Abstract
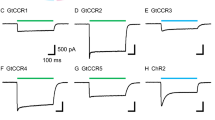
Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2), one of the algal light-gatedcation channel rhodopsins, contains five peculiar glutamic acid residues in the N-terminal region corresponding to the second to third transmembrane helices. Here we made systematic mutations of these polar amino acid residues of ChR2 into nonpolar alanine, and evaluated their photocurrent properties. Amongst them, the photocurrent generated by the E97A mutation, ChR2(E97A), was much smaller than expected from its expression. The ChR2(E97A) photocurrent was similar to wild-type ChR2 in the kinetic profiles, the reversal potential and the dependency to the light power density. Our results suggest that the residue E97 is one of the molecular determinants involved in the ion flux regulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kateriya, G. Nagel, E. Bamberg and P. Hegemann, “Vision” in single-celled algae, News Physiol Sci, 2004, 19, 133–137.
M. Melkonian and H. Robenek, Eyespot membranes of Chlamydomonas reinhardii: a freeze-fracture study, J Ultrastruct Res, 1980, 72, 90–102.
O. A. Sineshchekov, K. H. Jung and J. L. Spudich, Two rhodopsins mediate phototaxis to low- and high-intensity light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2002, 99, 8689–8694.
T. Suzuki, K. Yamasaki, S. Fujita, K. Oda, M. Iseki, K. Yoshida, M. Watanabe, H. Daiyasu, H. Toh, E. Asamizu, S. Tabata, K. Miura, H. Fukuzawa, S. Nakamura and T. Takahashi, Archaeal-type rhodopsins in Chlamydomonas: model structure and intracellular localization, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2003, 301, 711–717.
G. Nagel, D. Ollig, M. Fuhrmann, S. Kateriya, A. M. Musti, E. Bamberg and P. Hegemann, Channelrhodopsin-1: a light-gated proton channel in green algae, Science, 2002, 296, 2395–2398.
G. Nagel, T. Szellas, W. Huhn, S. Kateriya, N. Adeishvili, P. Berthold, D. Ollig, P. Hegemann and E. Bamberg, Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2003, 100, 13940–13945.
G. Nagel, T. Szellas, S. Kateriya, N. Adeishvili, P. Hegemann and E. Bamberg, Channelrhodopsins: directly light-gated cation channels, Biochem Soc Trans, 2005, 33, 863–866.
T. Ishizuka, M. Kakuda, R. Araki and H. Yawo, Kinetic evaluation of photosensitivity in genetically engineered neurons expressing green algae light-gated channels, Neurosci Res, 2006, 54, 85–94.
X. Li, D. V. Gutierrez, M. G. Hanson, J. Han, M. D. Mark, H. Chiel, P. Hegemann, L. T. Landmesser and S. Herlitze, Fast noninvasive activation and inhibition of neural and network activity by vertebrate rhodopsin and green algae channelrhodopsin, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2005, 102, 17816–17821.
E. S. Boyden, F. Zhang, E. Bamberg, G. Nagel and K. Deisseroth, Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity, Nat Neurosci, 2005, 8, 1263–1268.
P. Hegemann, Algal sensory photoreceptors, Annu Rev Plant Biol, 2008, 59, 167–189.
C. Bamann, T. Kirsch, G. Nagel and E. Bamberg, Spectral characteristics of the photocycle of channelrhodopsin-2 and its implication for channel function, J Mol Biol, 2008, 375, 686–694.
O. P. Ernst, P. A. Sanchez Murcia, P. Daldrop, S. P. Tsunoda, S. Kateriya and P. Hegemann, Photoactivation of channelrhodopsin, J Biol Chem, 2008, 283, 1637–1643.
F. Zhang, M. Prigge, F. Beyriere, S. P. Tsunoda, J. Mattis, O. Yizhar, P. Hegemann and K. Deisseroth, Red-shifted optogenetic excitation: a tool for fast neural control derived from Volvox carteri, Nat Neurosci, 2008, 11, 631–633.
L. Adamian, Z. Ouyang, Y. Y. Tseng and J. Liang, Evolutionary patterns of retinal-binding pockets of type I rhodopsins and their functions, Photochem Photobiol, 2006, 82, 1426–1435.
E. Pebay-Peyroula, A. Royant, E. M. Landau and J. Navarro, Structural basis for sensory rhodopsin function, Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1565, 196–205.
P. Hegemann, S. Ehlenbeck and D. Gradmann, Multiple photocycles of channelrhodopsin, Biophys J, 2005, 89, 3911–3918.
J. K. Lanyi, Mechanism of ion transport across membranes - bacteriorhodopsin as a prototype for proton pumps, J Biol Chem, 1997, 272, 31209–31212.
R. Neutze, E. Pebay-Peyroula, K. Edman, A. Royant, J. Navarro and E. M. Landau, Bacteriorhodopsin: a high-resolution structural view of vectorial proton transport, Biochim Biophys Acta, 2002, 1565, 144–167.
T. Mogi, L. J. Stern, T. Marti, B. H. Chao and H. G. Khorana, Asparitic acid substitutions affect proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1988, 85, 4148–4152.
M. Kataoka, H. Kamikubo, F. Tokunaga, L. S. Brown, Y. Yamazaki, A. Maeda, M. Sheves, R. Needleman and J. K. Lanyi, Energy coupling in an ion pump - the reprotonation switch of bacteriorhodopsin, J Mol Biol, 1994, 243, 621–638.
L. S. Brown, H. Kamikubo, L. Zimányi, M. Kataoka, F. Tokunaga, P. Verdegem, J. Lugtenburg and J. K. Lanyi, A local electrostatic change is the cause of the large-scale protein conformation shift in bacteriorhodopsin, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1997, 94, 5040–5044.
P. Berthold, S. P. Tsunoda, O. P. Ernst, W. Mages, D. Gradmann and P. Hegemann, Channelrhodopsin-1 initiates phototaxis and photophobic responses in Chlamydomonas by immediate light-induced depolarization, Plant Cell, 2008, 20, 1665–1677.
B. Hille, Ion channels of excitable membranes, third ed., Sinauer Associates, Massachusetts, USA, 2001.
R. MacKinnon, Pore loops: an emerging theme in ion channel structure, Neuron, 1995, 14, 889–892.
G. Owsianik, K. Talavera, T. Voets and B. Nilius, Permeation and selectivity of TRP channels, Annu Rev Physiol, 2006, 68, 685–717.
P. H. Seeburg, F. Single, T. Kuner, M. Higuchi and R. Sprengel, Genetic manipulation of key determinants of ion flow in glutamate receptor channels in the mouse, Brain Res, 2001, 907, 233–243.
M. H. Akabas, D. A. Stauffer, M. Xu and A. Karlin, Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants, Science, 1992, 258, 307–310.
H. Luecke, B. Schobert, J. K. Lanyi, E. N. Spudich and J. L. Spudich, Crystal structure of sensory rhodopsin II at 2.4 angstroms: insights into color tuning and transducer interaction, Science, 2001, 293, 1499–1503.
A. Miyazawa, Y. Fujiyoshi and N. Unwin, Structure and gating mechanism of the acetylcholine receptor pore, Nature, 2003, 423, 949–955.
D. Huber, L. Petreanu, N. Ghitani, S. Ranade, T. Hromadka, Z. Mainen and K. Svoboda, Sparse optical microstimulation in barrel cortex drives learned behaviour in freely moving mice, Nature, 2008, 451, 61–64.
S. J. Kuhlman and Z. J. Huang, High-resolution labeling and functional manipulation of specific neuron types in mouse brain by Cre-activated viral gene expression, PLoS ONE, 2008, 3, e2005.
L. Petreanu, D. Huber, A. Sobczyk and K. Svoboda, Channelrhodopsin-2-assisted circuit mapping of long-range callosal projections, Nat Neurosci, 2007, 10, 663–668.
N. Toni, D. A. Laplagne, C. Zhao, G. Lombardi, C. E. Ribak, F. H. Gage and A. F. Schinder, Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells, Nat Neurosci, 2008, 11, 901–907.
Y. P. Zhang and T. G. Oertner, Optical induction of synaptic plasticity using a light-sensitive channel, Nat Methods, 2007, 4, 139–141.
G. Nagel, M. Brauner, J. F. Liewald, N. Adeishvili, E. Bamberg and A. Gottschalk, Light activation of channelrhodopsin-2 in excitable cells of Caenorhabditis elegans triggers rapid behavioral responses, Curr Biol, 2005, 15, 2279–2284.
A. D. Douglass, S. Kraves, K. Deisseroth, A. F. Schier and F. Engert, Escape behavior elicited by single, channelrhodopsin-2-evoked spikes in zebrafish somatosensory neurons, Curr Biol, 2008, 18, 1133–1137.
B. R. Arenkiel, J. Peca, I. G. Davison, C. Feliciano, K. Deisseroth, G. J. Augustine, M. D. Ehlers and G. Feng, In vivo light-induced activation of neural circuitry in transgenic mice expressing channelrhodopsin-2, Neuron, 2007, 54, 205–218.
A. Bi, J. Cui, Y. P. Ma, E. Olshevskaya, M. Pu, A. M. Dizhoor and Z. H. Pan, Ectopic expression of a microbial-type rhodopsin restores visual responses in mice with photoreceptor degeneration, Neuron, 2006, 50, 23–33.
S. Herlitze and L. T. Landmesser, New optical tools for controlling neuronal activity, Curr Opin Neurobiol, 2007, 17, 87–94.
P. S. Lagali, D. Balya, G. B. Awatramani, T. A. Munch, D. S. Kim, V. Busskamp, C. L. Cepko and B. Roska, Light-activated channels targeted to ON bipolar cells restore visual function in retinal degeneration, Nat Neurosci, 2008, 11, 667–675.
H. Tomita, E. Sugano, H. Yawo, T. Ishizuka, H. Isago, S. Narikawa, S. Kügler and M. Tamai, Restoration of visual response in aged dystrophic RCS rats using AAV-mediated channelopsin-2 gene transfer, Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2007, 48, 3821–3826.
H. Wang, Y. Sugiyama, T. Hikima, E. Sugano, H. Tomita, T. Takahashi, T. Ishizuka and H. Yawo, J. Biol. Chem. 10.1074/jbc.M807632200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/b815762f
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sugiyama, Y., Wang, H., Hikima, T. et al. Photocurrent attenuation by a single polar-to-nonpolar point mutation of channelrhodopsin-2. Photochem Photobiol Sci 8, 328–336 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b815762f
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/b815762f