Abstract
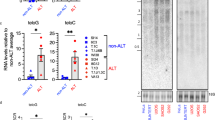
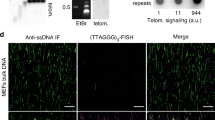
It has been repeatedly suspected that telomere shortening might be one possible trigger of the p53-dependent cell cycle arrest, although the mechanism of this arrest remained unclear. Telomeres in human cells under mild oxidative stress accumulate single-strand damage faster than interstitial repetitive sequences. In MRC-5 fibroblasts and U87 glioblastoma cells, which both express wild-type p53, oxidative stress-mediated production of single-strand damage in telomeres is concomitant to the accumulation of p53 and p21 and to cell cycle arrest. This response can be modeled by treatment of cells with short single stranded telomeric G-rich DNA fragments. The arrest is transient in U87 cells. Recovery from it is accompanied by up-regulation of telomerase activity and elongation of telomeres. Overexpression of mutated p53 is sufficient to reverse the phenotype of inhibition as well as the delayed activation of telomerase. These data suggest that the production of G-rich single stranded fragments during the course of telomere shortening is sufficient to trigger a p53 dependent cell cycle arrest.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsopp RC and Harley CB. . 1995 Exp. Cell Res. 219: 130–136
Asai A, Miyagi Y, Sugiyama A, Gamanuma M, Hong SH, Takamoto S, Nomura K, Matsutani M, Takakura K and Kuchino Y. . 1994 J. Neurooncol. 19: 259–268.
Baker SJ, Markowitz S, Fearon ER, Willson JKV and Vogelstein B. . 1990 Science 249: 912–915.
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichsteiner S and Wright WE. . 1998 Science 279: 349–352.
Counter CM, Hirte HW, Bacchetti S and Harley CB. . 1994 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 2900–2904.
DiLeonardo A, Linke SP, Clarkin K and Wahl GM. . 1994 Genes Dev. 8: 2540–2551.
Garvik B, Carson M and Hartwell LH. . 1995 Mol. Cell. Biol. 15: 6128–6138.
Harley CB, Futcher AB and Greider CW. . 1990 Nature 345: 458–460.
Huang LC, Clarkin KC and Wahl GM. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 4827–4832.
Hyeon Joo O, Hande MP, Lansdorp PM and Natarajan AT. . 1998 Mutat. Res. 401: 121–131.
Jayaraman L and Prives C. . 1995 Cell 81: 1021–1029.
Karlseder J, Broccoli D, DaiY, Hardy S and de Lange T. . 1999 Science 283: 1321–1325.
Kornbluth S, Smythe C and Newport JW. . 1992 Mol. Cell. Biol. 12: 3216–3223.
Krauskopf A and Blackburn EH. . 1996 Nature 383: 354–357.
Laemmli UK. . 1970 Nature 227: 680–685.
Leteurte F, Li X, Gluckman E and Carosella ED. . 1997 Leukemia 11: 1681–1689.
Lin JJ and Zakian VA. . 1996 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93: 13760–13765.
Linke SP, Clarkin KC and Wahl GM. . 1997 Cancer Res. 57: 1171–1179.
Makarov VL, Hirose Y and Langmore JP. . 1997 Cell 88: 657–666.
Marcand S, Gilson E and Shore D. . 1997 Science 275: 986–990.
Mukhopadhyay T, Multani AS, Roth JA, Pathak S. . 1998 Oncogene 17: 901–906.
Nagasawa H, Li CY, Maki CG, Imrich AC and Little JB. . 1995 Cancer Res. 55: 1842–1846.
Negrini M, Sabbioni S, Haldar S, Possati L, Castagnoli A, Corallini A, Barbanti-Brodano G and Croce CM. . 1994 Cancer Res. 54: 1818–1824.
Petersen S, Saretzki G and von Zglinicki T. . 1998 Exp. Cell Res. 239: 152–160.
Poulos NE, Farmer AA, Chan KWK and Stanbridge EJ. . 1996 Cancer Res. 56: 1719–1723.
Reed M, Woelker B, Wang P, Wang Y, Anderson ME and Tegtmeyer P. . 1995 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 9455–9459.
Saretzki G, Feng J, von Zglinicki T and Villeponteau B. . 1998 J. Gerontol. 53A: B438–B442.
Shay JW and Bacchetti S. . 1997 Eur. J. Cancer 33: 787–791.
Shay JW, Van Der Haegen BA, Ying Y and Wright WE. . 1993 Exp. Cell Res. 209: 45–52.
Sitte N, Saretzki G and von Zglinicki T. . 1998 Free Rad. Biol. Med. 24: 885–893.
van Steensel B, Smogorzewska A and de Lange T. . 1998 Cell 92: 401–413.
Vaziri H and Benchimol S. . 1996 Exp. Gerontol. 31: 295–301.
Vaziri H, West MD, Allsopp RC, Davison TS, Wu YS, Arrowsmith CH, Poirier GG and Benchimol S. . 1997 EMBO J. 16: 6018–6033.
von Zglinicki T, Saretzki G, Döcke W and Lotze C. . 1995 Exp. Cell Res. 220: 186–193.
Wellinger RJ and Sen D. . 1997 Eur. J. Cancer 33: 735–749.
Wright WE, Brasiskyte D, Piatyszek MA and Shay JW. . 1996 EMBO J. 15: 1734–1741.
Wynford-Thomas D, Bond JA, Wyllie F and Jones CJ. . 1995 Mol. Carcinogen. 12: 119–123.
Yaginuma Y and Westphal H. . 1992 Cancer Res. 52: 4196–4199.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, from VerUm e.V. and from the Berliner Krebshilfe e.V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saretzki, G., Sitte, N., Merkel, U. et al. Telomere shortening triggers a p53-dependent cell cycle arrest via accumulation of G-rich single stranded DNA fragments. Oncogene 18, 5148–5158 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202898
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202898
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Stress reactivity elicits a tissue-specific reduction in telomere length in aging zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Association of leukocyte telomere length and the risk of age-related hearing impairment in Chinese Hans
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Senescent cells: SASPected drivers of age-related pathologies
Biogerontology (2014)
-
Low oxygen delays fibroblast senescence despite shorter telomeres
Biogerontology (2008)