Abstract
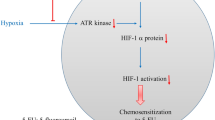
Colon cancer is the third most frequent cancer and the fourth most common cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide and the standard therapy is surgical resection plus adjuvant chemotherapy. Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has been proposed as an adjuvant therapy because it can prevent the tumor recurrence after surgical excision in colon cancer patients. Hypoxia is a common feature in solid tumors and leads to chemo/radioresistance. Recently, it has been shown that in response to hypoxia, cells can induce HIF-1α-mediated autophagy to survive in this hostile microenvironment. Moreover, hypoxia and autophagy have been implicated in the resistance to antitumor PDT. However, the molecular signals by which HIF-1α induces autophagy in the PDT context have not been studied yet. Here we evaluate the interplay between HIF-1α and autophagy as well as the underlying mechanism in the PDT resistance of colon cancer cells. Our study demonstrates that HIF-1α stabilization significantly increases VMP1-related autophagy through binding to hypoxia responsive elements in the VMP1 promoter. We show that HIF-1α-induced autophagy increases colon cancer cell survival as well as decreases cell death after PDT. Moreover, here we demonstrate that HIF-1α-induced autophagy is mediated by VMP1 expression, since the downregulation of VMP1 by the RNA interference strategy reduces HIF-1α-induced autophagy and cell survival after PDT. In conclusion, PDT induces autophagy as a survival mechanism and the induction of the novel HIF-1α/VMP1-autophagic pathway may explain, at least in part, the resistance of colon cancer cells to PDT. The knowledge of the molecular mechanisms involved in PDT resistance may lead to more accurate therapeutic strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. L. Longo, and W. B. Strum, Colorectal Adenomas, N. Engl. J. Med., 2016, 374, 11, 1065–1075.
K. De Greef, C. Rolfo, and A. Russo, {etet al.}, Multisciplinary management of patients with liver metastasis from colorectal cancer, World J. Gastroenterol., 2016, 22, 32, 7215–7225.
R. M. Heaney, C. Shields, and J. Mulsow, Outcome following incomplete surgical cytoreduction combined with intraperitoneal chemotherapy for colorectal peritoneal metastases, World J. Gastrointest. Oncol., 2015, 7, 12, 445–454.
S. B. Brown, E. A. Brown, and I. Walker, The present and future role of photodynamic therapy in cancer treatment, Lancet Oncol., 2004, 5, 8, 497–508.
A. Oniszczuk, K. A. Wojtunik-Kulesza, T. Oniszczuk, and K. Kasprzak, The potential of photodynamic therapy (PDT)—Experimental investigations and clinical use, Biomed. Pharmacother., 2016, 83, 912–929.
A. P. Castano, T. N. Demidova, and M. R. Hamblin, Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: part two—cellular signaling, cell metabolism and modes of cell death, Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther., 2005, 2, 1, 1–23.
J.-O. Yoo, and K.-S. Ha, New insights into the mechanisms for photodynamic therapy-induced cancer cell death, Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol., 2012, 295, 139–174.
N. Shishkova, O. Kuznetsova, and T. Berezov, Photodynamic therapy in gastroenterology, J. Gastrointest. Cancer., 2013, 44, 3, 251–259.
H. Barr, A. J. MacRobert, C. J. Tralau, P. B. Boulos, and S. G. Bown, The significance of the nature of the photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy: quantitative and biological studies in the colon, Br. J. Cancer., 1990, 62, 5, 730–735.
J.-P. Cosse, and C. Michiels, Tumour hypoxia affects the responsiveness of cancer cells to chemotherapy and promotes cancer progression, Anticancer Agents Med. Chem., 2008, 8, 7, 790–797.
K. Balamurugan, HIF-1 at the crossroads of hypoxia, inflammation, and cancer, Int. J. Cancer., 2016, 138, 5, 1058–1066.
C. Michiels, C. Tellier, and O. Feron, Cycling hypoxia: A key feature of the tumor microenvironment, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Rev. Cancer., 2016, 1866, 1, 76–86.
I. Amelio, and G. Melino, The p53 family and the hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs): determinants of cancer progression, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2015, 40, 8, 425–434.
L. Lin, and E. H. Baehrecke, Autophagy, cell death, and cancer, Mol. Cell. Oncol., 2015, 2, 3, e985913.
L. Harhaji-Trajkovic, U. Vilimanovich, T. Kravic-Stevovic, V. Bumbasirevic, and V. Trajkovic, AMPK-mediated autophagy inhibits apoptosis in cisplatin-treated tumour cells, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2009, 13, 9B, 3644–3654.
D. Liu, Y. Yang, Q. Liu, and J. Wang, Inhibition of autophagy by 3-MA potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells, Med. Oncol., 2011, 28, 1, 105–111.
B. Del Bello, M. Toscano, D. Moretti, and E. Maellaro, Cisplatin-induced apoptosis inhibits autophagy, which acts as a pro-survival mechanism in human melanoma cells, PLoS One., 2013, 8, 2, e57236.
A. Terman, and U. T. Brunk, Autophagy in cardiac myocyte homeostasis, aging, and pathology, Cardiovasc. Res., 2005, 68, 3, 355–365.
X. Yang, D.-D. Yu, and F. Yan, {etet al.}, The role of autophagy induced by tumor microenvironment in different cells and stages of cancer, Cell Biosci., 2015, 5, 1, 14.
A. François, S. Marchal, F. Guillemin, and L. Bezdetnaya, mTHPC-based photodynamic therapy induction of autophagy and apoptosis in cultured cells in relation to mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum stress, Int. J. Oncol., 2011, 39, 6, 1537–1543.
T. R. O’Donovan, G. C. O’Sullivan, and S. L. McKenna, Induction of autophagy by drug-resistant esophageal cancer cells promotes their survival and recovery following treatment with chemotherapeutics, Autophagy., 2011, 7, 5, 509–524.
M.-F. Wei, M.-W. Chen, and K.-C. Chen, {etet al.}, Autophagy promotes resistance to photodynamic therapy-induced apoptosis selectively in colorectal cancer stem-like cells, Autophagy, 2014, 10, 7, 1179–1192.
A. Ropolo, D. Grasso, and R. Pardo, {etet al.}, The pancreatitis-induced vacuole membrane protein 1 triggers autophagy in mammalian cells, J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282, 51, 37124–37133.
M. I. Vaccaro, A. Ropolo, D. Grasso, and J. L. Iovanna, A novel mammalian trans-membrane protein reveals an alternative initiation pathway for autophagy, Autophagy., 2008, 4, 3, 388–390.
M. I. Molejon, A. Ropolo, and M. I. Vaccaro, VMP1 is a new player in the regulation of the autophagy-specific phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex activation, Autophagy., 2013, 9, 6, 933–935.
M. I. Molejon, A. Ropolo, A. Lo Re, V. Boggio, and M. I. Vaccaro, The VMP1-Beclin 1 interaction regulates autophagy induction, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 1055.
D. Grasso, A. Ropolo, and A. Lo Ré, {etet al.}, Zymophagy, a novel selective autophagy pathway mediated by VMP1-USP9x-p62, prevents pancreatic cell death, J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 286, 10, 8308–8324.
A. E. Lo Ré, M. G. Fernández-Barrena, and L. L. Almada, {etet al.}, Novel AKT1-GLI3-VMP1 pathway mediates KRAS oncogene-induced autophagy in cancer cells, J. Biol. Chem., 2012, 287, 30, 25325–25334.
R. Pardo, A. Lo Ré, and C. Archange, {etet al.}, Gemcitabine induces the VMP1-mediated autophagy pathway to promote apoptotic death in human pancreatic cancer cells, Pancreatology, 2010, 10, 1, 19–26.
D. Vordermark, P. Kraft, and A. Katzer, {etet al.}, Glucose requirement for hypoxic accumulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha), Cancer Lett., 2005, 230, 1, 122–133.
M. J. Curtis, R. A. Bond, and D. Spina, {etet al.}, Experimental design and analysis and their reporting: new guidance for publication in BJP, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2015, 172, 14, 3461–3471.
L. M. Lopez-Sánchez, C. Jimenez, and A. Valverde, {etet al.}, CoCl2, a mimic of hypoxia, induces formation of polyploid giant cells with stem characteristics in colon cancer, PLoS One, 2014, 9, 6, e99143.
E. L. LaGory, and A. J. Giaccia, The ever-expanding role of HIF in tumour and stromal biology, Nat. Cell Biol., 2016, 18, 4, 356–365.
T. Shibata, A. J. Giaccia, and J. M. Brown, Development of a hypoxia-responsive vector for tumor-specific gene therapy, Gene Ther., 2000, 7, 6, 493–498.
Y. Kabeya, N. Mizushima, and T. Ueno, {etet al.}, LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing, EMBO J., 2000, 19, 21, 5720–5728.
S. Wilkinson, J. O’Prey, M. Fricker, and K. M. Ryan, Hypoxia-selective macroautophagy and cell survival signaled by autocrine PDGFR activity, Genes Dev., 2009, 23, 11, 1283–1288.
Y. Sun, X. Xing, and Q. Liu, {etet al.}, Hypoxia-induced autophagy reduces radiosensitivity by the HIF-1α/miR-210/Bcl-2 pathway in colon cancer cells, Int. J. Oncol., 2015, 46, 2, 750–756.
M. B. Gariboldi, E. Taiana, and M. C. Bonzi, {etet al.}, The BH3-mimetic obatoclax reduces HIF-1α levels and HIF-1 transcriptional activity and sensitizes hypoxic colon adenocarcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil, Cancer Lett., 2015, 364, 2, 156–164.
D. J. Klionsky, The molecular machinery of autophagy: unanswered questions, J. Cell. Sci., 2005, 118, Pt 1, 7–18.
J. M. Brown, and W. R. Wilson, Exploiting tumour hypoxia in cancer treatment, Nat. Rev. Cancer., 2004, 4, 6, 437–447.
Z. Ji, G. Yang, and S. Shahzidi, {etet al.}, Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha overexpression by cobalt chloride enhances cellular resistance to photodynamic therapy, Cancer Lett., 2006, 244, 2, 182–189.
A. Casas, G. Di Venosa, and T. Hasan, Al Batlle, Mechanisms of resistance to photodynamic therapy, Curr. Med. Chem., 2011, 18, 16, 2486–2515.
X.-H. Ma, S. Piao, and D. Wang, {etet al.}, Measurements of tumor cell autophagy predict invasiveness, resistance to chemotherapy, and survival in melanoma, Clin. Cancer Res., 2011, 17, 10, 3478–3489.
S. Mitra, S. E. Cassar, D. J. Niles, J. A. Puskas, J. G. Frelinger, and T. H. Foster, Photodynamic therapy mediates the oxygen-independent activation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, Mol. Cancer Ther., 2006, 5, 12, 3268–3274.
L. Milla Sanabria, M. E. Rodríguez, and I. S. Cogno, {etet al.}, Direct and indirect photodynamic therapy effects on the cellular and molecular components of the tumor microenvironment, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2013, 1835, 1, 36–45.
A. Tittarelli, B. Janji, K. Van Moer, M. Z. Noman, and S. Chouaib, The selective degradation of synaptic connexin 43 protein by hypoxia-induced autophagy impairs natural killer cell-mediated tumor cell killing, J. Biol. Chem., 2015, 290, 39, 23670–23679.
D. J. Klionsky, K. Abdelmohsen, and A. Abe, {etet al.}, Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition), Autophagy, 2016, 12, 1, 1–222.
B. Levine, and J. Yuan, Autophagy in cell death: an innocent convict?, J. Clin. Invest., 2005, 115, 10, 2679–2688.
P. Maycotte, S. Aryal, C. T. Cummings, J. Thorburn, M. J. Morgan, and A. Thorburn, Chloroquine sensitizes breast cancer cells to chemotherapy independent of autophagy, Autophagy., 2012, 8, 2, 200–212.
C. Fan, W. Wang, B. Zhao, S. Zhang, and J. Miao, Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells, Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2006, 14, 9, 3218–3222.
T. Liu, L. Zhao, and W. Chen, {etet al.}, Inactivation of von Hippel-Lindau increases ovarian cancer cell aggressiveness through the HIF1α/miR-210/VMP1 signaling pathway, Int. J. Mol. Med., 2014, 33, 5, 1236–1242.
R. Scherz-Shouval, E. Shvets, E. Fass, H. Shorer, L. Gil, and Z. Elazar, Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4, EMBO J., 2007, 26, 7, 1749–1760.
T. H. Foster, R. S. Murant, R. G. Bryant, R. S. Knox, S. L. Gibson, and R. Hilf, Oxygen consumption and diffusion effects in photodynamic therapy, Radiat. Res., 1991, 126, 3, 296–303.
T. M. Sitnik, J. A. Hampton, and B. W. Henderson, Reduction of tumour oxygenation during and after photodynamic therapy in vivo: effects of fluence rate, Br. J. Cancer., 1998, 77, 9, 1386–1394.
S.-N. Jung, W. K. Yang, and J. Kim, {etet al.}, Reactive oxygen species stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha protein and stimulate transcriptional activity via AMP-activated protein kinase in DU145 human prostate cancer cells, Carcinogenesis, 2008, 29, 4, 713–721.
J. Y. Lee, S. A. Hirota, L. E. Glover, G. D. Armstrong, P. L. Beck, and J. A. MacDonald, Effects of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species on HIF-1a stabilization following Clostridium difficile toxin exposure of the Caco-2 epithelial cell line, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2013, 32, 2, 417–430.
Y.-N. Li, M.-M. Xi, Y. Guo, C.-X. Hai, W.-L. Yang, and X.-J. Qin, NADPH oxidase-mitochondria axis-derived ROS mediate arsenite-induced HIF-1α stabilization by inhibiting prolyl hydroxylases activity, Toxicol. Lett., 2014, 224, 2, 165–174.
M. Dewaele, W. Martinet, and N. Rubio, {etet al.}, Autophagy pathways activated in response to PDT contribute to cell resistance against ROS damage, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2011, 15, 6, 1402–1414.
P. Tu, Q. Huang, and Y. Ou, {etet al.}, Aloe-emodin-mediated photodynamic therapy induces autophagy and apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cell line MG-63 through the ROS/JNK signaling pathway, Oncol. Rep., 2016, 35, 6, 3209–3215.
H. Choi, C. Merceron, and L. Mangiavini, {etet al.}, Hypoxia promotes noncanonical autophagy in nucleus pulposus cells independent of MTOR and HIF1A signaling, Autophagy, 2016, 12, 9, 1631–1646.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr Thomas Foster for providing the 5HREhCMV- d2EGFP plasmid, Dr Eric Metzen for providing the pLKO.1-shRNAHIF-1α-1 and PLKO.1-shScrambled plasmids and Dr Edurne Berra for providing the pcDNA3-HA-DN-HIF-1α plasmid.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodríguez, M.E., Catrinacio, C., Ropolo, A. et al. A novel HIF-1α/VMP1-autophagic pathway induces resistance to photodynamic therapy in colon cancer cells. Photochem Photobiol Sci 16, 1631–1642 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00161d
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00161d