Abstract
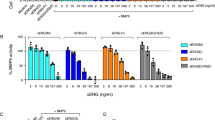
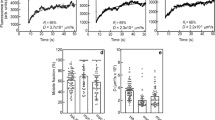
Heparin affin regulatory peptide (HARP) is an heparin-binding molecule involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. Here, we report that HARP inhibited the biological activity induced by the 165-amino-acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF165) on human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Endothelial-cell proliferation induced by VEGF165 showed about 50% inhibition in the presence of HARP in a concentration of 3 nM. In similar range of concentrations, HARP blocked tube formation induced by VEGF165 in three-dimensional angiogenesis assay. In vivo studies showed that HARP inhibited the VEGF165-induced Matrigel™ infiltration of endothelial cells. We then investigated the mechanisms of this inhibition and shown that HARP inhibited the binding of 125I-VEGF165 to the VEGF receptors of endothelial cells. Additional studies using VEGF soluble receptors indicated that binding of 125I-VEGF165 to kinase insert domain-containing receptor and neuropilin receptor was inhibited by HARP, but conversely the binding of 125I-VEGF165 to fms-like tyrosine kinase I receptor was unaffected. A competitive affinity-binding assay demonstrated that HARP interacted directly with VEGF165 with a dissociation coefficient of 1.38 nM. Binding assay using deletion mutants of HARP revealed that the thrombospondin type-1 repeats domains were involved in this interaction. These data demonstrate for the first time that the angiogenic factor HARP can also negatively regulates the angiogenic activity of VEGF165.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HARP:
-
heparin affin regulatory peptide
- VEGF165:
-
165-amino-acid form of vascular endothelial growth factor
- HUVECs:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- TSR:
-
thrombospondin repeat
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffer saline
- DSS:
-
disuccinimidyl suberate
- TSP-1:
-
thrombospondin 1
- flt-1:
-
fms-like tyrosine kinase-1
- KDR:
-
kinase insert domain containing receptor, NP-1 neuropilin-1
- GST:
-
glutathione S-transferase
References
Bernard-Pierrot I, Delbe J, Rouet V, Vigny M, Kerros ME, Caruelle D, Raulais D, Barritault D, Courty J and Milhiet PE . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 32071–32077.
Bork P . (1993). FEBS Lett., 327, 125–130.
Bradham DM, Igarashi A, Potter RL and Grotendorst GR . (1991). J. Cell Biol., 114, 1285–1294.
Brigstock DR, Steffen CL, Kim GY, Vegunta RK, Diehl JR and Harding PA . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 20275–20282.
Cao Y . (2001). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 33, 357–369.
Choudhuri R, Zhang HT, Donnini S, Ziche M and Bicknell R . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 1814–1819.
Clapp C, Martial JA, Guzman RC, Rentier-Delure F and Weiner RI . (1993). Endocrinology, 133, 1292–1299.
Courty J, Dauchel MC, Caruelle D, Perderiset M and Barritault D . (1991). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 180, 145–151.
Cross MJ and Claesson-Welsh L . (2001). Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 22, 201–207.
Delbe J, Katsoris P, Milhiet PE, Barritault D, Caruelle D and Courty J . (1999). Pathol. Biol. (Paris), 47, 352–357.
Fang W, Hartmann N, Chow DT, Riegel AT and Wellstein A . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 25889–25897.
Ferrara N and Henzel WJ . (1989). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 161, 851–858.
Folkman J . (1971). N. Engl. J. Med., 285, 1182–1186.
Folkman J . (1995). Nat. Med., 1, 27–31.
Folkman J and Shing Y . (1992). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 10931–10934.
Good DJ, Polverini PJ, Rastinejad F, Le Beau MM, Lemons RS, Frazier WA and Bouck NP . (1990). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 87, 6624–6628.
Guo NH, Krutzsch HC, Negre E, Vogel T, Blake DA and Roberts DD . (1992a). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 89, 3040–3044.
Guo NH, Krutzsch HC, Negre E, Zabrenetzky VS and Roberts DD . (1992b). J. Biol. Chem., 267, 19349–19355.
Gupta SK, Hassel T and Singh JP . (1995). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 92, 7799–7803.
Igarashi A, Nashiro K, Kikuchi K, Sato S, Ihn H, Fujimoto M, Grotendorst GR and Takehara K . (1996). J. Invest. Dermatol., 106, 729–733.
Igarashi A, Okochi H, Bradham DM and Grotendorst GR . (1993). Mol. Biol. Cell., 4, 637–645.
Inoki I, Shiomi T, Hashimoto G, Enomoto H, Nakamura H, Makino K, Ikeda E, Takata S, Kobayashi K and Okada Y . (2002). FASEB J., 16, 219–221.
Iruela-Arispe ML, Lombardo M, Krutzsch HC, Lawler J and Roberts DD . (1999). Circulation, 100, 1423–1431.
Keyt BA, Nguyen HV, Berleau LT, Duarte CM, Park J, Chen H and Ferrara N . (1996). J. Biol. Chem., 271, 5638–5646.
Kilpelainen I, Kaksonen M, Avikainen H, Fath M, Linhardt RJ, Raulo E and Rauvala H . (2000). J. Biol. Chem., 275, 13564–13570.
Laaroubi K, Delb J, Vacherot F, Desgranges P, Tardieu M, Jaye M, Barritault D and Courty J . (1994). Growth Factors, 10, 89–98.
Ledoux D, Caruelle D, Sabourin JC, Liu J, Crepin M, Barritault D and Courty J . (1997). J. Histochem. Cytochem., 45, 1239–1245.
Maione TE, Gray GS, Hunt AJ and Sharpe RJ . (1991). Cancer Res., 51, 2077–2083.
Milhiet PE, Vacherot F, Caruelle JP, Barritault D, Caruelle D and Courty J . (1998). J. Endocrinol., 158, 389–399.
Munson PJ . (1983). Methods Enzymol., 92, 543–576.
Myers EW and Miller W . (1988). Comput. Appl. Biosci., 4, 11–17.
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR and Folkman J . (1997). Cell, 88, 277–285.
O'Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS, Cao Y, Sage EH and Folkman J . (1994). Cell, 79, 315–328.
Papadimitriou E, Heroult M, Courty J, Polykratis A, Stergiou C and Katsoris P . (2000). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 274, 242–248.
Papadimitriou E, Polykratis A, Courty J, Koolwijk P, Heroult M and Katsoris P . (2001). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 282, 306–313.
Pipili-Synetos E, Papadimitriou E and Maragoudakis ME . (1998). Br. J. Pharmacol., 125, 1252–1257.
Plouet J, Moro F, Bertagnolli S, Coldeboeuf N, Mazarguil H, Clamens S and Bayard F . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 13390–13396.
Plouet J and Moukadiri H . (1990). J. Biol. Chem., 265, 22071–22074.
Plouet J, Schilling J and Gospodarowicz D . (1989). EMBO J., 8, 3801–3806.
Rauvala H . (1989). EMBO J., 8, 2933–2941.
Rauvala H, Huttunen HJ, Fages C, Kaksonen M, Kinnunen T, Imai S, Raulo E and Kilpelainen I . (2000). Matrix Biol., 19, 377–387.
Robinson CJ and Stringer SE . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 853–865.
Seddon AP, Hulmes JD, Decker MM, Kovesdi I, Fairhurst JL, Backer J, Dougher-Vermazen M and Bohlen P . (1994). Protein Expr. Purif., 5, 14–21.
Shimo T, Nakanishi T, Kimura Y, Nishida T, Ishizeki K, Matsumura T and Takigawa M . (1998). J. Biochem. (Tokyo), 124, 130–140.
Shimo T, Nakanishi T, Nishida T, Asano M, Kanyama M, Kuboki T, Tamatani T, Tezuka K, Takemura M, Matsumura T and Takigawa M . (1999). J. Biochem. (Tokyo), 126, 137–145.
Souttou B, Raulais D and Vigny M . (2001). J. Cell Physiol., 187, 59–64.
Tolsma SS, Volpert OV, Good DJ, Frazier WA, Polverini PJ and Bouck N . (1993). J. Cell Biol., 122, 497–511.
Tomanek RJ and Schatteman GC . (2000). Anat. Rec., 261, 126–135.
Vacherot F, Caruelle D, Chopin D, Gil-Diez S, Barritault D, Caruelle JP and Courty J . (1999). Prostate, 38, 126–136.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from four non-profit sources, namely, the Association pour la Recherche sur le Cancer (No. 4248), the Ministère de l'Education Nationale (DRED), the CNRS, and the Research Committee of the University of Patras. We thank Dr D Caruelle for helpful discussions and critically reading this manuscript. MH received a grant from a non-profit organization, the Association pour la Recherche sur la Polyarthrite.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Héroult, M., Bernard-Pierrot, I., Delbé, J. et al. Heparin affin regulatory peptide binds to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis. Oncogene 23, 1745–1753 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206879
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206879
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Skeleton-vasculature chain reaction: a novel insight into the mystery of homeostasis
Bone Research (2021)
-
CCN2 (Cellular Communication Network factor 2) in the bone marrow microenvironment, normal and malignant hematopoiesis
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Molecular mechanisms and clinical management of cancer bone metastasis
Bone Research (2020)
-
Pleiotrophin selectively binds to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 and inhibits or stimulates cell migration depending on ανβ3 integrin expression
Angiogenesis (2020)
-
Isolation and differential transcriptome of vascular smooth muscle cells and mid-capillary pericytes from the rat brain
Scientific Reports (2018)