Abstract
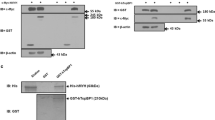
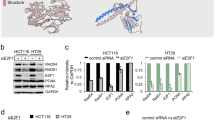
Colon cancer remains one of the most common digestive system malignancies in the World. This study investigated the possible interaction between RAD51 and minichromosome maintenance proteins (MCMs) in HCT116 cells, which can serve as a model system for forming colon cancer foci. The interaction between RAD51 and MCMs was detected by mass spectrometry. Silenced MCM vectors were transfected into HTC116 cells. The expressions of RAD51 and MCMs were detected using Western blotting. Foci forming and chromatin fraction of RAD51 in HCT116 cells were also analyzed. The results showed that RAD51 directly interacted with MCM2, MCM3, MCM5, and MCM6 in colon cancer HTC116 cells. Suppression of MCM2 or MCM6 by shRNA decreased the chromatin localization of RAD51 in HTC116 cells. Moreover, silenced MCM2 or MCM6 decreased the foci forming of RAD51 in HTC116 cells. Our study suggests that the interaction between MCMs and RAD51 is essential for the chromatin localization and foci forming of RAD51 in HCT116 cell DNA damage recovery, and it may be a theoretical basis for analysis of RAD51 in tumor samples of colon cancer patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSBs:
-
DNA double-stranded breaks
- HR:
-
homologous recombination
- MCM:
-
minichromosome maintenance (proteins)
- shRNA:
-
short hairpin RNA
References
Kim, E. Y., Kwon, K. A., Choi, I. J., Ryu, J. K., and Hahm, K. B. (2014) International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2014: turnpike to the future, Clin. Endosc., 47, 371–382.
Bakker, I. S., Snijders, H. S., Grossmann, I., Karsten, T. M., Havenga, K., and Wiggers, T. (2016) High mortality rates after non-elective colon cancer resection: results of a national audit, Col. Dis., 18, 612–621.
Yuriko, T., Sachiko, I., Reina, O., Nana, C., Naomi, N., and Ken-Ichi, I. (2015) Effects of growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible protein 34 (GADD34) on inflammation-induced colon cancer in mice, Br. J. Cancer, 113, 669–679.
Hochster, H. S., and Sargent, D. J. (2016) One good DNA-damage deserves another: oxaliplatin in MSI-high colon cancer, J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 108, doi: 10.1093/jnci/ djw011.
Seiwert, N., Neitzel, C., Stroh, S., Frisan, T., Audebert, M., Toulany, M., Kaina, B., and Fahrer, J. (2017) AKT2 suppresses pro-survival autophagy triggered by DNA dou-ble-strand breaks in colorectal cancer cells, Cell Death Dis., 8, e3019.
Mahaney, B. L., Katheryn, M., and Lees-Miller, S. P. (2009) Repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA doublestrand breaks by non-homologous end-joining, Biochem. J., 417, 639650.
Thompson, L. H. (2012) Recognition, signaling, and repair of DNA double-strand breaks produced by ionizing radia-tion in mammalian cells: the molecular choreography, Mutat. Res., 751, 158–246.
Barnard, S., Bouffler, S., and Kai, R. (2013) The shape of the radiation dose response for DNA double-strand break induction and repair, Gen. Integr., 4, 1.
Rong, Y. S., and Golic, K. G. (2004) The homologous chromosome is an effective template for the repair of mitot-ic DNA double-strand breaks in Drosophila, Genetics, 165, 1831–1842.
Yi-Hsuan, L., Chia-Ching, C., Chui-Wei, W., and Shu-Chun, T. (2009) Recruitment of Rad51 and Rad52 to short telomeres triggers a Mec1-mediated hypersensitivity to double-stranded DNA breaks in senescent budding yeast, PLoS One, 4, e8224.
Jasin, M. (2001) Double-Strand Break Repair and Homo-logous Recombination in Mammalian Cells, Humana Press.
Sharma, A., Singh, K., and Almasan, A. (2012) Histone H2AX phosphorylation: a marker for DNA damage, Methods Mol. Biol., 920, 613–626.
Kyungsoo, H., Warren, F., Soon, C. D., Srividya, B., Leandro, C., Devaraj, S. G. T., Bhavin, S., Sunil, S., Chang, J. C., and Melnick, A. M. (2014) Histone deacety-lase inhibitor treatment induces “BRCAness” and synergis-tic lethality with PARP inhibitor and cisplatin against human triple negative breast cancer cells, Oncotarget, 5, 5637–5650.
Veelen, L. R. V., Essers, J., Van de Rakt, M. W., Odijk, H., Pastink, A., Zdzienicka, M. Z., Paulusma, C. C., and Kanaar, R. (2005) Ionizing radiation-induced foci forma-tion of mammalian Rad51 and Rad54 depends on the Rad51 paralogs, but not on Rad52, Mutat. Res., 574, 34–49.
Mladenov, E., Anachkova, B., and Tsaneva, I. (2006) Subnuclear localization of Rad51 in response to DNA damage, Genes Cells, 11, 513–524.
Madalena, T., Derek, D., and West, S. C. (2003) BRCA2-dependent and independent formation of RAD51 nuclear foci, Oncogene, 22, 1115–1123.
Bindra, R. S., Schaffer, P. J., Meng, A., Woo, J., Maseide, K., Roth, M. E., Lizardi, P., Hedley, D. W., Bristow, R. G., and Glazer, P. M. (2004) Down-regulation of Rad51 and decreased homologous recombination in hypoxic cancer cells, Mol. Cell. Biol., 24, 8504–8518.
Lei, M. (2005) The MCM complex: its role in DNA replication and implications for cancer therapy, Curr. Cancer Drug Targets, 5, 365–380.
Hyrien, O. (2016) How MCM loading and spreading specify eukaryotic DNA replication initiation sites, F1000Res., 5.
Shukla, A., Navadgi, V. M., Mallikarjuna, K., and Rao, B. J. (2005) Interaction of hRad51 and hRad52 with MCM complex: a cross-talk between recombination and replication proteins, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 329, 1240–1245.
Park, J., Long, D. T., Lee, K. Y., Abbas, T., Shibata, E., Negishi, M., Luo, Y., Schimenti, J. C., Gambus, A., Walter, J. C., and Dutta, A. (2013) The MCM8–MCM9 complex promotes RAD51 recruitment at DNA damage sites to facilitate homologous recombination, Mol. Cell. Biol., 33, 1632–1644.
Xiangzi, H., Aaron, A., Kang, F., Toshiya, T., and Youwei, Z. (2014) The interaction between checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) and the minichromosome maintenance (MCM) complex is required for DNA damage-induced Chk1 phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 24716–24723.
Purcell, D. J., Chauhan, S., Jimenez-Stinson, D., Elliott, K. R., Tsewang, T. D., Lee, Y. H., Marples, B., and Lee, D. Y. (2015) Novel CARM1-interacting protein, DZIP3, is a transcriptional coactivator of estrogen receptor-alpha, Mol. Endocrinol., 29, 1708–1719.
Lu, J., Kashaev, N., and Huber, N. (2001) Werner helicase relocates into nuclear foci in response to DNA damaging agents and co-localizes with RPA and Rad51, Genes Cells, 6, 421–430.
Tianju, L., Hong, J., Matthew, U., Biao, H., Naozumi, H., Bethany, M., Andrew, M. K., Lukacs, N. W., and Phan, S. H. (2004) Regulation of found in inflammatory zone 1 expression in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis: role of IL-4/IL-13 and mediation via STAT-6, J. Immunol., 173, 3425–3431.
Wang, H., Zhang, X., Teng, L., and Legerski, R. J. (2015) DNA damage checkpoint recovery and cancer development, Exp. Cell Res., 334, 350–358.
Glover, K. P., Markell, L. K., Donner, E. M., and Xan, H. (2014) Protein kinase C-activating tumor promoters modulate the DNA damage response in UVC-irradiated TK6 cells, Toxicol. Lett., 229, 210–219.
Delmas, S., Shunburne, L., Ngo, H. P., and Allers, T. (2009) Mre11–Rad50 promotes rapid repair of DNA damage in the polyploid archaeon Haloferax volcanii by restraining homologous recombination, PLoS Genet., 5, e1000552.
Gachechiladze, M., Skarda, J., Soltermann, A., and Joerger, M. (2017) RAD51 as a potential surrogate marker for DNA repair capacity in solid malignancies, Int. J. Cancer, 141, 1286–1294.
Zhao, Q., Guan, J., Zhang, Z., Lv, J., Wang, Y., Liu, L., Zhou, Q., and Mao, W. (2017) Inhibition of Rad51 sensitizes breast cancer cells with wild-type PTEN to olaparib, Biomed. Pharmacother., 94, 165–168.
Simon, N. E., and Schwacha, A. (2014) The Mcm2-7 replicative helicase: a promising chemotherapeutic target, 549719.
Labib, K., Tercero, J. A., and Diffley, J. F. (2000) Uninterrupted MCM2-7 function required for DNA replication fork progression, Science, 288, 1643–1647.
Liu, Y., He, G., Wang, Y., Guan, X., Pang, X., and Zhang, B. (2013) MCM-2 is a therapeutic target of trichostatin A in colon cancer cells, Toxicol. Lett., 221, 23–30.
Giaginis, C., Georgiadou, M., Dimakopoulou, K., Tsourouflis, G., Gatzidou, E., Kouraklis, G., and Theocharis, S. (2009) Clinical significance of MCM-2 and MCM-5 expression in colon cancer: association with clinicopathological parameters and tumor proliferative capacity, Dig. Dis. Sci., 54, 282–291.
Courilleau, C., Chailleux, C., Jauneau, A., Grimal, F., Briois, S., Boutet-Robinet, E., Boudsocq, F., Trouche, D., and Canitrot, Y. (2012) The chromatin remodeler p400 ATPase facilitates Rad51-mediated repair of DNA doublestrand breaks, J. Cell Biol., 199, 1067–1081.
Reh, W. A., Nairn, R. S., Lowery, M. P., and Vasquez, K. M. (2017) The homologous recombination protein RAD51D protects the genome from large deletions, Nucleic Acids Res., 45, 1835–1847.
Han, X., Aslanian, A., Fu, K., Tsuji, T., and Zhang, Y. (2014) The interaction between checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) and the minichromosome maintenance (MCM) complex is required for DNA damage-induced Chk1 phosphorylation, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 24716–24723.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM17-211, November 6, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, J., Luo, HL., Pan, H. et al. Interaction between RAD51 and MCM complex is essential for RAD51 foci forming in colon cancer HCT116 cells. Biochemistry Moscow 83, 69–75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297918010091
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297918010091