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Is there a role for early postnatal steroids in very preterm infants exposed to chorioamnionitis?
Pediatric Research (2024)
-
Preterm lung and brain responses to mechanical ventilation and corticosteroids
Journal of Perinatology (2023)
-
11β-HSD1 participates in epileptogenesis and the associated cognitive impairment by inhibiting apoptosis in mice
Journal of Translational Medicine (2022)
-
Optimizing respiratory management in preterm infants: a review of adjuvant pharmacotherapies
Journal of Perinatology (2021)
-
Novel role for mineralocorticoid receptors in control of a neuronal phenotype
Molecular Psychiatry (2021)