Abstract
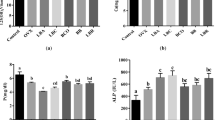
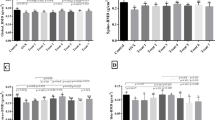
Prebiotics affect mineral absorption, in part by increasing solubility due to short chain fatty acid generation. Prebiotics stimulate the growth of probiotics in the gut and probiotics may affect mineral absorption by similar mechanisms. The objectives of this study were to measure (1) the effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain HN001 (HN001) on mineral absorption in growing male rats and (2) whether HN001 can reduce bone loss and affect bone properties in female ovariectomised (OVX) rats. Study 1: Twenty-two 3-week-old Sprague-Dawley rats were weaned onto a milk powder-based diet supplying 20% protein and 0.5% calcium. After a week, the rats were randomised into two groups: one continuing on the base diet and the other receiving 109 cfu HN001 per day in the diet. After 3 weeks, the animals were housed in metabolic cages for 8 days. Food intake was measured, and urine and faeces were collected for 3 days. Calcium and magnesium balances were calculated. Study 2: Forty 5.5-month-old female Sprague-Dawley rats were ovariectomised or sham-operated and randomised into three groups. The sham (n = 10) and OVX control groups (n = 15) remained on a caseinate-based control diet, while the experimental group (n = 15) received 109 cfu HN001 per day in the diet. After 12 weeks, bone density was measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and bone and blood samples were collected. HN001 improved calcium and magnesium retention in the growing male rats, but due to differences in food intake, data was inconclusive. However, HN001-fed OVX rats had a reduced rate of bone loss and a higher final bone density in the spine and femur at week 12 compared to the OVX control group. HN001 may improve mineral bioavailability and have a positive effect on bone mineral density and mineral content. The underlying mechanisms need to be researched.
Abstract
(1) Lb HN001 (Lactobacillus rhamnosus) ; (2) Lb HN001 (OVX) : (1) 22 3 Sprague-Dawley 20% 0.5% 109 cfu Lb HN001 3 8 d 3 d (2) 40 5.5 Sprague-Dawley 3 (n = 10) OVX (n = 15) (n = 15) 109 cfu Lb HN001 12 X Lb HN001 OVX 12 Lb HN001-OVX Lb HN001
Résumé
Les prébiotiques ont un effet sur l’absorption minérale, en partie en augmentant la solubilité due à la génération d’acides gras à chaîne courte. Les prébiotiques stimulent la croissance des probiotiques dans l’intestin et les probiotiques peuvent affecter l’absorption minérale par des mécanismes similaires. Les objectifs de l’étude ont été de mesurer : (1) l’effet de Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (HN001) sur l’absorption minérale chez le rat mâle en croissance, (2) si HN001 peut réduire la perte osseuse et affecter les propriétés des os chez la ratte ovariectomisée (OVX). Étude 1 : 22 rats Sprague-Dawley de 3 semaines ont été sevrés puis soumis à un régime à base de poudre de lait apportant 20 % de protéines et 0,5 % de calcium. Après une semaine, les rats ont été répartis au hasard en deux groupes : l’un continuant le régime de base, l’autre recevant en plus 109 ufc HN001 par jour. Après 3 semaines, les animaux ont été installés dans des cages métaboliques pour 8 jours. La prise alimentaire a été mesurée, et l’urine et les fèces récoltés pendant 3 jours. Les équilibres en calcium et magnésium ont été calculés. Étude 2 : 40 rattes Sprague-Dawley de 5 mois et demi ont été ovariectomisées ou opérées de façon fictive puis réparties au hasard en 3 groupes. Les groupes « fictif » (n = 10) ou OVX de contrôle (n = 15) étaient maintenus au régime contrôle à base de caséinate tandis que le groupe expérimental (n = 15) recevait le même régime additionné de 109 ufc HN001 par jour. Après 12 semaines, la densité osseuse a été mesurée par absorptiométrie à rayons X biphotonique et des échantillons d’os et de sang ont été collectés. HN001 améliorait la rétention de calcium et magnésium chez les rats mâles en croissance, mais, en raison de différences dans la prise alimentaire, les données étaient peu concluantes. Cependant, les rattes OVX nourries avec HN001 montraient moins de perte osseuse et une densité osseuse finale plus élevée dans la colonne vertébrale et le fémur à 12 semaines que les rattes du groupe contrôle. HN001 pourrait améliorer la biodisponibilité minérale et avoir un effet positif sur la densité minérale osseuse et la teneur en minéraux. Les mécanismes qui sous-tendent cette activité restent à déterminer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beynen A.C., Baas J.C., Hoekemeijer P.E., Kappert H.J., Bakker M.H., Koopman J.P., Lemmens A.G., Faecal bacterial profile, nitrogen excretion and mineral absorption in healthy dogs fed supplemental oligofructose, J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 86 (2002) 298–305.
Bronner F., Mechanisms of intestinal calcium absorption, J. Cell Biochem. 88 (2003) 387–393.
Chow J.-M.C., Probiotics and prebiotics: a brief overview, J. Renal Nutr. 12 (2002) 76–86.
Ghanem K.Z., Badawy I.H., Abdel-Salam A.M., Influence of yoghurt and probiotic yoghurt on the absorption of calcium, magnesium, iron and bone mineralisation in rats, Milk Sci. Int. 59 (2004) 472–475.
Kelleher S.L., Casas I., Carbajal N., Lonnerdal B., Supplementation of infant formula with the probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri and zinc: impact on enteric infection and nutrition in infant rhesus monkeys, J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 35 (2002) 163–168.
Lutz T., Scharrer E., Effects of short-chain fatty acids on calcium absorption in the rat colon, Exp. Physiol. 76 (1991) 615–618.
Minamida K., Sujaya I.N., Tamura A., Shigematsu N., Sone T., Yokota A., Asano K., Benno Y., Tomita F., The effects of di-D-fructofuranose-1,2:2,3-dianhydride (DFA III) administration on human intestinal microbiota, J. Biosci. Bioeng. 98 (2004) 244–250.
Moskilde L., Assessing bone quality — animal models in preclinical osteoporosis research, Bone 17 (1995) 343S-352S.
Narva M., Collin M., Lamberg-Allardt C., Karkkainen M., Poussa T., Vapaatalo H., Korpela R., Effects of long-term intervention with Lactobacillus helveticus-fermented milk on bone mineral density and bone mineral content in growing rats, Ann. Nutr. Metab. 48 (2004) 228–234.
Narva M., Nevala R., Poussa T., Korpela R., The effect of Lactobacillus helveticus fermented milk on acute changes in calcium metabolism in postmenopausal women, Eur. J. Nutr. 43 (2004) 61–68.
Narva M., Rissanen J., Jussi H., Heiki V., Kalervo V., Riita K., Effects of bioactive peptide, valyl-prolyl-proline (VPP), and Lactobacillus helveticus fermented milk containing VPP on bone loss in ovariectomized rats, Ann. Nutr. Metab. 51 (2007) 65–74.
National Research Council, Nutrient Requirements of Laboratory Animals, 4th edn., National Academic Press, Washington, DC, 1995.
Perez-Conesa D., Lopez G., Abellan P., Ros G., Bioavailability of calcium, magnesium and phosphorous in rats fed probiotic, prebiotic and symbiotic powder follow-up infant formulas and their effect on physiological and nutritional parameters, J. Sci. Food Agric. 86 (2006) 2327–2336.
Perez-Conesa D., Lopez G., Ros G., Effects of probiotic, prebiotic and symbiotic follow-up infant formulas on large intestine morphology and bone mineralisation in rats, J. Sci. Food Agric. 87 (2007) 1059–1068.
Raschka L., Daniel H., Diet composition and age determine the effects of inulin-type fructans on intestinal calcium absorption in the rat, Eur. J. Nutr. 44 (2005) 360–364.
Roberfroid M.B., Prebiotics and probiotics: are they functional foods?, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71 (2000) 1682S-1687S.
Scholz-Ahrens K.E., Ade P., Marten B., Weber P., Timm W., Asil Y., Gluer C.-C., Schrezenmeir J., Prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics affect mineral absorption, bone mineral content and bone structure, J. Nutr. 137 (2007) 838S-846S.
Scholz-Ahrens K.E., Schaafsma G., Van der Heuvel E.G.H.M., Schrezenmeier J., Effects of prebiotics on mineral metabolism, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73 (2001) 459S-464S.
Scholz-Ahrens K.E., Schrezenmeier J., Inulin, oligofructose and mineral metabolism — experimental data and mechanism, Br. J. Nutr. 87 (2002) S179-S186.
Scholz-Ahrens K.E., van Loo J., Schrezenmeier J., Effect of oligofructose on bone mineralization in ovariectomised rats is affected by dietary calcium, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73 (2001) 498S (abstr.).
Scholz-Ahrens K.E., van Loo J., Schrezenmeier J., Long-term effect of oligofructose on bone trabecular structure in ovariectomised rats, J. Clin. Nutr. 73 (2001) 498 (abstr.).
Zhao L.J., Papasian C.J., Drees B., Hamilton J., Deng H.W., Correlation of obesity and osteoporosis: effects of fat mass on the determination of osteoporosis, J. Bone Miner. Res. 23 (2008) 17–29.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kruger, M.C., Fear, A., Chua, WH. et al. The effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 on mineral absorption and bone health in growing male and ovariectomised female rats. Dairy Sci. Technol. 89, 219–231 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1051/dst/2009012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1051/dst/2009012