Abstract
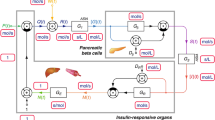
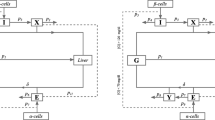
The ability to evaluate the pancreatic insulin secretion rate (ISR) is essential for a quantitative understanding of the glucose regulation system in man. Various approaches have been developed for evaluation of the ISR in vivo. The aim of this study was to compare input/output and compartmental models of C-peptide to reconstruct the ISR in response to both physiological and nonphysiological glucose stimuli in healthy humans. In particular we applied the nonparametric stochastic deconvolution and the C-peptide minimal model approaches to the graded up&down glucose infusion protocol, where glucose was infused at progressively increasing and then decreasing rates, and to the intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT), where an impulse dose of glucose was administered. Our results show that the two models give virtually identical results when glucose and C-peptide (and thus ISR) profiles are smooth and regular, but when vigorous nonstationarities are present, like during the first 4 min of the IVGTT, the two ISR profiles are different (but not their areas under the curve). The C-peptide minimal model, albeit requiring, at variance with deconvolution, the knowledge of glucose data, has the advantage of providing quantitative indices of the β-cell function, which is important in the parametric definition of different physiopathological states. © 2001 Biomedical Engineering Society.
PAC01: 8715Rn, 8714Ee, 8716Ac
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barret, P. H. R., B. M. Bell, C. Cobelli, H. Golde, A. Schumitzky, P. Vicini, and D. Foster. SAAM II: Simulation, analysis and modeling software for tracer and pharmacokinetic studies. Metabolism47:484–492, 1998.
Carson, E. R., C. Cobelli, and L. Finkelstein. The Mathematical Modeling of Metabolic and Endocrine Systems. New York: Wiley, 1983.
Cobelli, C., D. Foster, and G. Toffolo. Tracer Kinetic in Biomedical Research: From Data to Model. New York: Kluwer Academic, 2000.
De Nicolao, G.and D. Liberati. Linear and nonlinear techniques for the deconvolution of hormone time-series. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.40:440–455, 1993.
De Nicolao, G., G. Sparacino, and C. Cobelli. Nonparametric input estimation in physiological systems: Problems, methods, case studies. Automatica33:851–870, 1997.
Eaton, R. P., R. C. Allen, D. S. Schade, K. M. Erickson, and J. Standefer. Prehepatic insulin production in man: Kinetic analysis using peripheral connecting peptide behaviour. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.51:520–28, 1980.
Faber, O. K., C. Binder, J. Markussen, L. G. Heding, V. K. Naithani, H. Kuzuya, P. Blix, D. L. Horwitz, and A. H. Rubenstein. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes27:170–177, 1978.
Hovorka, R., L. Chassin, S. D. Luzio, R. Playle, and D. R. Owens. Pancreatic β cell responsiveness during meal tolerance test: Model assessment in normal subjects and subjects with newly diagnosed noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.83:744–750, 1998.
Hovorka, R., P. A. Soons, and M. A. Young. ISEC: A program to calculate insulin secretion. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed.50:253–264, 1996.
Polonsky, K. S.and A. H. Rubenstein. C-peptide as a measure of the secretion and hepatic extraction of insulin: Pitfalls and limitations. Diabetes33:486–494, 1984.
Polonsky, K. S., J. Licinio-Paixao, B. D. Given, W. Pugh, P. Rue, J. Galloway, T. Karrison, and B. Frank. Use of biosynthetic human C-peptide in the measurement of insulin secretion rates in normal volunteers and type I diabetic patients. J. Clin. Invest.51:98–105, 1986.
Sparacino, G.and C. Cobelli. A stochastic deconvolution method to reconstruct insulin secretion rate after a glucose stimulus. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.43:512–529, 1996.
Sparacino, G., G. Pillonetto, M. Capello, G. De Nicolao, and C. Cobelli. WINSTODEC: A Stochastic Deconvolution interactive program for physiological and pharmacokinetic systems. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. (in press).
Toffolo, G., E. Breda, M. K. Cavaghan, D. A. Ehrmann, K. S. Polonsky, and C. Cobelli. Quantitative indexes of β cell function during graded up&down glucose infusion from C-peptide minimal models. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.280:E2–E10, 2001.
Toffolo, G., F. De Grandi, and C. Cobelli. Estimation of β-cell sensitivity from IVGTT C-peptide data. Knowledge of the kinetics avoids errors in modeling the secretion. Diabetes44:845–854, 1995.
Van Cauter, E., F. Mestrez, J. Sturie, and K. S. Polonsky. Estimation of insulin secretion rates from C-peptide levels. Comparison of individual and standard kinetic parameters for C-peptide clearance. Diabetes41:368–377, 1992.
Vølund, A., K. S. Polonsky, and R. N. Bergman. Calculated pattern of interportal insulin appearance without independent assessment of C-peptide kinetics. Diabetes36:1195–1202, 1987.
Watanabe, R. M., A. Vølund, S. Roy, and R. N. Bergman. Pre-hepatic beta-cell secretion during the intravenous glucose tolerance test in humans: Application of a combined model of insulin and C-peptide kinetics. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.69:790–797, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Breda, E., Cobelli, C. Insulin Secretion Rate During Glucose Stimuli: Alternative Analyses of C-Peptide Data. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 29, 692–700 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1385804
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1114/1.1385804