Abstract
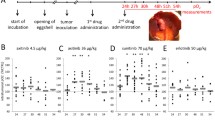
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a therapeutic modality in which a photosensitizer is locally or systemically administered followed by light irradiation of suitable wavelength to achieve selective tissue damage. In addition, PDT is an oxygen-consuming reaction, that causes hypoxia mediated destruction of tumor vasculature that results in effective treatment. However, the hypoxic condition within tumors can cause stress-related release of angiogenic growth factors and cytokines and this inflammatory response could possibly diminish the efficacy of PDT by promoting tumor regrowth. In such circumstances, PDT effectiveness can be enhanced by combining angiogenesis inhibitors into the treatment regimen. Avastin (bevacizumab), a vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) specific monoclonal antibody in combination with chemotherapy is offering hope to patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. In this study we evaluated the combination of hypericin-mediated PDT and Avastin on VEGF levels as well as its effect on overall tumor response. Experiments were conducted on bladder carcinoma xenografts established subcutaneously in Balb/c nude mice. Antibody array, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) were performed to assess VEGF concentrations in the various treatment groups. Our results demonstrated that the targeted therapy by Avastin along with PDT can improve tumor responsiveness in bladder tumor xenografts. Immunostaining showed minimal expression of VEGF in tumors treated with combination therapy of PDT and Avastin. Angiogenic proteins e.g., angiogenin, basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF) and interleukins (IL-6 and IL-8) were also found to be downregulated in groups treated with combination therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. J. Dougherty, C. J. Gomer, B. W. Henderson, G. Jori, D. Kessel, M. Korbelik, J. Moan, Q. Peng, Photodynamic Therapy, Review, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 1998, 90, 889–905.
A. R. Kamuhabwa, P. Agostinis, B. Ahmed, W. Landuyt, B. V. Cleynenbreugel, H. V. Poppel, P. A. de Witte, Hypericin as a potential phototherapeutic agent in superficial transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2004, 3, 772–780.
M. A. D’Hallewin, A. R. Kamuhabwa, T. Roskams, P. A. De Witte, L. Baert, Hypericin-based fluorescence diagnosis of bladder carcinoma, BJU Int., 2002, 89, 760–763.
M. Olivo, W. Lau, V. Manivasager, P. H. Tan, K. C. Soo, C. Cheng, Macro-microscopic fluorescence of human bladder cancer using hypericin fluorescence cystoscopy and laser confocal microscopy, Int. J. Oncol., 2003, 23, 983–990.
T. M. Busch, Local physiological changes during photodynamic therapy, Lasers Surg. Med., 2006, 38, 494–499.
C. J. Gomer, A. Ferrario, M. Luna, N. Rucker, S. Wong, Photodynamic therapy: combined modality approaches targeting the tumor microenvironment, Lasers Surg. Med., 2006, 38, 516–521.
J. Folkman, The role of angiogenesis in tumor growth, Cancer Biol., 1992, 3, 65–71.
N. Ferrara, Vascular endothelial growth factor as a target for anticancer therapy, The Oncology, 2004, 9, 2–10.
C. C. Yang, K. C. Chu, W. M. Yeh, The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder is correlated with cancer progression, Urol. Oncol., 2004, 22, 1–6.
Z. M. Shao, M. Nguyen, Angiogenic factors and bladder cancer, Front. Biosci., 2002, 7, 33–35.
J. P. Crew, T. O’Brien, M. Bradburn, S. Fuggle, R. Bicknell, D. Cranston, A. L. Harris, Vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of relapse and stage progression in superficial bladder, Cancer Res., 1997, 57, 5281–5285.
A. Jones, J. Crew, Vascular endothelial growth factor and its correlation with superficial bladder cancer recurrence rates and stage progression, Urol. Clin. North Am., 2000, 27, 191–197.
T. O’Brien, D. Cranston, S. Fuggle, R. Bicknell, A. L. Harris, Different angiogenic pathways characterize superficial and invasive bladder cancer, Cancer Res., 1995, 55, 510–513.
T. Shih, C. Lindley, Bevacizumab: an angiogenesis inhibitor for the treatment of solid malignancies, Clin. Ther., 2006, 28, 1779–1802.
A. Ferrario, C. J. Gomer, Avastin enhances photodynamic therapy treatment of Kaposi’s sarcoma in a mouse tumor model, J. Environ. Path. Toxicol. Oncol., 2006, 25, 251–259.
B. W. Henderson, S. O. Gollnick, J. W. Snyder, T. M. Busch, P. C. Kousis, R. T. Cheney, J. Morgan, Choice of oxygen-conserving treatment regimen determines the inflammatory response and outcome of photodynamic therapy of tumors, Cancer Res., 2004, 64, 2120–2126.
G. Powis, L. Kirkpatrick, Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha as a cancer drug target, Mol. Cancer Ther., 2004, 3, 647–654.
A. Ferrario, K. F. von Tiehl, N. Rucker, M. A. Schwarz, P. S. Gill, C. J. Gomer, Antiangiogenic treatment enhances photodynamic therapy responsiveness in a mouse mammary carcinoma, Cancer Res., 2000, 60, 4066–4069.
P. M. Gullino, Considerations on the mechanism of the angiogenic response, Anticancer Res., 1986, 6, 153–158.
N. Solban, P. K. Selbo, A. K. Sinha, S. K. Chang, T. Hasan, Mechanistic investigation and implications of photodynamic therapy induction of vascular endothelial growth factor in prostate cancer, Cancer Res., 2006, 66, 5633–5640.
R. Bhuvaneswari, Y. Y. Gan, K. K. Yee, K. C. Soo, M. Olivo, Effect of hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy on the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma, Int. J. Mol. Med., 2007, 20, 421–428.
Q. Chen, Z. Huang, H. Chen, H. Shapiro, J. Beckers, F. W. Hetzel, Improvement of tumor response by manipulation of tumor oxygenation during photodynamic therapy, Photochem. Photobiol., 2002, 76, 197–203.
T. H. Foster, R. S. Murant, R. G. Bryant, R. S. Knox, S. L. Gibson, R. Hilf, Oxygen consumption and diffusion effects in photodynamic therapy, Radiant. Res., 1991, 126, 296–303.
T. M. Sitnik, J. A. Hampton, B. W. Henderson, Reduction of tumour oxygenation during and after photodynamic therapy in vivo: effects of fluence rate, Br. J. Cancer, 1998, 77, 1386–1394.
B. J. Tromberg, A. Orenstein, S. Kimel, S. J. Barker, J. Hyatt, J. S. Nelson, M. W. Berns, In vivo tumour oxygen tension measurements for the evaluation of the efficiency of photodynamic therapy, Photochem. Photobiol., 1990, 52, 375–385.
B. W. Henderson, T. M. Busch, J. W. Snyder, Fluence rate as a modulator of PDT mechanisms, Lasers Surg. Med., 2006, 38, 489–493.
H. W. Wang, M. E. Putt, M. J. Emanuele, D. B. Shin, E. Glatstein, A. G. Yodh, T. M. Busch, Treatment-induced changes in tumor oxygenation predict photodynamic therapy outcome, Cancer Res., 2004, 64, 7553–7561.
W. C. Liang, X. Wu, F. V. Peale, C. V. Lee, G. Meng, J. Gutierrez, L. Fu, A. K. Malik, H. P. Gerber, N. Ferrara, G. Fuh, Cross-species vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-blocking antibodies completely inhibit the growth of human tumor xenografts and measure the contribution of stromal VEGF, J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 951–961.
E. Barbera-Guillem, J. K. Nyhus, C. C. Wolford, C. R. Friece, J. W. Sampsel, Vascular endothelial growth factor secretion by tumor-infiltrating macrophages essentially supports tumor angiogenesis, and IgG immune complexes potentiate the process, Cancer Res., 2002, 62, 7042–7049.
S. A. Borg, K. E. Kerry, J. A. Royds, R. D. Battersby, T. H. Jones, Correlation of VEGF production with IL-1a and IL-6 secretion by human pituitary adenoma cells, Eur. J. Endocrinol., 2005, 152, 293–300.
H. Saito, S. Tsujitani, A. Kondo, M. Ikeguchi, M. Maeta, N. Kaibar, Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor correlates with hematogenous recurrence in gastric carcinoma, Surgery, 1999, 125, 195–201.
M. E. Harper, E. Glynne-Jones, L. Goddard, V. J. Thurston, K. Griffths, Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in prostatic tumours and its relationship to neuroendocrine cells, Br. J. Cancer, 1996, 74, 910–916.
K. L. Talks, H. Turley, K. C. Gatter, P. H. Maxwell, C. W. Pugh, P. J. Ratcliffe, A. L. Harris, The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1 and HIF-2 in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages, Am. J. Pathol., 2000, 157, 411–421.
A. Hartmann, M. Kunz, S. Köstlin, R. Gillitzer, A. Toksoy, E.-B. Bröcker, C. E. Klein, Hypoxia-induced up-regulation of angiogenin in human malignant melanoma, Cancer Res., 1999, 59, 1578–1583.
L. Campo, H. Turley, C. Han, F. Pezzella, K. C. Gatter, A. L. Harris, S. B. Fox, Angiogenin is up-regulated in the nucleus and cytoplasm in human primary breast carcinoma and is associated with markers of hypoxia but not survival, J. Pathol., 2005, 205, 585–91.
Y. Chen, S. Zhang, Y. P. Chen, J. Y. Lin, Increased expression of angiogenin in gastric carcinoma in correlation with tumor angiogenesis and proliferation, World J. Gastroenterol., 2006, 12, 5135–5139.
A. Alavi, J. D. Hood, R. Frausto, D. G. Stupack, D. A. Cheresh, Role of Raf in vascular protection from distinct apoptotic stimuli, Science, 2003, 301, 94–96.
M. S. Pepper, N. Ferrara, L. Orci, R. Montesano, Potent synergism between vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in the induction of angiogenesis in vitro, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1992, 189, 824–831.
M. Calvani, A. Rapisarda, B. Uranchimeg, R. H. Shoemaker, G. Melillo, Hypoxic induction of an HIF-1-dependent bFGF autocrine loop drives angiogenesis in human endothelial cells, Blood, 2006, 107, 2705–2712.
F. Ciardiello, Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in cancer treatment, Future Oncol., 2005, 1, 221–234.
P. Vaupel, The role of hypoxia-induced factors in tumor progression, Oncologist, 2004, 9, 10–17.
J. Tabernero, The role of VEGF and EGFR inhibition: implications for combining anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR agents, Mol. Cancer Res., 2007, 5, 203–220.
Y. Cao, P. Linden, D. Shima, F. Browne, J. Folkman, In vivo angiogenic activity and hypoxia induction of heterodimers of placenta growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor, J. Clin. Invest., 1996, 98, 2507–2511.
A. Ahmed, C. Dunk, S. Ahmad, A. Khaliq, Regulation of placental vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and placenta growth factor (PIGF) and soluble Flt-1 by oxygen-a review, Placenta, 2000, 21, 16–24.
T. Cohen, D. Nahari, L. W. Cerem, G. Neufeld, B. Z. Levi, Interleukin 6 induces the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271, 736–741.
O. Würtz, A. S. Schrohl, N. M. Sørensen, U. Lademann, I. J. Christensen, H. Mouridsen, N. Brünner, Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in breast cancer, Endocr. Relat. Cancer, 2005, 12, 215–227.
A. Ferrario, C. F. Chantrain, K. von Tiehl, S. Buckley, N. Rucker, D. R. Shalinsky, H. Shimada, Y. A. DeClerck, C. J. Gomer, The matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor prinomastat enhances photodynamic therapy responsiveness in a mouse tumor model, Cancer Res., 2004, 64, 2328–2332.
J. A. Nagy, E. Vasile, D. Feng, C. Sundberg, L. F. Brown, M. J. Detmar, J. A. Lawitts, L. Benjamin, X. Tan, E. J. Manseau, A. M. Dvorak, H. F. Dvorak, Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor induces lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis, J. Exp. Med., 2002, 196, 1497–1506.
A. Hoeben, B. Landuyt, M. S. Highley, H. Wildiers Van Oosterom, E. A. De Bruijn, Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis, Pharmacol. Rev., 2004, 56, 549–580.
B. Kosharskyy, N. Solban, S. K. Chang, I. Rizvi, Y. Chang, T. Hasan, A mechanism-based combination therapy reduces local tumor growth and metastasis in an orthotopic model of prostate cancer, Cancer Res., 2006, 66, 10953–10958.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuvaneswari, R., Yuen, G.Y., Chee, S.K. et al. Hypericin-mediated photodynamic therapy in combination with Avastin (bevacizumab) improves tumor response by downregulating angiogenic proteins. Photochem Photobiol Sci 6, 1275–1283 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1039/b705763f
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b705763f