Abstract
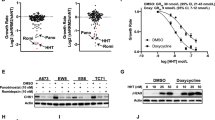
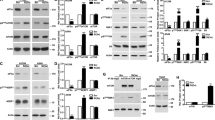
Translation initiation in eukaryotes is a rate-limiting step in protein synthesis. It is a complicated process that involves many eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs). Altering the expression level or the function of eIFs may influence the synthesis of some proteins and consequently cause abnormal cell growth and malignant transformation. P170, the largest putative subunit of eIF3, has been found elevated in human breast, cervical, esophageal, and lung cancers, suggesting that p170 may have a potential role in malignant transformation and/or cell growth control. Our recent studies suggested that p170 is likely a translational regulator and it may mediate the effect of mimosine on the translation of a subset mRNAs. Mimosine, a plant nonprotein amino acid, inhibits mammalian DNA synthesis, an essential event of cell growth. The rate-limiting step in DNA synthesis is the conversion of the ribonucleotides to their corresponding deoxyribonucleotides catalysed by ribonucleotide reductase of which the activity is regulated by the level of its M2 subunit. It has been reported that inhibiting the activity of M2 also inhibits cell growth. To understand the relationship between protein and DNA synthesis and between p170 and cell growth control, we investigated in this study whether p170 regulates the synthesis of M2 and, thus, cell growth. We found that altering the expression level of p170 changes the synthesis rate of both M2 and DNA. Decreasing p170 expression in human lung cancer cell line H1299 and breast cancer cell line MCF7 significantly reversed their malignant growth phenotype. However, the overall [35S]methionine incorporation following dramatic decrease in p170 expression was only ∼25% less than the control cells. These observations, together with our previous findings, suggest that p170 may regulate the translation of a subset mRNAs and its elevated expression level may be important for cancer cell growth and for maintaining their malignant phenotype.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abid MR, Li Y, Anthony C and De Benedetti A . (1999). J. Biol. Chem., 274, 35991–35998.
Amara FM, Chen FY and Wright JA . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 6709–6715.
Andrus L, Szabo P, Grady RW, Hanauske AR, Huima-Byron T, Slowinska B, Zagulska S and Hanauske-Abel HM . (1998). Biochem. Pharmacol., 55, 1807–1818.
Bachmann F, Banziger R and Burger MM . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 988–994.
Benne R and Hershey JW . (1976). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 73, 3005–3009.
Bjorklund S, Skog S, Tribukait B and THeLander L . (1990). Biochemistry, 29, 5452–5458.
Bjorklund S, Skogman E and THeLander L . (1992). EMBO J., 11, 4953–4959.
Block KL, Vornlocher HP and Hershey JW . (1998). J. Biol. Chem., 273, 31901–31908.
Buratti E, Tisminetzky S, Zotti M and Baralle FE . (1998). Nucleic Acids Res., 26, 3179–3187.
Chaudhuri J, Chakrabarti A and Maitra U . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 30975–30983.
Chen G and Burger MM . (1999). Int. J. Cancer, 84, 95–100.
Chen S, Zhou B, He F and Yen Y . (2000). Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev., 10, 111–116.
De Benedetti A and Harris AL . (1999). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 31, 59–72.
De Benedetti A, Joshi-Barve S, Rinker-Schaeffer C and Rhoads RE . (1991). Mol. Cell. Biol., 11, 5435–5445.
Dellas A, Torhorst J, Bachmann F, Banziger R, Schultheiss E and Burger MM . (1998). Cancer, 83, 1376–1383.
Dong Z and Zhang JT . (2003). Mol. Biol. Cell, 14, 3942–3951.
Dong Z, Wang X, Zhao Q, Townsend Jr CM and Evers BM . (1998). Am. J. Physiol., 274, G535–43.
Donze O, Jagus R, Koromilas AE, Hershey JW and Sonenberg N . (1995). EMBO J., 14, 3828–3834.
Engstrom Y, Eriksson S, Jildevik I, Skog S, THeLander L and Tribukait B . (1985). J. Biol. Chem., 260, 9114–9116.
Eriksson S, Graslund A, Skog S, THeLander L and Tribukait B . (1984). J. Biol. Chem., 259, 11695–11700.
Fan H, Villegas C and Wright JA . (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 14036–14040.
Fernandez J, Yaman I, Merrick WC, Koromilas A, Wek RC, Sood R, Hensold J and Hatzoglou M . (2002). J. Biol. Chem., 277, 2050–2058.
Fukuchi-Shimogori T, Ishii I, Kashiwagi K, Mashiba H, Ekimoto H and Igarashi K . (1997). Cancer Res., 57, 5041–5044.
Gilbert DM, Neilson A, Miyazawa H, DePamphilis ML and Burhans WC . (1995). J. Biol. Chem., 270, 9597–9606.
Han B and Zhang JT . (2002). Mol. Cell. Biol., 22, 7372–7384.
Hanauske-Abel HM, Park MH, Hanauske AR, Popowicz AM, Lalande M and Folk JE . (1994). Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1221, 115–124.
Hanauske-Abel HM, Slowinska B, Zagulska S, Wilson RC, Staiano-Coico L, Hanauske AR, McCaffrey T and Szabo P . (1995). FEBS Lett., 366, 92–98.
Hershey JWB and Merrick WC . (2000). Translational Control of Gene Expression. Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB and Mathews MB (eds). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 33–88.
Hershey JWB and Miyamoto S . (2000). Translational Control of Gene Expression, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB and Mathews MB (eds). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories Press: New York, pp 637–654.
Hurta RA and Wright JA . (1995). J. Cell. Biochem., 57, 543–556.
Jiang W, Kahn SM, Zhou P, Zhang YJ, Cacace AM, Infante AS, Doi S, Santella RM and Weinstein IB . (1993). Oncogene, 8, 3447–3457.
Kalejta RF and Hamlin JL . (1997). Exp. Cell Res., 231, 173–183.
Kang HA and Hershey JW . (1994). J. Biol. Chem., 269, 3934–3940.
Lazaris-Karatzas A, Montine KS and Sonenberg N . (1990). Nature, 345, 544–547.
Lee Y, Vassilakos A, Feng N, Lam V, Xie H, Wang M, Jin H, Xiong K, Liu C, Wright J and Young A . (2003). Cancer Res., 63, 2802–2811.
Li Q, Kasten-Jolly J, Yen Y and Freed BM . (1998). Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol., 150, 154–157.
Manjeshwar S, Rao PM, Rajalakshmi S and Sarma DS . (1999). Mol. Carcinog., 24, 188–196.
Mann GJ, Musgrove EA, Fox RM and THeLander L . (1988). Cancer Res., 48, 5151–5156.
Mayeur GL and Hershey JW . (2002). FEBS Lett., 514, 49–54.
Methot N, Rom E, Olsen H and Sonenberg N . (1997). J. Biol. Chem., 272, 1110–1116.
Methot N, Song MS and Sonenberg N . (1996). Mol. Cell. Biol., 16, 5328–5334.
Park JB and Levine M . (2000). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 267, 651–657.
Pincheira R, Chen Q and Zhang JT . (2001). Br. J. Cancer, 84, 1520–1527.
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T . (1989). Molecular Cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Tanaka H, Arakawa H, Yamaguchi T, Shiraishi K, Fukuda S, Matsui K, Takei Y and Nakamura Y . (2000). Nature, 404, 42–49.
Wright JA, Chan AK, Choy BK, Hurta RA, McClarty GA and Tagger AY . (1990). Biochem. Cell Biol., 68, 1364–1371.
Yarbro JW . (1992). Semin. Oncol., 19, 1–10.
Zhou B and Yen Y . (2001). Cytogenet. Cell Genet., 95, 52–59.
Zhou BS, Hsu NY, Pan BC, Doroshow JH and Yen Y . (1995). Cancer Res., 55, 1328–1333.
Zhou BS, Tsai P, Ker R, Tsai J, Ho R, Yu J, Shih J and Yen Y . (1998). Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 16, 43–49.
Acknowledgements
Technical assistance from Mr Min Choi is appreciated. Critical comments on an earlier version of this manuscript from Drs David Ohannesian and Martin Smith are also greatly appreciated. We also would like to thank Drs Keith R Johnson, Tang K Tang, Max M Burger, and Andrew Koff for their generosity in providing the necessary materials for this study. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants (CA64539, GM59475, and CA94961) and Department of Defense Grant (DAMD170010297). J-TZ was a recipient of a Career Investigator Award from the American Lung Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Z., Liu, L., Han, B. et al. Role of eIF3 p170 in controlling synthesis of ribonucleotide reductase M2 and cell growth. Oncogene 23, 3790–3801 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207465
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207465
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
eIF3a regulation of mTOR signaling and translational control via HuR in cellular response to DNA damage
Oncogene (2022)
-
Systematic analyses of the role of prognostic and immunological EIF3A, a reader protein, in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
Cancer Cell International (2021)
-
The emerging role of RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in breast cancer
Biomarker Research (2021)
-
Cytosolic Cysteine Synthase Switch Cysteine and Mimosine Production in Leucaena leucocephala
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2018)
-
MiR-488 inhibits proliferation and cisplatin sensibility in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells by activating the eIF3a-mediated NER signaling pathway
Scientific Reports (2017)