Abstract
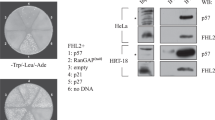
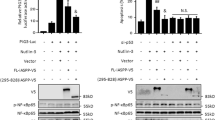
The nuclear factor κB, a transcription factor regulating the expression of multiple genes including genes essential for cell cycle control, is found in most cells in a dormant state in the cytoplasm bound to the inhibitory family IκB via an ankyrin repeat domain. Stimulation of cells with a variety of inducers inactivates IκB proteins. The active dimeric NF-κB complex, often composed of 50- and 65-kilodalton subunits of the Rel family, translocates into the nucleus, where the NF-κBp65 subunit stimulates transcription. Here we report that a family of proteins containing ankyrin repeats, the inhibitors of Cdk4 (INK4) is able to bind NF-κBp65. The association of p16INK4 with NF-κBp65 is considerable in HeLa- or 293 cells, if the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα is degraded in response to TNFα stimulation. Overexpression of INK4 molecules suppresses the transactivational ability of NF-κB significantly. In contrast to INK4 proteins, the cell cycle inhibitor p27 enhances NF-κB transactivation activity. Thus, the effect of INK4 proteins on NF-κB function possibly modifies NF-κB mediated transcriptional activation of cell cycle associated factors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin AJ, Azizkhan JC, Jensen DE, Beg AA and Coodly LR . 1991 Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 4943–4951.
Bash J, Zong WX and Gelinas C . 1997 Mol. Cell. Biol. 17: 6526–6535.
Baeuerle PA and Baichwal VR . 1997 Adv. Immun. 65: 111–137.
Blanard MA and Rutter WJ . 1992 Science 256: 1014–1018.
Bork P . 1993 Prot. Struct. Funct. Genet. 17: 363–374.
Caldas C, Hahn SA, da Costa LT, Redston MS, Schutte M, Seymour AB, Weinstein CL, Hruban RH, Yeo CJ and Kern SE . 1994 Nature Genetics 8: 27–32.
Chan FKM, Zhang J, Cheng L, Shapiro DN and Winoto A . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 2682–2688.
Della Ragione F, Russo GL, Oliva A, Mercurio C, Mastropietro S, Della Pietra V and Zappia V . 1996 J. Biol. Chem. 271: 15942–15949.
Duyao MP, Buckler AJ and Sonenshein GE . 1990 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 87: 4727–4731.
Gerritsen ME, Williams AJ, Neish AS, Moore S, Shi Y and Collins T . 1997 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94: 2927–2932.
Hatada EN, Nieters A, Wulczyn FG, Naumann M, Meyer R, Nucifora G, McKeithan TW and Scheidereit C . 1992 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 2489–2493.
Hatada EN, Naumann M and Scheidereit C . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 2781–2788.
Hirst K, Fisher F, McAndrew PC and Goding CR . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 5410–5420.
Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver-Feldhaus J, Liu Q, Harshman K, Tavtigian SV, Stockert E, Day III RS, Johnson BE and Skolnick MHA . 1994 Science 264: 436–440.
Low KG, Dorner LF, Fernando DB, Grossmann J, Jeang KT and Comb MJ . 1997 J. Virol. 71: 1956–1962.
Luh FY, Archer SJ, Domaille PJ, Smith BO, Owen D, Brotherton DH, Raine ARC, Xu X, Brizuela L, Brenner SL and Laue ED . 1997 Nature 389: 999–1003.
Lukas J, Parry D, Aagaard L, Mann DJ, Bartkova J, Strauss M, Peters G and Bartek J . 1995 Nature 375: 503–506.
Luque I and Gelinas C . 1997 Sem. Cancer Biol. 8: 103–111.
Mosialos G . 1997 Sem. Cancer Biol. 8: 121–129.
Naumann M, Wulczyn FG and Scheidereit C . 1993 EMBO J. 12: 213–222.
Naumann M and Scheidereit C . 1994 EMBO J. 13: 4597–4607.
Naumann M, Savitskaia N, Eilert C, Schramm A, Kalthoff H and Schmiegel W . 1996 Gastroenterology 110: 1215–1224.
Paal K, Baeuerle PA and Schmitz ML . 1997 Nucl. Acids Res. 25: 1050–1055.
Peter M and Herskowitz I . 1994 Cell 79: 181–184.
Perkins ND, Felzien LK, Betts JC, Leung K, Beach DH and Nabel GJ . 1997 Science 275: 523–527.
Schmitz ML, Indorf A, Limourg F, Staedtler H, Traenckner EBM and Baeuerle PA . 1996 Mol. Cell. Biol. 16: 4052–4063.
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM . 1995 Genes Dev. 9: 1149–1165.
Suzuki T, Kitao S, Matsushime H and Yoshida M . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 1607–1614.
Wulczyn FG, Naumann M and Scheidereit C . 1992 Nature 358: 597–599.
Wulczyn FG, Krappmann D and Scheidereit C . 1996 J. Mol. Med. 74: 749–769.
Acknowledgements
We thank J Bartek for the plasmid expressing c-myc-p16INK4, D Krappmann and C Scheidereit for the plasmid expressing IκBα, and C Bartsch for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by a grant from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Na-292/2-1) to M Naumann.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolff, B., Naumann, M. INK4 cell cycle inhibitors direct transcriptional inactivation of NF-κB. Oncogene 18, 2663–2666 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202617
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202617
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Exercise enhances skeletal muscle regeneration by promoting senescence in fibro-adipogenic progenitors
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Nfkb1 is a haploinsufficient DNA damage-specific tumor suppressor
Oncogene (2015)
-
The diverse and complex roles of NF-κB subunits in cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2012)
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 1 expression is inhibited by p16INK4a at the post-transcriptional level through the microRNA pathway
Oncogene (2011)
-
Downregulation of the tumour suppressor p16INK4A contributes to the polarisation of human macrophages toward an adipose tissue macrophage (ATM)-like phenotype
Diabetologia (2011)