Abstract
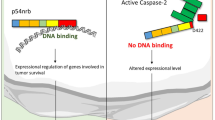
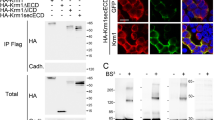
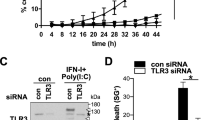
The drs gene was originally isolated as a suppressor against v-src transformation. Expression of drs mRNA was markedly downregulated in a variety of human cancer cell lines and tissues, suggesting that the drs gene acts as a tumor suppressor. In this study, we found that ectopic expression of the Drs protein induced apoptosis in human cancer cell lines. Analyses using deletion mutants of drs revealed that both the C-terminal region and the three consensus repeats in the N-terminal region are essential for the induction of apoptosis. Caspase-12, -9, and -3 were sequentially activated by drs, and specific inhibitors of caspase-3 and -9 suppressed drs-induced apoptosis. The release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria into the cytoplasm was not observed in apoptosis by drs, suggesting that the mitochondrial pathway does not mediate drs-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, we found that the Drs protein can interact with ASY/Nogo-B/RTN-xS, an apoptosis-inducing protein localized in the endoplasmic reticulum, and that coexpression of these genes increased the efficiency of apoptosis. These results indicated that Drs induces apoptosis by a novel pathway mediated by ASY/Nogo-B/RTN-xS, caspase-12, -9, and -3.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annis MG, Zamzami N, Zhu W, Penn LZ, Kroemer G, Leber B and Andrews DW . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 1939–1952.
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM . (1998). Science, 281, 1305–1308.
Bellacosa A, Testa JR, Staal SP and Tsichlis PN . (1991). Science, 254, 274–277.
Bevilacqua MP, Stengelin S, Gimbrone Jr MA and Seed B . (1989). Science, 243, 1160–1165.
Bitko V and Barik S . (2001). J. Cell. Biochem., 80, 441–454.
Chen MS, Huber AB, van der Haar ME, Frank M, Schnell L, Spillmann AA, Christ F and Schwab ME . (2000). Nature, 403, 434–439.
Ferri KF and Kroemer G . (2001). Nat. Cell Biol., 3, E255–E263.
Hacki J, Egger L, Monney L, Conus S, Rosse T, Fellay I and Borner C . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 2286–2295.
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA . (2000). Cell, 100, 57–70.
Hetz C, Russelakis-Carneiro M, Maundrell K, Castilla J and Soto C . (2003). EMBO J., 22, 5435–5445.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B and Harris CC . (1991). Science, 253, 49–53.
Inoue H, Pan J and Hakura A . (1998). J. Virol., 72, 2532–2537.
Johnston GI, Cook RG and McEver RP . (1989). Cell, 56, 1033–1044.
Kansas GS . (1996). Blood, 88, 3259–3287.
Kim CJ, Shimakage M, Kushima R, Mukaisho K, Shinka T, Okada Y and Inoue H . (2003). Hum. Pathol., 34, 654–657.
Lasky LA . (1992). Science, 258, 964–969.
Levine AJ . (1997). Cell, 88, 323–331.
Li Q, Qi B, Oka K, Shimakage M, Yoshioka N, Inoue H, Hakura A, Kodama K, Stanbridge EJ and Yutsudo M . (2001). Oncogene, 20, 3929–3936.
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H, Shibata T and Yasuhiko Y . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 34287–34294.
Mukaisho K, Suo M, Shimakage M, Kushima R, Inoue H and Hattori T . (2002). Jpn. J. Cancer Res., 93, 888–893.
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA and Yuan J . (2000). Nature, 403, 98–103.
Norman DG, Barlow PN, Baron M, Day AJ, Sim RB and Campbell ID . (1991). J. Mol. Biol., 219, 717–725.
Oertle T, Merkler D and Schwab ME . (2003). Oncogene, 22, 1390–1399.
Okabe M, Ikawa M, Kominami K, Nakanishi T and Nishimune Y . (1997). FEBS Lett., 407, 313–319.
Pan J, Nakanishi K, Yutsudo M, Inoue H, Li Q, Oka K, Yoshioka N and Hakura A . (1996). FEBS Lett., 383, 21–25.
Rao RV, Hermel E, Castro-Obregon S, del Rio G, Ellerby LM, Ellerby HM and Bredesen DE . (2001). J. Biol. Chem., 276, 33869–33874.
Reid KB and Day AJ . (1989). Immunol. Today, 10, 177–180.
Rudner J, Lepple-Wienhues A, Budach W, Berschauer J, Friedrich B, Wesselborg S, Schulze-Osthoff K and Belka C . (2001). J. Cell Sci., 114, 4161–4172.
Scorrano L, Oakes SA, Opferman JT, Cheng EH, Sorcinelli MD, Pozzan T and Korsmeyer SJ . (2003). Science, 300, 135–139.
Shen Y and White E . (2001). Adv. Cancer Res., 82, 55–84.
Shimakage M, Kawahara K, Kikkawa N, Sasagawa T, Yutsudo M and Inoue H . (2000). Int. J. Cancer, 87, 5–11.
Shimakage M, Takami K, Kodama K, Mano M, Yutsudo M and Inoue H . (2002). Hum. Pathol., 33, 615–619.
Siegelman MH, van de Rijn M and Weissman IL . (1989). Science, 243, 1165–1172.
Tagami S, Eguchi Y, Kinoshita M, Takeda M and Tsujimoto Y . (2000). Oncogene, 19, 5736–5746.
Tsujimoto Y, Finger LR, Yunis J, Nowell PC and Croce CM . (1984). Science, 226, 1097–1099.
Yamashita A, Hakura A and Inoue H . (1999). Oncogene, 18, 4777–4787.
Acknowledgements
We thank Hiroshi Okuno and Takefumi Yamamoto (Central Research Laboratory, Shiga University of Medical Science) for technical assistance. This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas (C) (Grant No. 14028032), and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (Grant No. 13670211) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan (H. Inoue). This work was also supported by a grant from the NOVARTIS Foundation (Japan) for the Promotion of Science (H. Inoue).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tambe, Y., Isono, T., Haraguchi, S. et al. A novel apoptotic pathway induced by the drs tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 23, 2977–2987 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207419
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207419
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
MiR-590-5p inhibits pathological hypertrophy mediated heart failure by targeting RTN4
Journal of Molecular Histology (2021)
-
Sushi repeat-containing protein 1: a novel disease-associated molecule in cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Acta Neuropathologica (2017)
-
A widespread peroxiredoxin-like domain present in tumor suppression- and progression-implicated proteins
BMC Genomics (2010)
-
Negative correlation of Nogo-A with the malignancy of oligodendroglial tumor
Neuroscience Bulletin (2007)
-
Adaptor FADD is recruited by RTN3/HAP in ER-bound signaling complexes
Apoptosis (2006)