Abstract
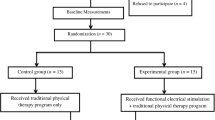
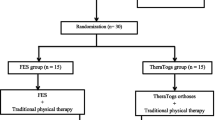
Cerebral palsy (CP) considerably impairs the ability to maintain upright stance. The effects of locomotor training and functional electrical stimulation (FES) on postural control were determined in 27 children aged 6–12 years with severe CP. The severity level of the clinical manifestations of CP was classified as 3 according to the Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS). All patients participated in 15 30-min mechanical therapy sessions using robot-assisted passive stepping. In 12 out of 27 children, the locomotion therapy was accompanied by FES. Stabilometry and plantography tests were performed in 23 healthy age-matched children. Postural control in children with CP differed from the stabilograms of healthy children in a forward shift of the center of pressure (COP) projection; higher values of the COP trajectory area and length, the mean amplitude of the COP oscillations, and the absence of COP response to the eyes closed condition. After treatment, the posturographic characteristics tended to normalize in relation to the values obtained in neurologically intact children. The improvement was observed in 43% of children without FES and in 75% of children in the group with FES. Analysis of plantograms revealed normalization of footprints in children who received FES. Thus, it was demonstrated that FES combined with locomotor training resulted in the improvement in vertical posture control in children with severe CP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vitenzon, A.S. and Petrushanskaya, K.A., Justification and results of using functional electric stimulation of muscles during walking in patients with various pathologies of locomotor system, Lech. Fizkul’t. Sport. Med., 2010, no. 2, p. 29.
Solopova, I.A., Moshonkina, T.R., Umnov, V.V., et al., Neurorehabilitation of patients with cerebral palsy, Hum. Physiol., 2015, vol. 41, no. 4, p. 448.
Ikoeva, G.A., Kivoenko, O.I., and Polozenko, O.D., Robotic-assisted mechanotherapy in rehabilitation after complex orthopedic surgery in children with cerebral palsy, Neirokhirurg. Nevrol. Det. Vozrasta, 2012, vol. 34, no. 4, p. 32.
Semenova, K.A., The problem of rehabilitation treatment of children with cerebral palsy, Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. im. S.S. Korsakova, 2012, vol. 2, no. 7, p. 9.
Semenova, K.A., Mastyukova, E.M., and Smuglin, M.Ya., Klinika i reabilitatsionnaya terapiya detskikh tserebral’nykh paralichei (Clinical and Rehabilitation Therapy of Infantile Cerebral Paralysis), Moscow, 1972.
Palisano, R., Rosenbaum, P., Walter, S., et al., Development and reliability of a system to classify gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy, Dev. Med. Child Neurol., 1997, vol. 39, no. 4, p. 214.
Krayushkin, A.I., Perepelkin, A.I., Smaglyuk, E.S., and Suleimanov, R.Kh., The characteristics of anatomical and functional parameters of young men’s feet by means of computer plantography, Vestn. Nov. Med. Tekhnol., 2011, vol. 18, no. 2, p. 258.
Perepelkin, A.I., Mandrikov, V.B., and Krayushkin, A.I., Vliyanie dozirovannoi nagruzki na izmenenie struktury i funktsii stopy cheloveka (The Effect of Controlled Activity on Changes in the Structure and Functions of Human Feet), Volgograd: Izd. Volgorgad. Gos. Med. Univ., 2012.
Naumochkina, N.A. and Nikityuk, I.E., Involvement of spinal marrow in the pathological process as a result of shoulder joint injury during birth: A biomechanical study, Vrach-Aspirant, 2013, vol. 1.3, no. 56, p. 388.
Kenis, V.M., Ivanov, S.V., and Stepanova, Yu.A., Postural disturbances and feet deformities in children with cerebral palsy, Travmatol. Ortop., 2011, no. 3, p. 40.
Skvortsov, D.V., Stabilometricheskoe issledovanie (Stabilometric Study), Moscow: Maska, 2010.
Kurenkov, A.L., Batysheva, T.T., Vinogradov, A.B., and Zyuzyaeva, E.K., Spasticity in children cerebral palsy: diagnosis and treatment strategies, Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. im. S.S. Korsakova, 2012, vol. 112, no. 7, p. 24.
Nemkova, S.A., Estimating the efectiveness of complex rehabilitation in children wih cerebral palsy and head injury, Ross. Neirokhir. Zh. im. A.L. Polenova, 2013, no. 5, p. 56.
Nashner, L.M., Shumway-Cook, A., and Marin, O., Stance posture control in select groups of children with cerebral palsy: deficits in sensory organization and muscular coordination, Exp. Brain Res., 1983, vol. 49, no. 3, p. 393.
Ferdjallah, M., Harris, G.F., Smith, P., and Wertsch, J.J., Analysis of postural control synergies during quiet standing in healthy children and children with cerebral palsy, Clin. Biomech., 2002, vol. 17, no. 3, p. 203.
Nemkova, S.A., Zavadenko, N.N., and Argunova, G.V., Regulation of vertical posture in children and adolescents with head injury, Vopr. Prakt. Pediatr., 2014, no. 1, p. 70.
Sinel’nikova, A.N., Sologubov, E.G., and Yavorskii, A.B., Interaction between visual and proprioceptive analyzers in vertical posture control, Hum. Physiol., 2001, vol. 27, no. 3, p. 312.
Sal’kov, V.N. and Khudoerkov, R.M., Structural changes in visual cortex area 17 in children with aftereffects of perinatal injury to the central nervous system, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2007, vol. 143, no. 6, p. 753.
Levchenkova, V.D. and Semenova, K.A., Modern views on the morphological basis of cerebral palsy in children, Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., 2012, vol. 7, no. 2, p. 4.
Brandt, T., Paulus, W., and Straube, A., Vision and posture, in Disorders of Posture and Gait, Bles, W. and Brandt, T., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1986, p. 157.
Druïbicki, M., Rusek, W., Szczepanik, M., et al., Assesment of the impact orthotic gait training on balance in children with cerebral palsy, Acta Bioeng. Biomech., 2010, vol. 12, no. 2, p. 53.
Grecco, L.A.C., Tomita, S.M., Christovão, T.C.L., et al., Effect of treadmill gait training on static and functional balance in children with cerebral palsy: a randomized controlled trial, Braz. J. Phys. Ther., 2013, vol. 17, no. 1, p. 17.
Petrushanskaya, K.A. and Vitenzon, A.S., Restorative therapy in patients with infantile cerebral palsy via functional electrical muscle stimulation during walking, Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr., 2009, no. 1, p. 27.
Chiu, H.C. and Ada, L., Effect of functional electrical stimulation on activity in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review, Pediatr. Phys. Ther., 2014, vol. 26, no. 3, p. 283.
Grigor’ev, A.I., Kozlovskaya, I.B., and Shenkman, B.S., Role of support afferent stimuli in the organization of tonic muscle system, Ross. Fiziol. Zh. im. I.M. Sechenova, 2004, vol. 90, no. 5, p. 508.
Ogurtsova, T.N., Metod obsledovaniya oporno-dvigatel’nogo apparata cheloveka po otpechatkam stop v dinamike i sintez bionicheskikh stelek. Promotsionnaya rabota (Method of Investigation of Human SupportMovement Apparatus by Foot Imprints in Dynamics and Synthesis of Bionic Insoles), Riga: Rizh. Tekhnol. Univ., 2006.
Anichkov, N.M., Kudryavtsev, V.A., and Minchenko, N.L., Clinical–Morphological parallels in broad forefoot, Travmatol. Ortop. Ross., 1995, no. 1, p. 15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © I.E. Nikityuk, T.R. Moshonkina, N.A. Shcherbakova, S.V. Vissarionov, V.V. Umnov, V.Yu. Rozhdestvenskii, Yu.P. Gerasimenko, 2016, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2016, Vol. 42, No. 3, pp. 37–46.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nikityuk, I.E., Moshonkina, T.R., Shcherbakova, N.A. et al. Effect of locomotor training and functional electrical stimulation on postural function in children with severe cerebral palsy. Hum Physiol 42, 262–270 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119716030129
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119716030129